Abstract
Fibronectin is a high-molecular-weight opsonic protein known to influence macrophage uptake of nonbacterial particulate matter. The concentration of fibronectin in serum and the quantity of fibronectin in the inflamed peritoneal space were examined in rats after intraperitoneal casein injection. Fibronectin levels were studied in relation to the opsonic activity of the serum, as assayed by the uptake of gelatin-coated. 51Cr-labeled, fixed sheep erythrocytes by adherent peritoneal macrophage monolayers. Intraperitoneal inflammation resulted in a marked increase in peritoneal fluid fibronectin that lasted throughout a 4-day observation period. The opsonic activity of serum also increased after casein challenge at 24, 48, and 72 h. The elevation in the level of fibronectin in the peritoneal space appeared to coincide with or closely precede the maximal increase in concentration of inflammatory peritoneal macrophages. After casein injection, when serum immunoreactive fibronectin increased, an enhancement in phagocytic clearance of blood-borne gelatin-coated test particles was also observed. It is suggested that the elevation of fibronectin in blood during intraperitoneal inflammation may mediate enhanced liver phagocytic function. The increased amount of fibronectin in the inflamed peritoneal space may also influence the phagocytic activity of peritoneal macrophages.
Full text
PDF



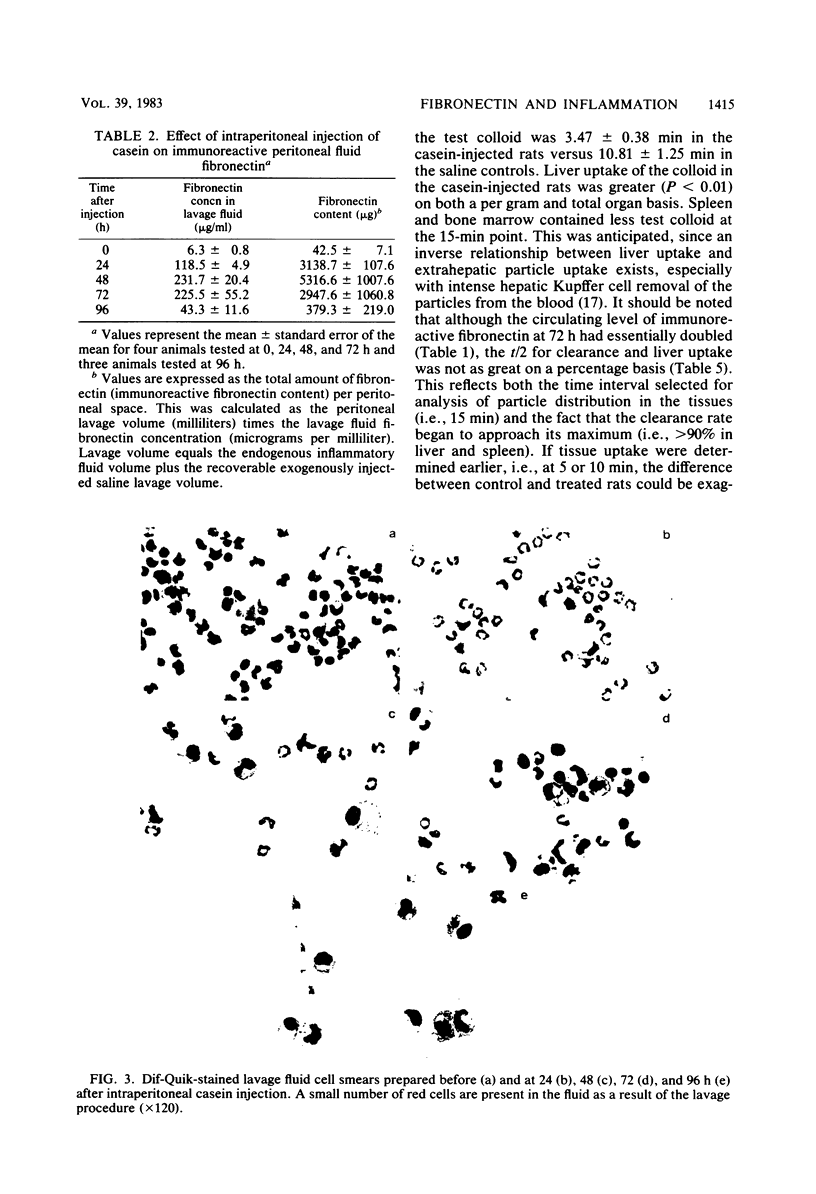


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenstock F. A., Saba T. M., Roccario E., Cho E., Kaplan J. E. Opsonic fibronectin after trauma and particle injection determined by a peritoneal macrophage monolayer assay. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Jul;30(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock F. A., Saba T. M., Weber P. An affinity method for the rapid purification of opsonic alpha 2 SB glycoprotein from serum. Adv Shock Res. 1979;2:55–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock F., Weber P., Saba T. M., Laffin R. Electroimmunoassay of alpha-2-opsonic protein during reticuloendothelial blockade. Am J Physiol. 1977 Mar;232(3):R80–R87. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1977.232.3.R80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daems W. T., Koerten H. K. The effects of various stimuli on the cellular composition of peritoneal exudates in the mouse. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jun 26;190(1):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00210035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Billingham R. E., Burgess L. Distribution of fibronectin during wound healing in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):181–189. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudewicz P. W., Molnar J., Lai M. Z., Beezhold D. W., Siefring G. E., Jr, Credo R. B., Lorand L. Fibronectin-mediated uptake of gelatin-coated latex particles by peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):427–433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Mosher D. F. Synthesis of fibronectin by cultured human endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:122–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Rubin K., Hök M., Ahlgren T., Seljelid R. In vitro biosynthesis of cold insoluble globulin (fibronectin) by mouse peritoneal macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80637-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser M. E., Saba T. M. Opsonic fibronectin deficiency and sepsis. Cause or effect? Ann Surg. 1982 Mar;195(3):340–345. