Abstract
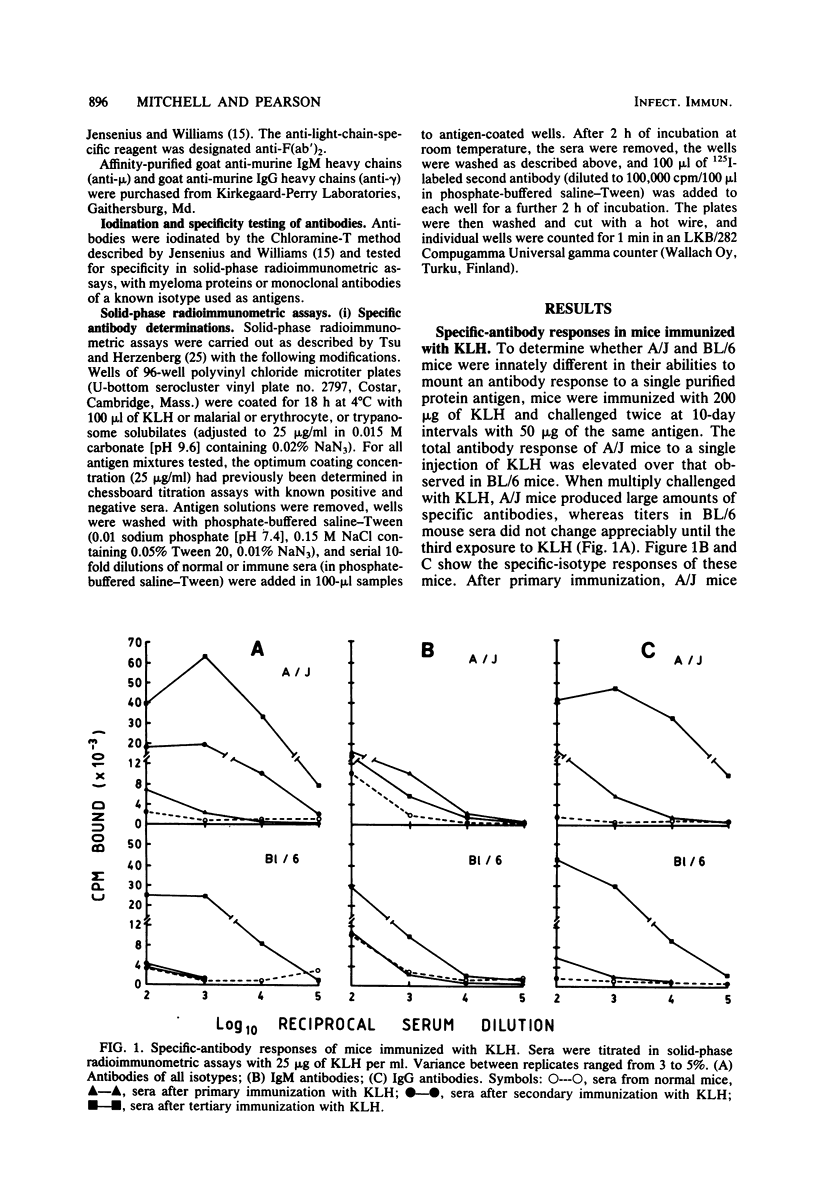
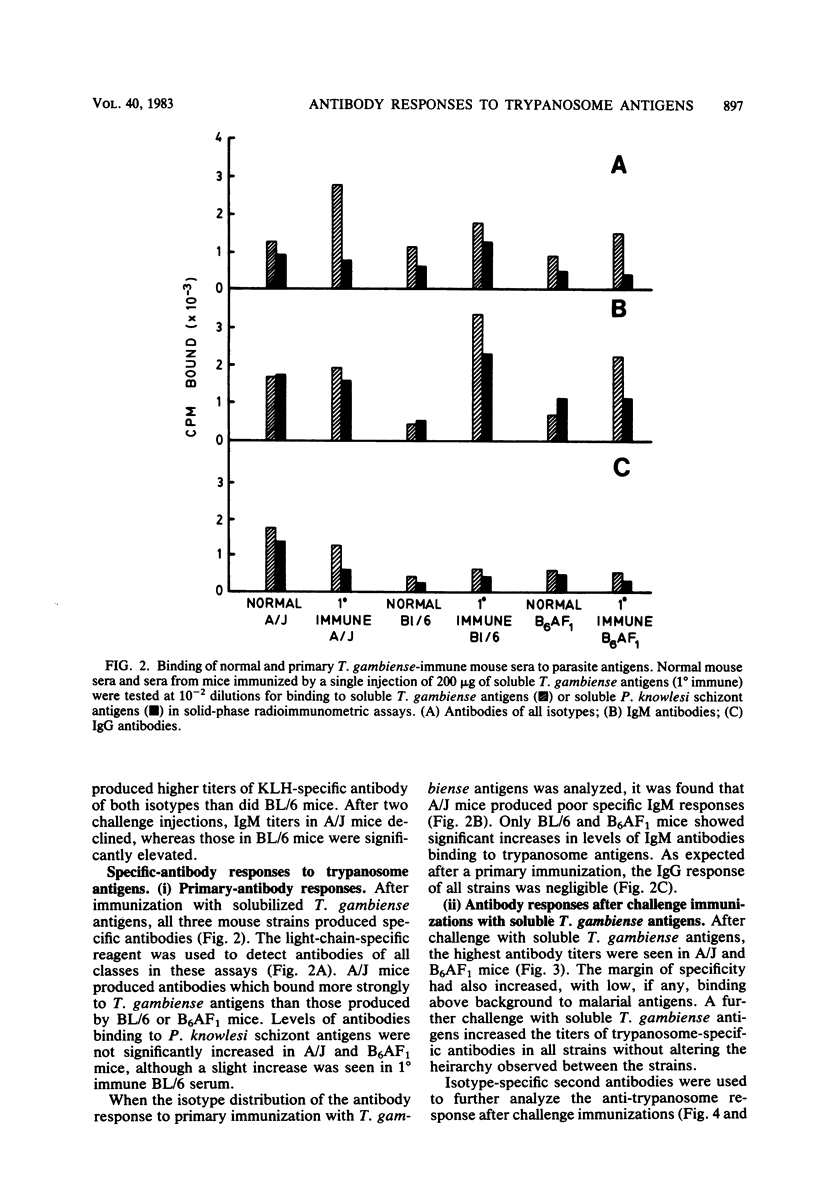
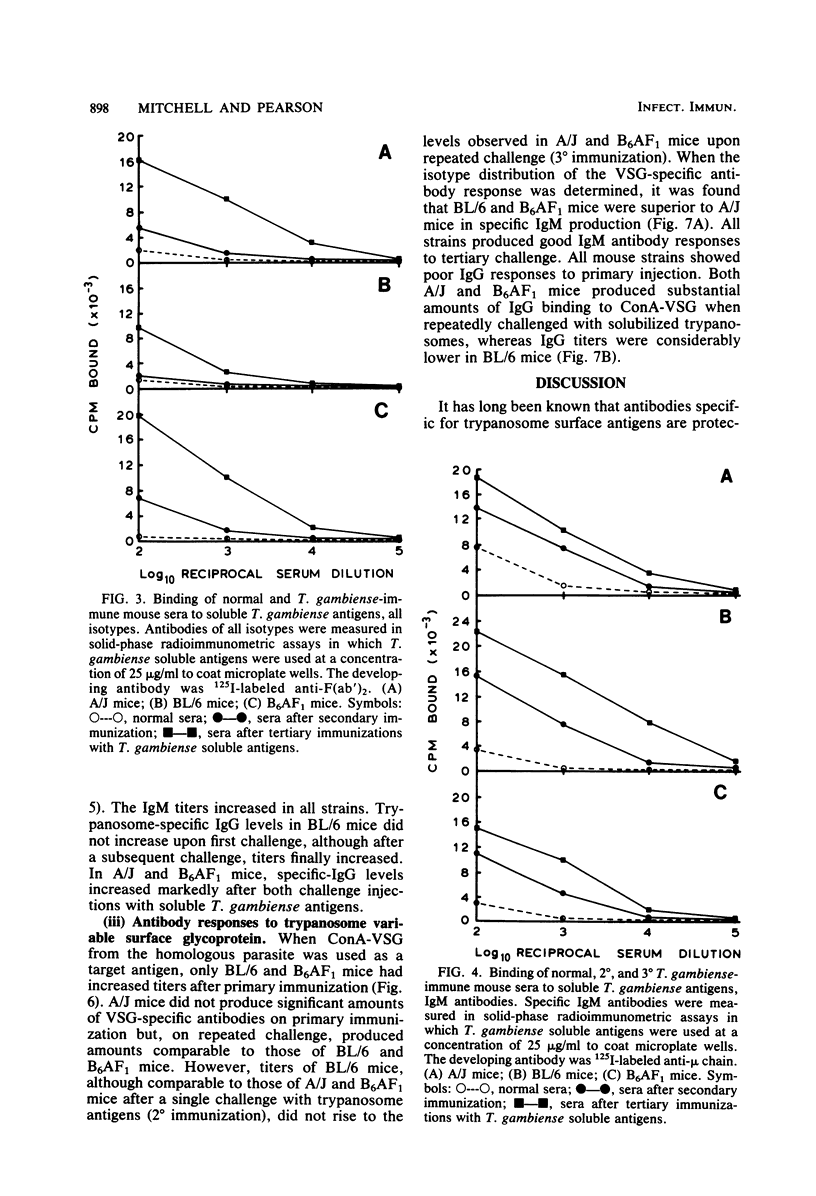
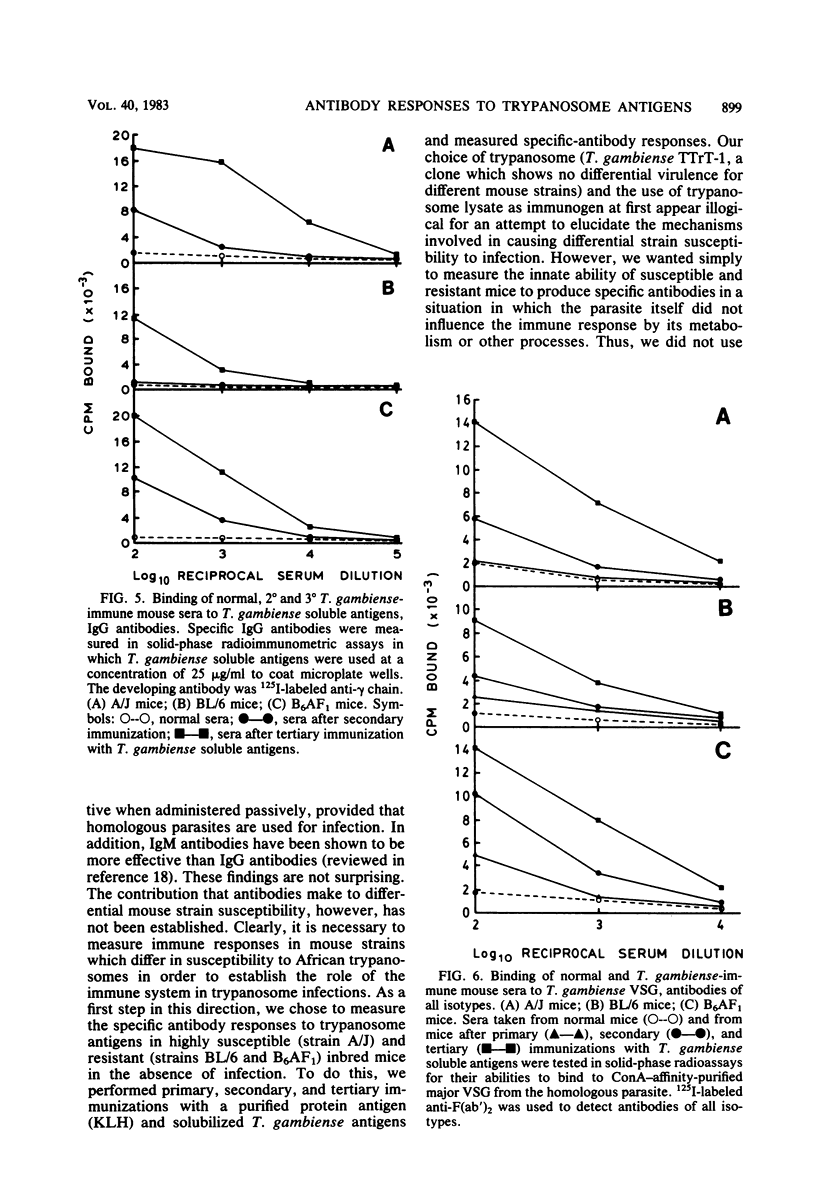
We tested the ability of inbred mice that were either susceptible (strain A/J) or resistant (strain C57BL/6 and A/J X C57BL/6 hybrids) to African trypanosomes to produce specific antibodies to trypanosome antigens in the absence of living parasites. This experiment was carried out to eliminate the influence of trypanosome growth or metabolism on immune responsiveness. Mice were immunized with keyhole limpet hemocyanin or solubilized Trypanosoma brucei gambiense, and serum antibodies were measured in solid-phase radioimmunometric assays after primary and challenge injections. Both susceptible and resistant mice showed increases in keyhole limpet hemocyanin-specific or trypanosome-specific immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G after immunization. When immunized with trypanosome antigens, resistant mice made qualitatively and quantitatively superior specific immunoglobulin M responses, particularly to the trypanosome major variable surface glycoprotein. Susceptible A/J mice produced good specific antibody responses, although these were predominantly of the immunoglobulin G isotypes. These results show that A/J and C57BL/6 mice respond differentially in terms of immunoglobulin isotype and repertoire in response to injected antigens. The possibility that this differential antibody response influences susceptibility to African trypanosomes is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Anderson N. L. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXI. