Abstract
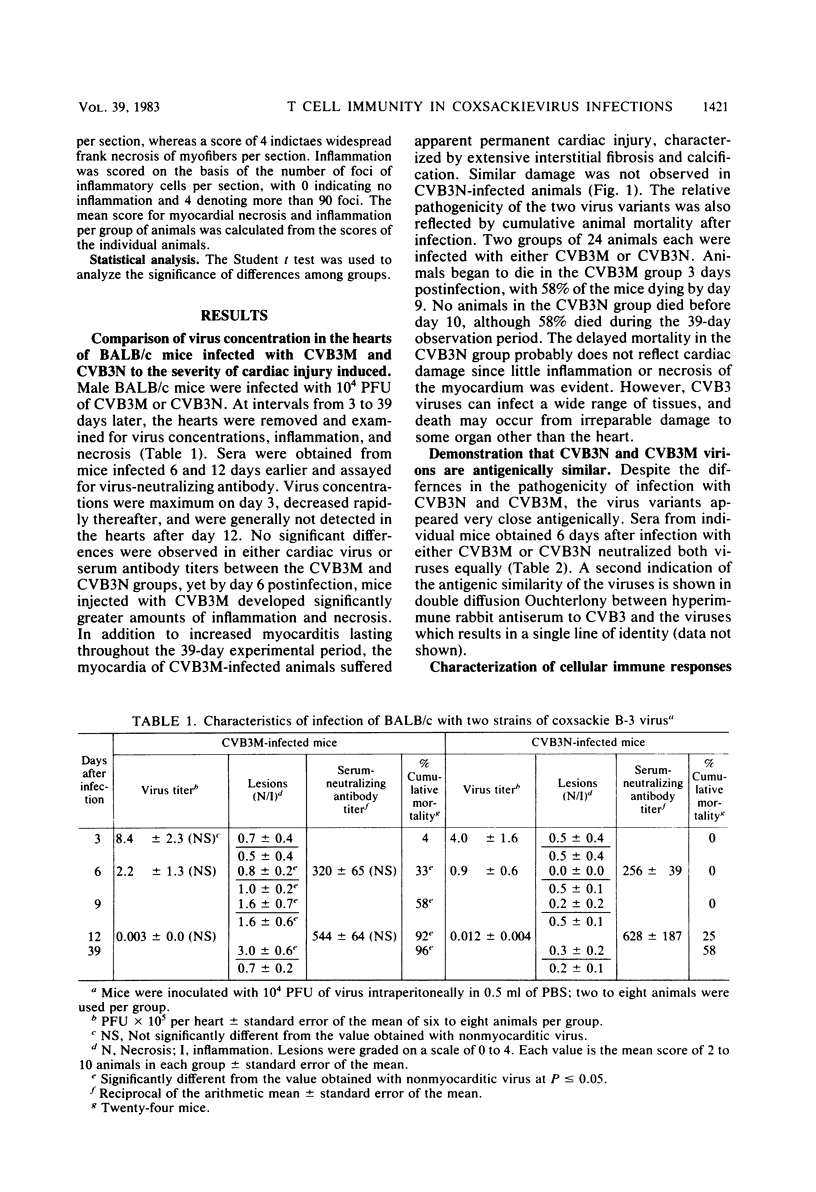
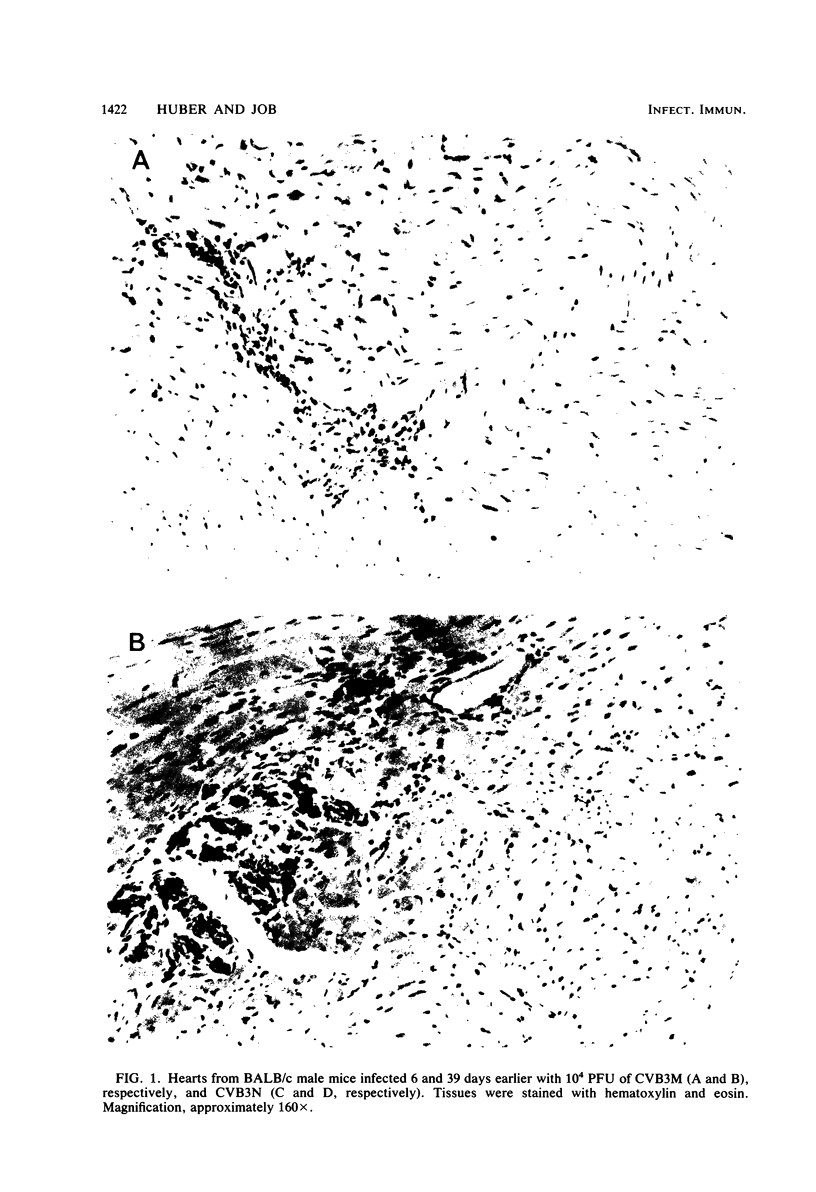
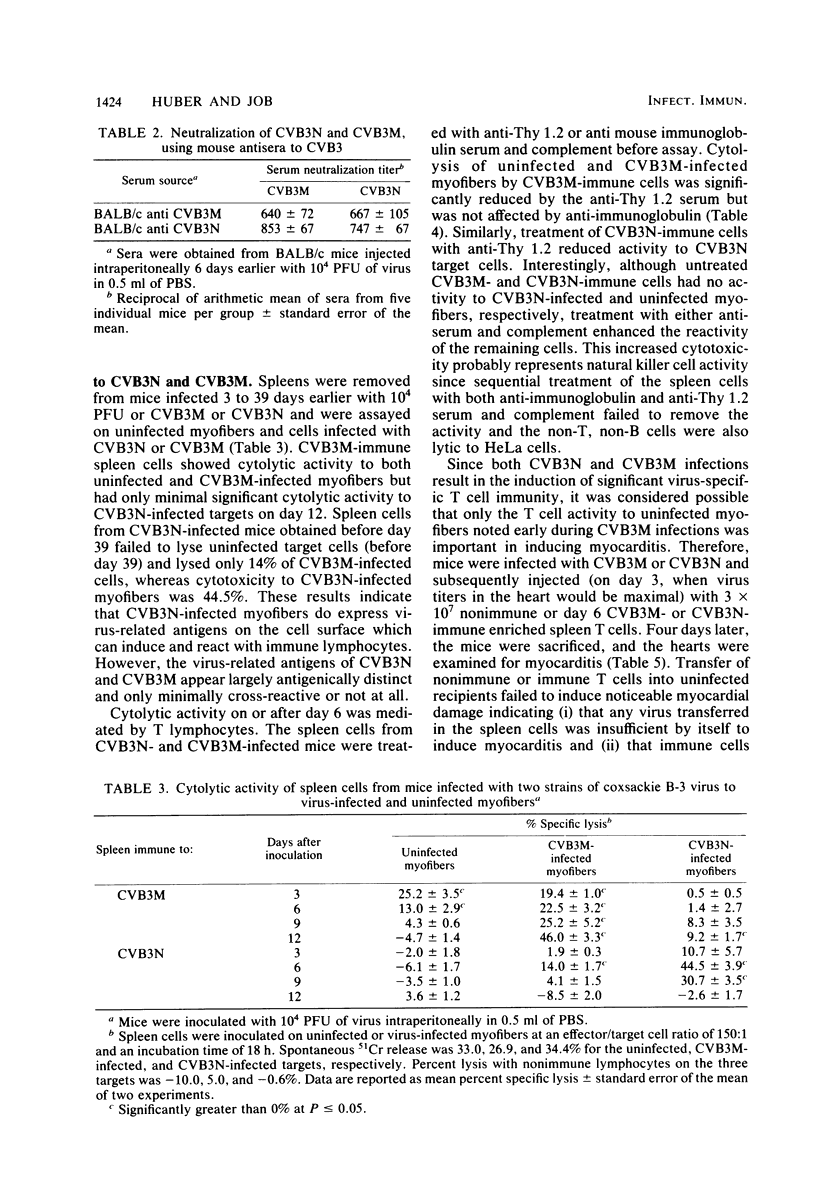
Two strains of coxsackie B-3 virus, indistinguishable by neutralization with acute mouse antiserum to coxsackie B-3 group virus, differ markedly in pathogenicity. One strain induces extensive mononuclear cell infiltration and necrosis in the heart, and 92% of the infected animals die by day 10 after infection. Inflammation, cardiac damage, and mortality are reduced in mice infected with the nonmyocarditic virus. Peak virus replication occurs on day 3 with both viruses. Virus concentrations decrease to undetectable levels after day 12 of infection. Cytolytic T cells could be isolated from the spleens of animals inoculated with either virus. The spleen cells preferentially lysed target cells infected with the immunizing virus strain. These results suggest that the myocarditic and nonmyocarditic viruses induce only minimally noncross-reacting virus-specific antigens on the target cell surface.
Full text
PDF
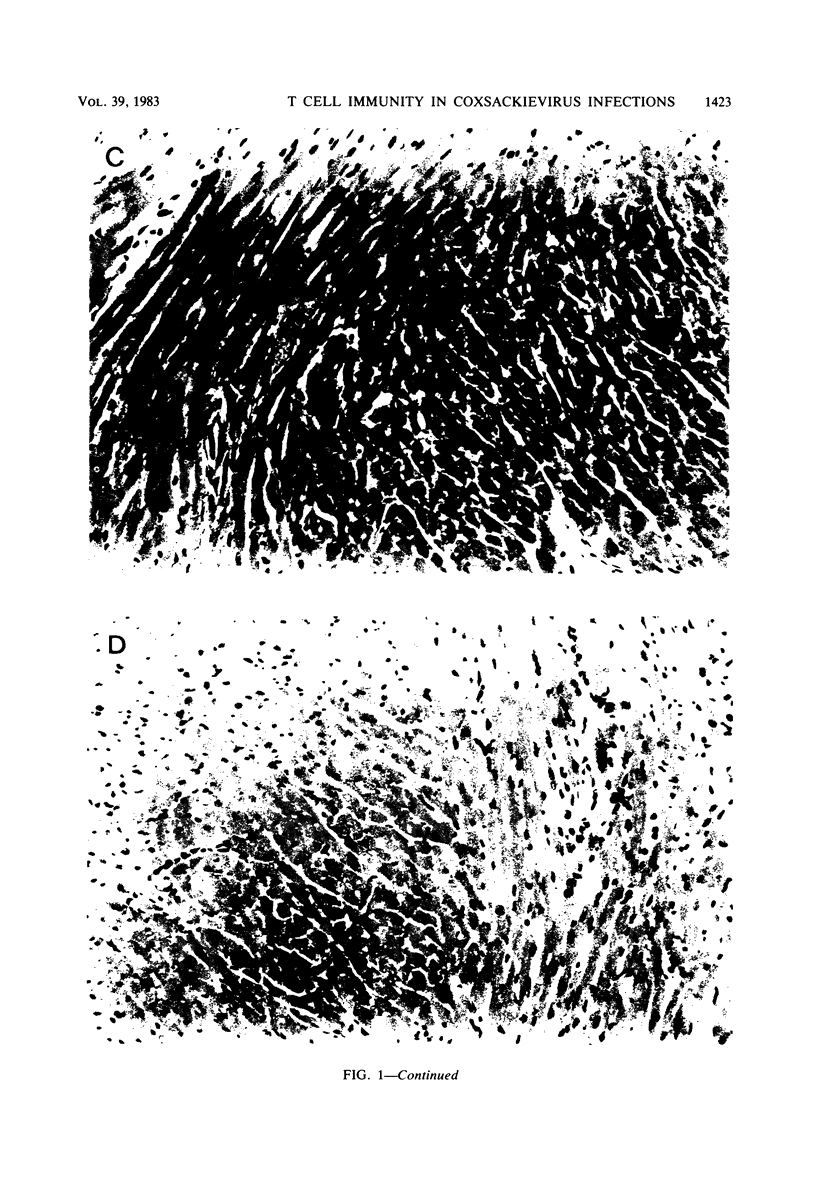





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORING W. D., WALKER D. L., ZU RHEIN G. M. Factors influencing host-virus interactions. II. Alteration of Coxsackie virus infection in adult mice by cold. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Nov;93(2):273–277. