Abstract
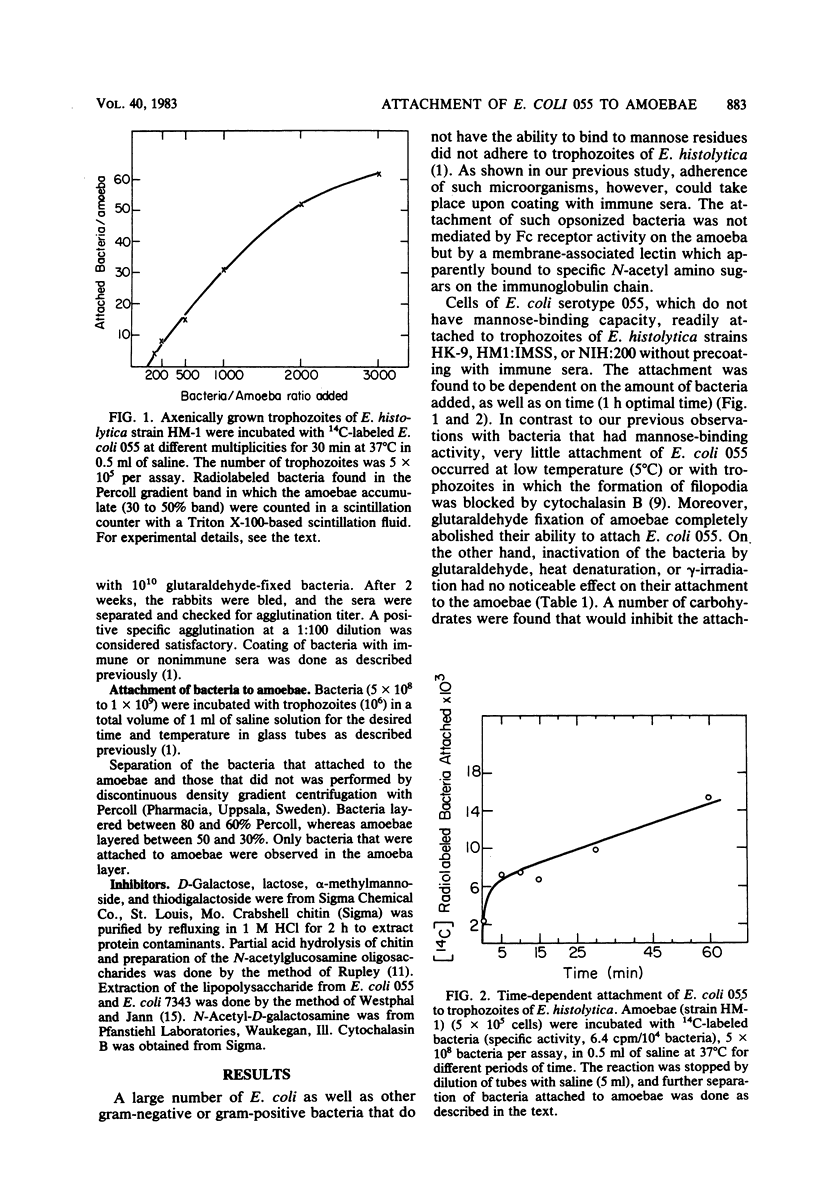
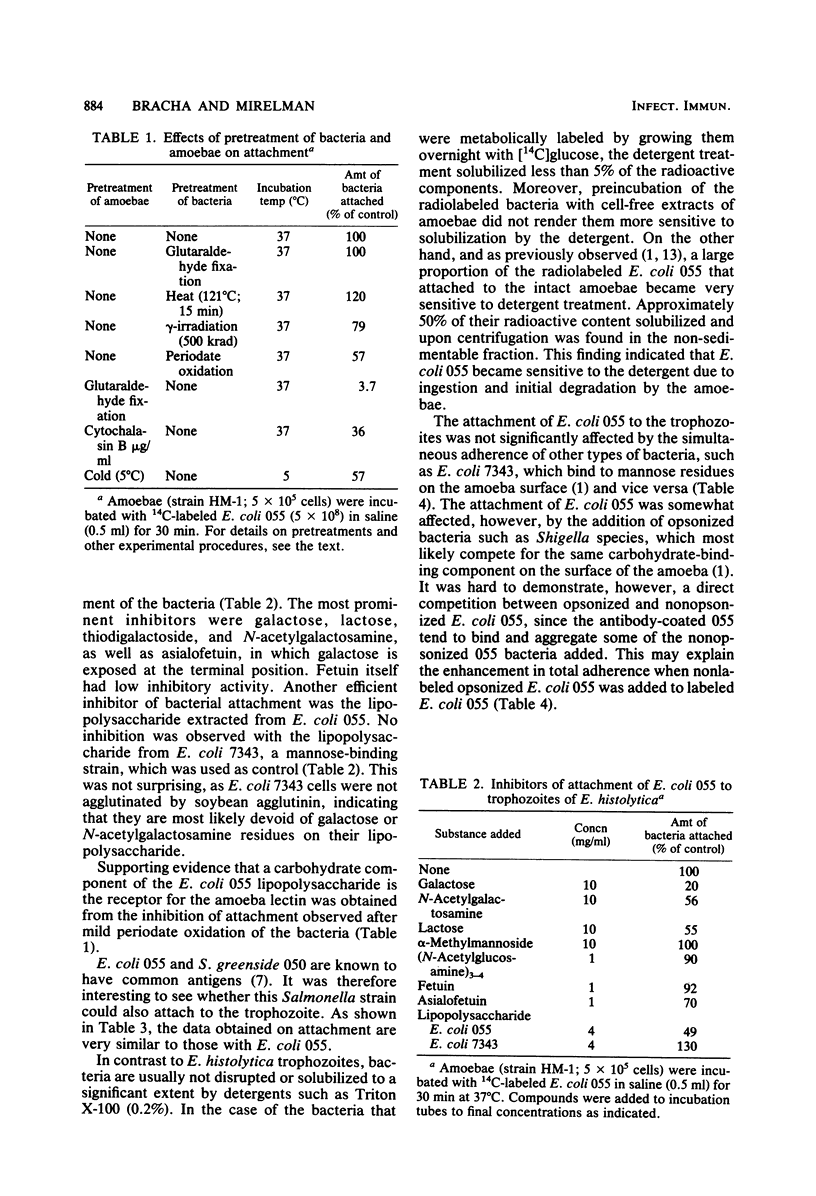
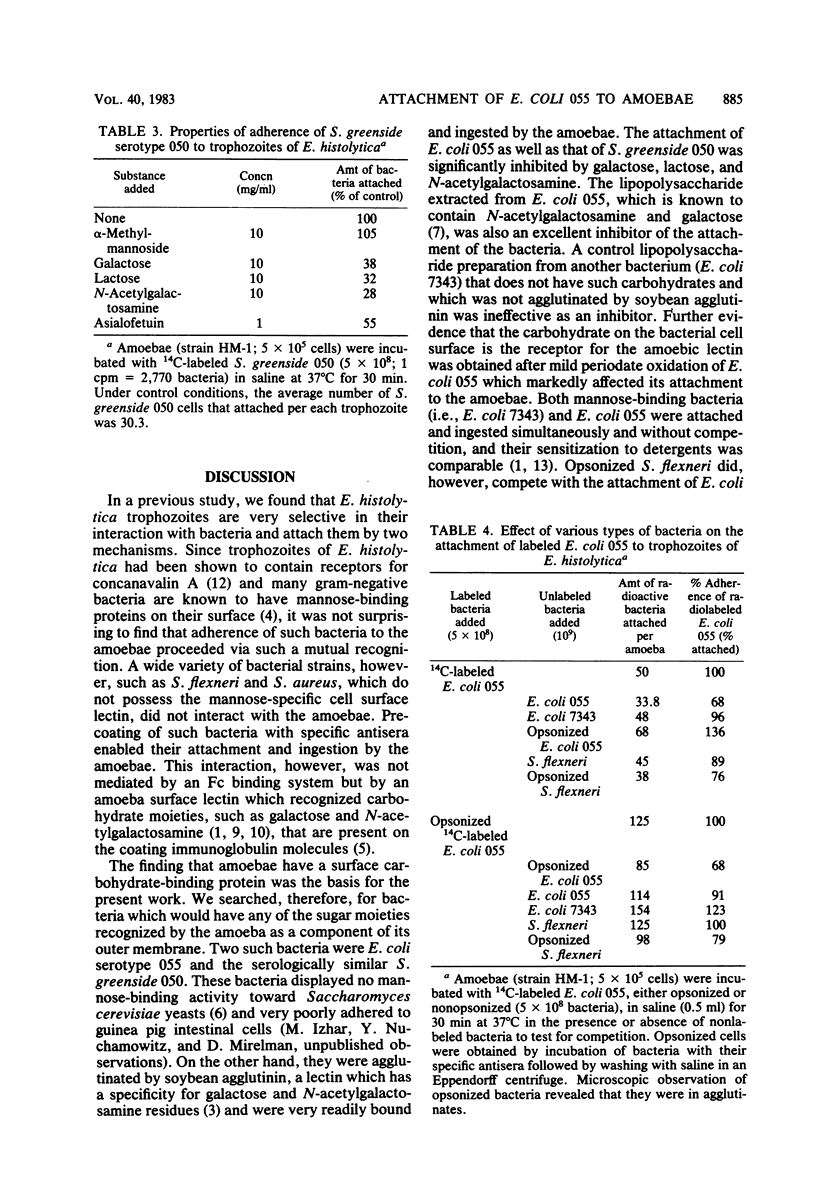
Carbohydrate-binding activity present on the Entamoeba histolytica cell surfaces was found to mediate the adherence of two types of bacteria, Escherichia coli serotype 055 and Salmonella greenside 050. Adherence was inhibited by low-molecular-weight carbohydrates (10 mg/ml) such as galactose, lactose, and N-acetylgalactosamine, as well as by asialofetuin and the lipopolysaccharide extracted from E. coli 055. Mild periodate oxidation of the bacteria inhibited their adherence, whereas heat inactivation, glutaraldehyde fixation, or gamma-irradiation had no effect. On the other hand, pretreatment of trophozoites with glutaraldehyde, cytochalasin B, or cold (5 degrees C) abolished adherence. None of these treatments, however, affected the attachment of bacteria that contain on their cell surface type I pili with mannose-binding capacity. These findings lend further support to our earlier observations on how amoebae interact with bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bracha R., Kobiler D., Mirelman D. Attachment and ingestion of bacteria by trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):396–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.396-406.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Altmann G., Eshdat Y. Screening of bacterial isolates for mannose-specific lectin activity by agglutination of yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.328-331.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeier W., Kirkland T., Acton R. T., Bennett J. C. The carbohydrate composition of immunoglobulins G. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. P., Gorstein F. Effects of different species of bacteria on the pathology of enteric amebiasis in monocontaminated guinea pigs. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Nov;15(6):863–868. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUPLEY J. A. THE HYDROLYSIS OF CHITIN BY CONCENTRATED HYDROCHLORIC ACID, AND THE PREPARATION OF LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT SUBSTRATES FOR LYSOZYME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 1;83:245–255. doi: 10.1016/0926-6526(64)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl D., Martínez-Palomo A., Argüello C., de la Torre M., de la Hoz R. Surface properties related to concanavalin A-induced agglutination. A comparative study of several Entamoeba strains. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):652–665. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel G., Thilo L., Schwarz H., Steinhart R. Mechanism of phagocytosis in Dictyostelium discoideum: phagocytosis is mediated by different recognition sites as disclosed by mutants with altered phagocytotic properties. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):456–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittner M., Rosenbaum R. M. Role of bacteria in modifying virulence of Entamoeba histolytica. Studies of amebae from axenic cultures. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Sep;19(5):755–761. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]