Abstract
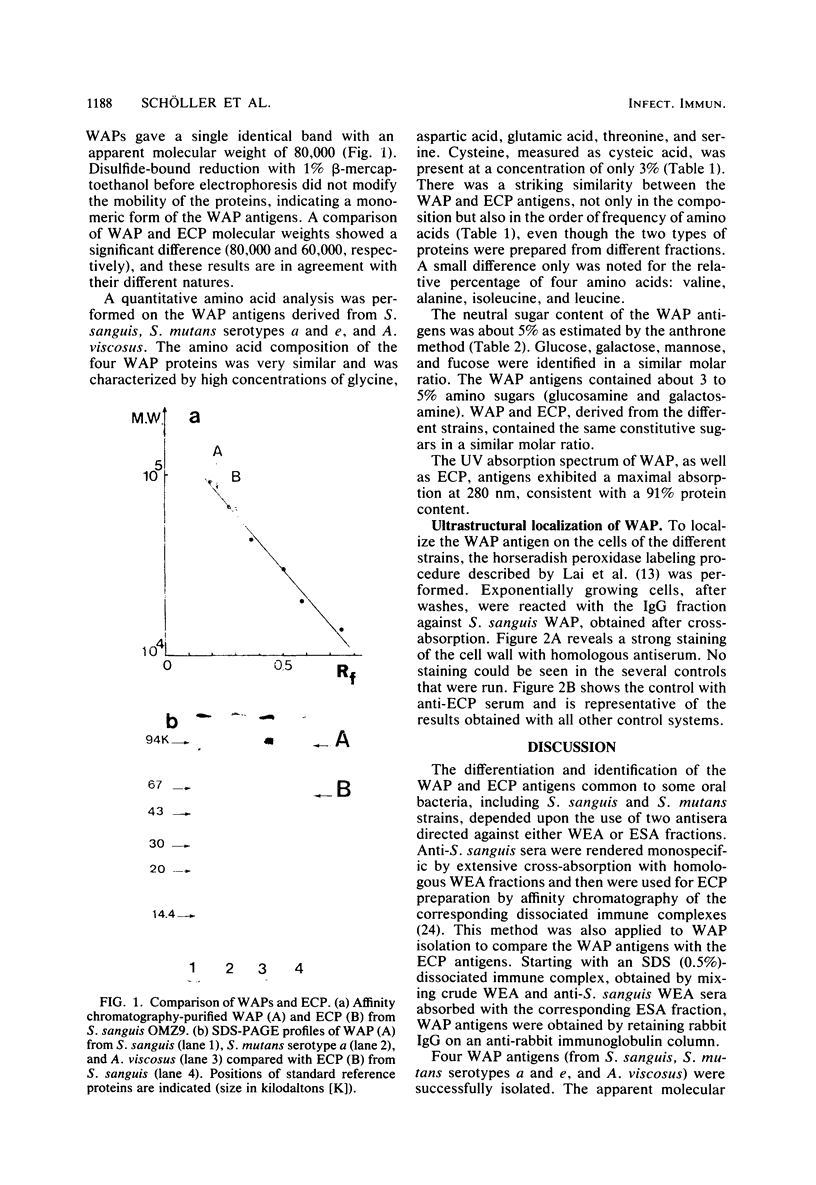
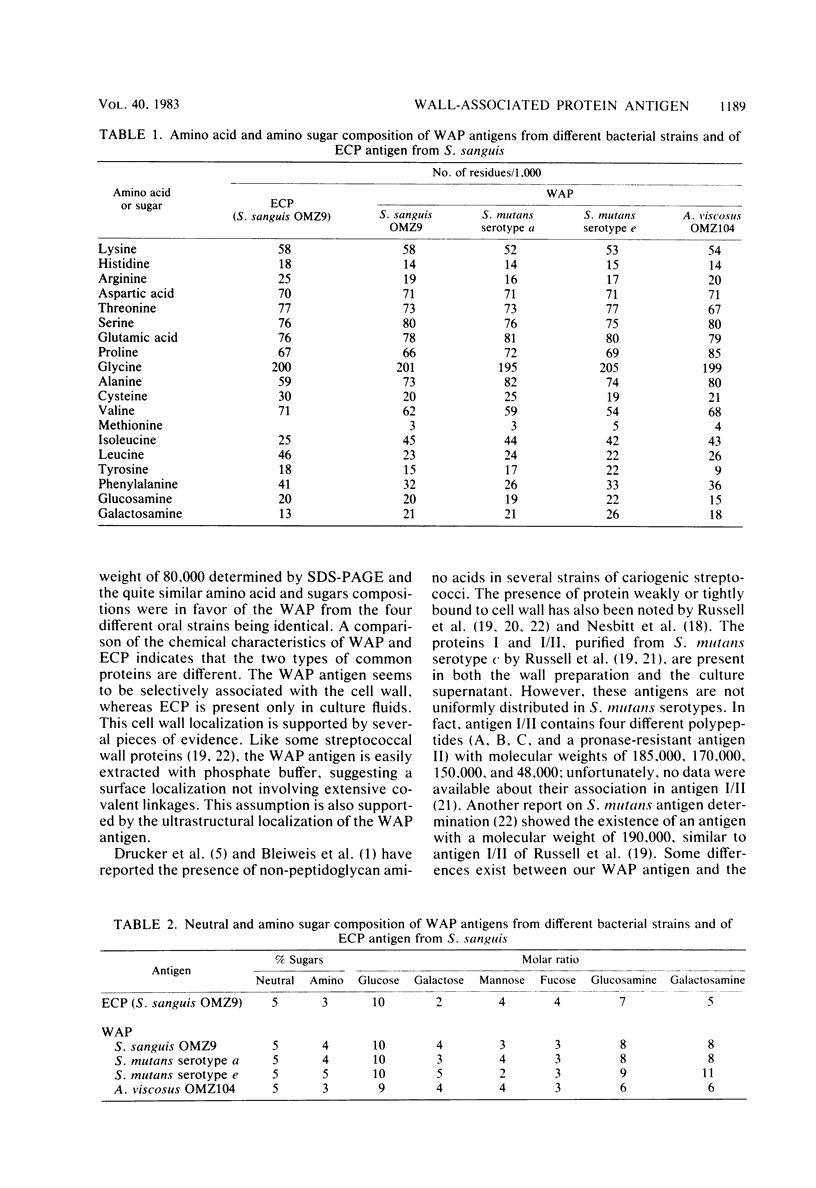
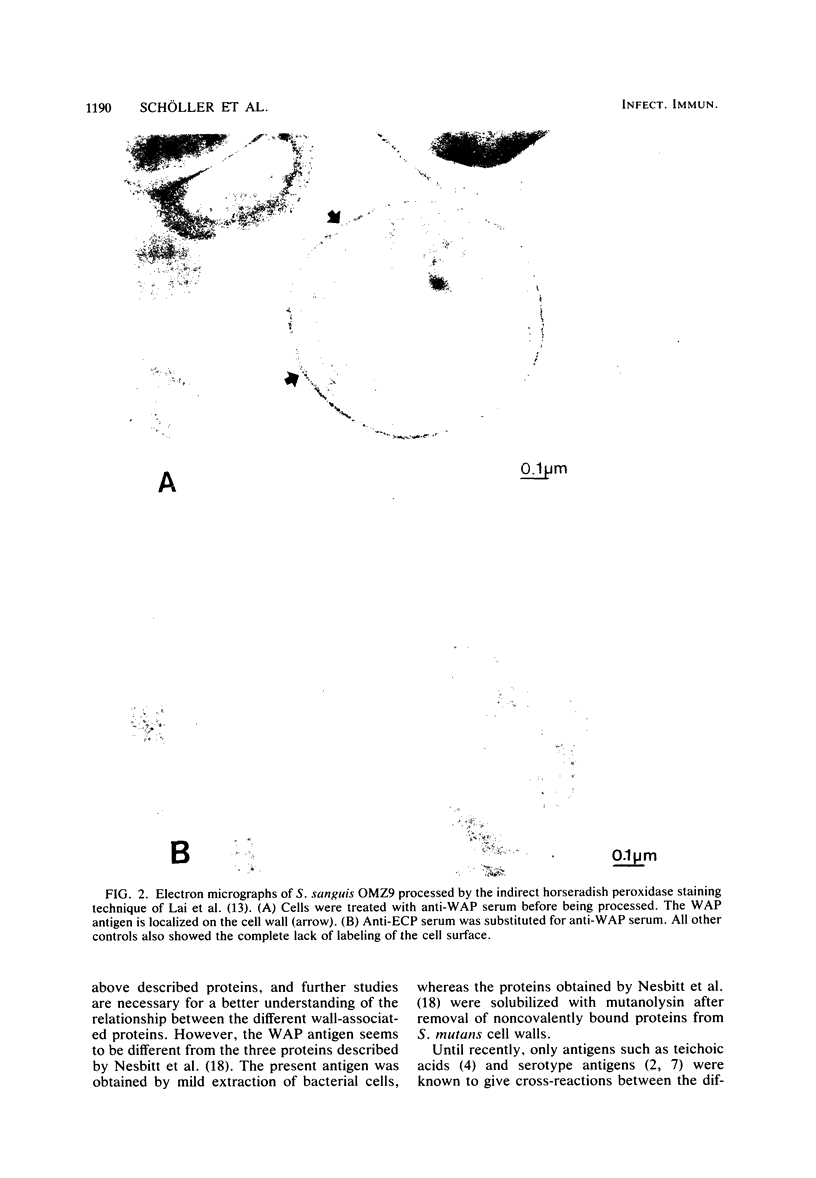
A soluble wall-associated common protein (WAP) has been isolated from cell wall-extracted antigens of exponentially growing cells of Streptococcus sanguis OMZ9, two serotypes (a and e), of Streptococcus mutans and Actinomyces viscosus OMZ104. The WAP antigens from the different strains were obtained by chromatography on an anti-rabbit immunoglobulin column of sodium dodecyl sulfate-dissociated immunoprecipitates. The affinity-isolated WAP antigens from the different oral bacteria were identical, as demonstrated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (showing an apparent molecular weight of 80,000) and amino acid and sugar compositions. This WAP antigen, common to all bacterial strains tested, consisted of 90% protein and 10% sugar. A comparison of the chemical properties of this WAP antigen and of the soluble extracellular common protein antigen showed that, although having similar amino acid and sugar compositions, the two proteins are different. Electron micrographs developed after immunocytological labeling of the WAP antigen on whole cells confirmed that it is located on the cell wall.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleiweis A. S., Craig R. A., Zinner D. D., Jablon J. M. Chemical composition of purified cell walls of cariogenic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):189–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.189-191.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Bleiweis A. S. Chemical, immunochemical, and structural studies of the cross-reactive antigens of Streptococcus mutans AHT and B13. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):326–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.326-336.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Nutritional requirements of Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Sep;17(9):1327–1332. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorpenning F. W., Cooper H. R., Rosen S. Cross-reactions of Streptococcus mutans due to cell wall teichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):586–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.586-591.