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. L., Anderson N. G. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXII. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple gradient-slab gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):341–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz T., Baltz D., Pautrizel R. Affinité de la concanavaline A pour Trypanosoma equiperdum applications a l'isolement de la fraction glycoprotéique spécifique du type antigénique. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Sep-Oct;127(5):761–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. H., Esser K. M., Phillips S. M. Trypanosoma rhodesiense infection in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):714–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.714-720.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. H., Esser K. M., Weinbaum F. I. Trypanosoma rhodesiense infection in B-cell-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):434–438. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.434-438.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E. Trypanosoma brucei: influence of host strain and parasite antigenic type on infections in mice. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Apr;44(2):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Identification, purification and properties of clone-specific glycoprotein antigens constituting the surface coat of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):393–417. doi: 10.1017/s003118200004717x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M. Possible role of a B-cell mitogen in hypergammaglobulinaemia in malaria and trypanosomiasis. Lancet. 1974 Mar 16;1(7855):435–436. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosskinsky C. M., Askonas B. A. Macrophages as primary target cells and mediators of immune dysfunction in African trypanosomiasis. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):149–155. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.149-155.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Waksman B. H., Eardley D. D. Activation of distinct helper and suppressor T cells in experimental trypanosomiasis. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):622–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Waksman B. H. Suppressor cells in experimentally trypanosomiasis. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):539–541. doi: 10.1038/265539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensenius J. C., Williams A. F. The binding of anti-immunoglobulin antibodies to rat thymocytes and thoracic duct lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Feb;4(2):91–97. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanham S. M., Godfrey D. G. Isolation of salivarian trypanosomes from man and other mammals using DEAE-cellulose. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Dec;28(3):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. F., Mansfield J. M. Genetics of resistance to African trypanosomes: role of the H-2 locus in determining resistance to infection with Trypanosoma rhodesiense. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):513–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.513-518.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. M., Bagasra O. Lymphocyte function in experimental African trypanosomiasis. I. B cell responses to helper T cell-independent and -dependent antigens. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. I., Roelants G. E., Mayor-Withey K. S., Murray M. Susceptibility of inbred strains of mice to Trypanosoma congolense: correlation with changes in spleen lymphocyte populations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Apr;32(1):25–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. W., Roelants G. E., Lundin L. B., Mayor-Withey K. S. Immune depression in trypanosome-infected mice. I. Depressed T lymphocyte responses. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Oct;8(10):723–727. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. W., Roelants G. E., Pinder M., Lundin L. B., Mayor-Withey K. S. Immune depression in trypanosome-infected mice. III. suppressor cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):200–204. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinwald E., Rautenberg P., Risse H. J. Trypanosoma congolense: mechanical removal of the surface coat in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Dec;48(3):384–397. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed J. R. Competition among serologically different clones of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense in vivo. J Protozool. 1978 Nov;25(4):526–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb04179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw D. D., Macaskill J. A., Holmes P. H., Jennings F. W., Urquhart G. M. Genetic resistance to Trypanosoma congolense infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):707–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.707-713.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


