Abstract
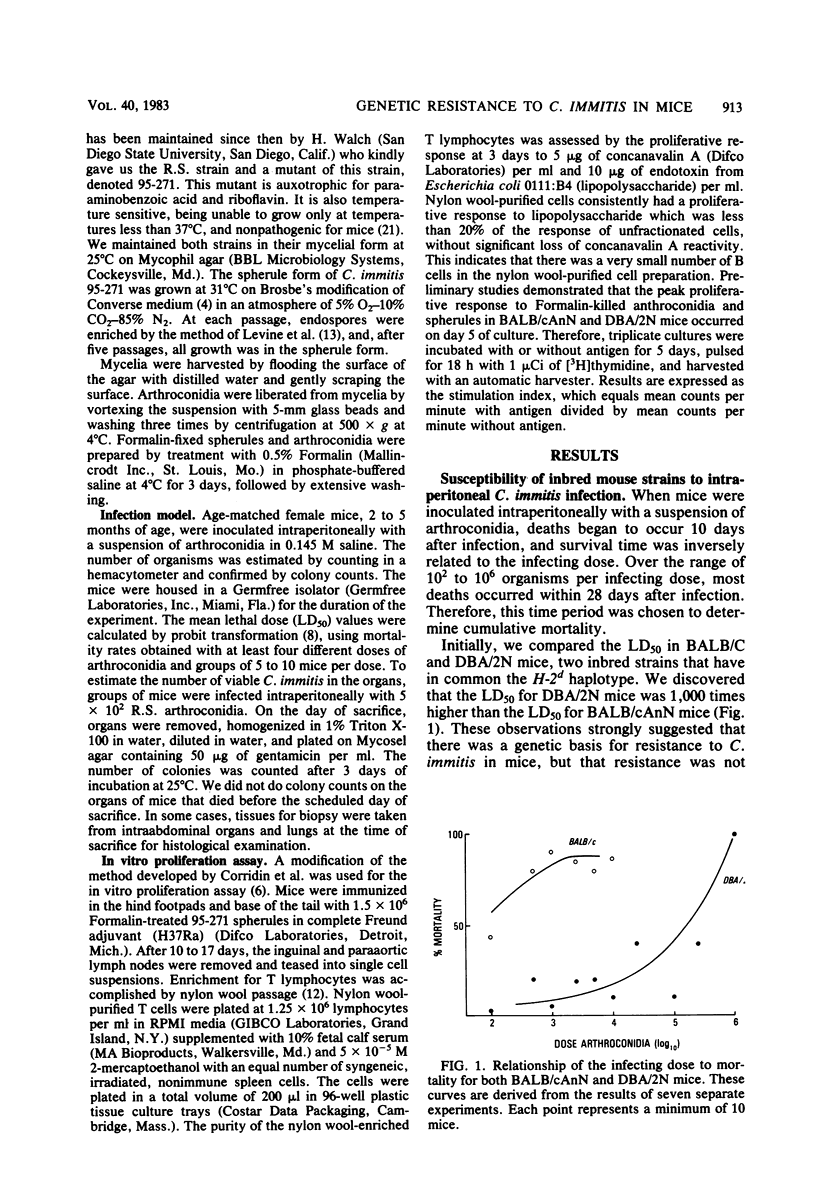
Inbred strains of mice were infected intraperitoneally with Coccidioides immitis, and the mean lethal dose was determined after 28 days. DBA/2N mice had a mean lethal dose of greater than 10(5) arthroconidia, whereas BALB/cAnN, C57BL/6N, and C57L/J mice had a mean lethal dose of less than or equal to 10(3). Since both BALB/c and DBA/2 mice are the H-2d haplotype, resistance is not primarily determined by the major histocompatibility locus. Resistance was the dominant phenotype. The pattern of C. immitis-resistant strains does not correspond to the strain distribution of the lsh gene or to the pattern of resistance to Blastomyces dermatitidis or Cryptococcus neoformans. Both resistant and susceptible mice, however, could be successfully immunized with a killed spherule vaccine, and susceptible BALB/cAnN mice were protected from an otherwise lethal infection by prior immunization with an attenuated mutant of C. immitis. Despite the evidence that BALB/cAnN mice could respond to immunization, nonimmune mice did not control the later phase of intraabdominal infection as well as DBA/2N mice. Dissemination of C. immitis to the lung occurred frequently in BALB/cAnN but not in DBA/2N mice. This suggests that BALB/cAnN mice cannot mount an effective immune response to C. immitis during the course of infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaman L. V., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Mechanisms of resistance to infection with Coccidioides immitis in mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):681–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.681-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Significance of T cells in resistance to experimental murine coccidioidomycosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):580–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.580-585.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosbe E. A. Use of refined agar for the in vitro propagation of the spherule phase of Coccidioides immitis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):497–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.497-498.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Etlinger H. M., Chiller J. M. Lymphocyte specificity to protein antigens. I. Characterization of the antigen-induced in vitro T cell-dependent proliferative response with lymph node cells from primed mice. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1048–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Catanzaro A. Coccidioidomycosis. Part II. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):727–771. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTINGTON R. W., Jr Morphology and racial distribution of fatal coccidioidomycosis; report of a ten-year autopsy series in an endemic area. J Am Med Assoc. 1959 Jan 10;169(2):115–118. doi: 10.1001/jama.1959.03000190017005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. Natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium in different inbred mouse strains. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):311–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. III. Nature and significance of specific suppression of cell-mediated immunity in mice highly susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):594–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunity to coccidioi-domycosis induced in mice by purified spherule, arthrospore, and mycelial vaccines. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr;22:436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1960.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi P. A., Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Strain differences in resistance to infection reversed by route of challenge: studies in blastomycosis. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):623–625. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.623-625.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi P. A., Halpern J. W., Stevens D. A. Susceptibility differences of inbred strains of mice to blastomycosis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.160-168.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J. E., Blackwell J. M., O'Brien A. D., Bradley D. J., Glynn A. A. Are the Lsh and Ity disease resistance genes at one locus on mouse chromosome 1? Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):510–511. doi: 10.1038/297510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Wicker L. S., Urba W. J. Genetic control of susceptibility to Cryptococcus neoformans in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.494-499.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., St Charles C., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):506–509. doi: 10.1038/297506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