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. B., Shuttleworth C. A., Melville T. H. A quantitative analysis of the cell wall amino acids of cariogenic and non-cariogenic streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Aug;13(8):937–940. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauconnet M., Rochemont J. A single-column amino acid analysis method which resolves hexosamines and several cysteine derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1978 Dec;91(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90525-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Purification and immunochemical characterization of type e polysaccharide antigen of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):68–76. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.68-76.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Funder-Nielsen T. D. Adhesion of dextran to Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):485–489. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. P., Schöller M., Frank R. Purification and some properties of free and cell-associated dextransucrase from Streptococcus sanguis. Biochimie. 1976 Nov 13;58(9):1047–1056. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Ingersoll L. Interaction of glucosyltransferase with the cell surface of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):652–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.652-659.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H., Ingersoll L. Immunological relationships between glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus mutans serotypes. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.636-644.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. H., Listgarten M. A., Rosan B. Immunoelectron microscopic identification and localization of Streptococcus sanguis with peroxidase-labeled antibody: localization of surface antigens in pure cultures. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):193–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.193-199.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Smith E. E. Origin of the cell-associated dextransucrase of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):829–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.829-838.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L. Quantitative Determination of Carbohydrates With Dreywood's Anthrone Reagent. Science. 1948 Mar 5;107(2775):254–255. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2775.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Extraction, purification, and chemical and immunological properties of the Streptococcus mutans group "a" polysaccharide cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):190–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.190-198.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Staat R. H., Rosan B., Taylor K. G., Doyle R. J. Association of protein with the cell wall of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.118-126.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Lehner T. Characterisation of antigens extracted from cells and culture fluids of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Zanders E. D., Bergmeier L. A., Lehner T. Affinity purification and characterization of protease-susceptible antigen I of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.999-1006.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöller M., Klein J. P., Frank R. M. Common antigens of streptococcal and non-streptococcal oral bacteria: immunochemical studies of extracellular and cell-wall-associated antigens from Streptococcus sanguis, Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacillus salivarius, and Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.52-60.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöller M., Klein J. P., Sommer P., Frank R. Common antigens of streptococcal and non-streptococcal oral bacteria: isolation and biochemical characterization of the extracellular protein antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2113–2120. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