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWELL R. L., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. VI. Sustained infection of HeLa cells by Coxsackie B3 virus and effect on superinfection. J Exp Med. 1961 Feb 1;113:419–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALLDORF G., GIFFORD R. Susceptibility of gravid mice to Coxsackie virus infection. J Exp Med. 1954 Jan 1;99(1):21–27. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg R., Weiner H. L., Fields B. N., Benacerraf B., Burakoff S. J. Generation of cytolytic T lymphocytes after reovirus infection: role of S1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEAR J. H. Coxsackie virus infections of the newborn. Prog Med Virol. 1958;1:106–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRODUMS E. I., DEMPSTER G. Myocarditis in experimental Coxsackie B-3 infection. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Dec;5:605–615. doi: 10.1139/m59-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J., Trousdale M. D., LaBadie D. R., Paque R. E., Nealon T. Properties of coxsackievirus B3 variants which are amyocarditic or myocarditic for mice. J Med Virol. 1979;3(3):207–220. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Job L. P., Auld K. R., Woodruff J. F. Sex-related differences in the rapid production of cytotoxic spleen cells active against uninfected myofibers during Coxsackievirus B-3 infection. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1336–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Job L. P., Woodruff J. F. Lysis of infected myofibers by coxsackievirus B-3-immune T lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1980 Mar;98(3):681–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B., Philipson L. Replication of poliovirus RNA studied by gel filtration and electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):305–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER A. M., DANIELS J. B., CHEEVER F. S., WELLER T. H. Lesions caused in suckling mice by certain viruses isolated from cases of so called non-paralytic poliomyelitis and of pleurodynia. J Exp Med. 1950 Aug;92(2):169–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paque R. E., Gauntt C. J., Nealon T. J., Trousdale M. D. Assessment of cell-mediated hypersensitivity against coxsackievirus B3 viral-induced myocarditis utilizing hypertonic salt extracts of cardiac tissue. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1672–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesing T. G., Landau B. J., Crowell R. L. Limited persistence of viral antigen in coxsackievirus B3 induced heart disease in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Mar;160(3):382–386. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERS V. VIRAL MYOCARDITIS. Am Heart J. 1963 Nov;66:707–713. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(63)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVEHAG S. E., MANDEL B. THE FORMATION AND PROPERTIES OF POLIOVIRUS-NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY. I. 19S AND 7S ANTIBODY FORMATION: DIFFERENCES IN KINETICS AND ANTIGEN DOSE REQUIREMENT FOR INDUCTION. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:1–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainani G. S., Krompotic E., Slodki S. J. Adult heart disease due to the Coxsackie virus B infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968 Mar;47(2):133–147. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196803000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. G. Coxsackie B myopericarditis in adults. Am Heart J. 1970 Jul;80(1):34–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(70)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. Y., Woodruff J. J., Woodruff J. F. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes during coxsackievirus B-3 infection. I. Model and viral specificity1. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1159–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F., Kilbourne E. D. The influence of quantitated post-weaning undernutrition on coxsackievirus B3 infection of adult mice. I. Viral persistence and increased severity of lesions. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):137–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F., Woodruff J. J. Involvement of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of coxsackie virus B3 heart disease. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1726–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]