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198203000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megirian R., Saba T. M., Stephenson J. B. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin induced macrophage stimulation: humoral aspects. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Nov;20(5):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh E., Pierschbacher M., Ruoslahti E. Deposition of plasma fibronectin in tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3218–3221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Isselbacher K. J., Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin synthesis by epithelial crypt cells of rat small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5548–5552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Blumenstock F. A., Weber P., Kaplan J. E. Physiologic role of cold-insoluble globulin in systemic host defense: implications of its characterization as the opsonic alpha 2-surface-binding glycoprotein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Cho E. Reticuloendothelial (RE) response to surgery as modified by intravenous administration of plasma cryoprecipitate or cold-insoluble globulin (plasma fibronectin) purified by affinity chromatography. Adv Shock Res. 1980;3:251–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Di Luzio N. R. Reticuloendothelial blockade and recovery as a function of opsonic activity. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jan;216(1):197–205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Jaffe E. Plasma fibronectin (opsonic glycoprotein): its synthesis by vascular endothelial cells and role in cardiopulmonary integrity after trauma as related to reticuloendothelial function. Am J Med. 1980 Apr;68(4):577–594. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M. Physiology and physiopathology of the reticuloendothelial system. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Dec;126(6):1031–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. S., Riggs J. L., Mosesson M. W. Production of fibronectin by human epithelial cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1979 Oct;39(10):4138–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Furth R., Diesselhoff-den Dulk M. C., Mattie H. Quantitative study on the production and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes during an acute inflammatory reaction. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1314–1330. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss B., Allam S., Rauterberg J., Ullrich K., Gieselmann V., von Figura K. Primary cultures of rat hepatocytes synthesize fibronectin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 29;90(4):1348–1354. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zardi L., Cecconi C., Barbieri O., Carnemolla B., Picca M., Santi L. Concentration of fibronectin in plasma of tumor-bearing mice and synthesis by Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1979 Sep;39(9):3774–3779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]