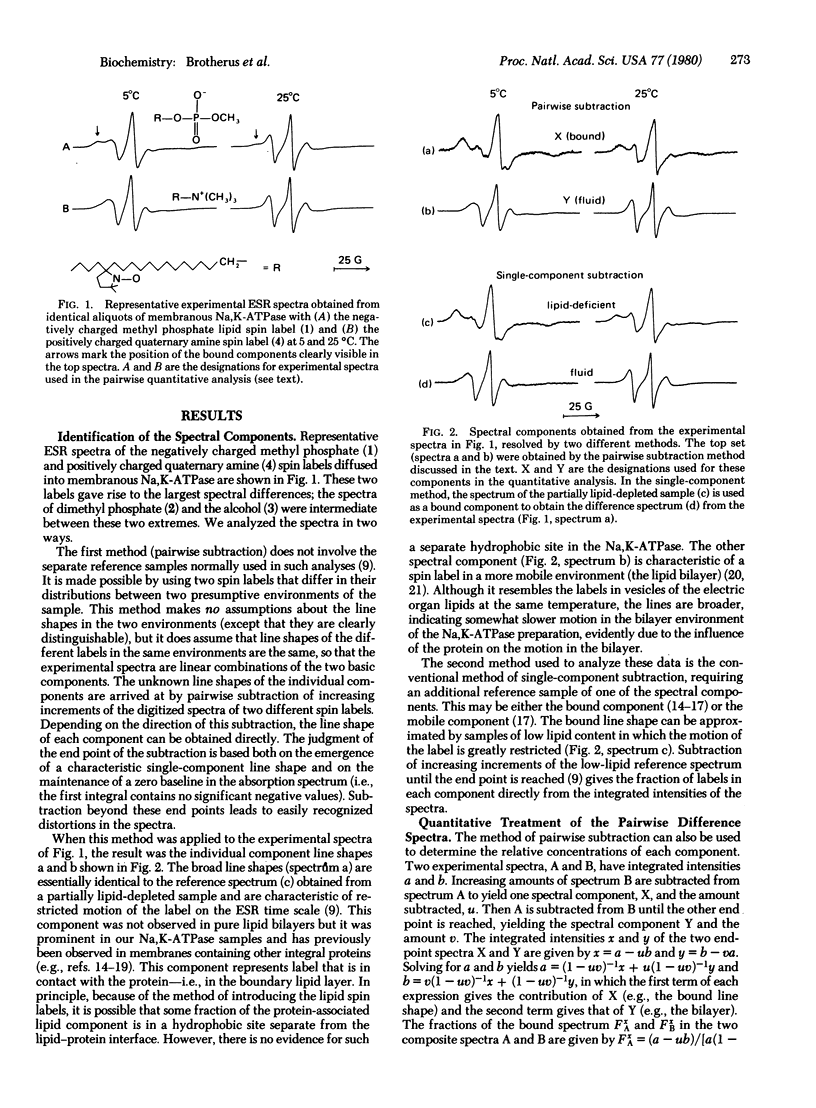
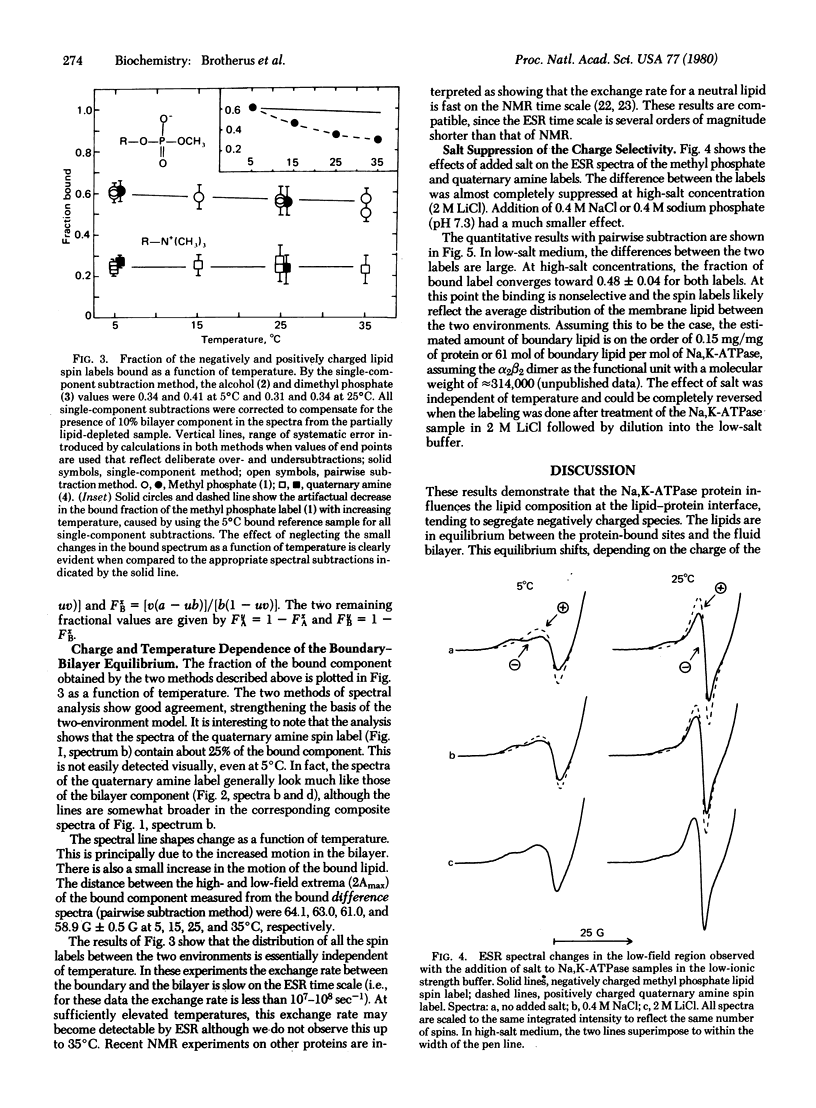
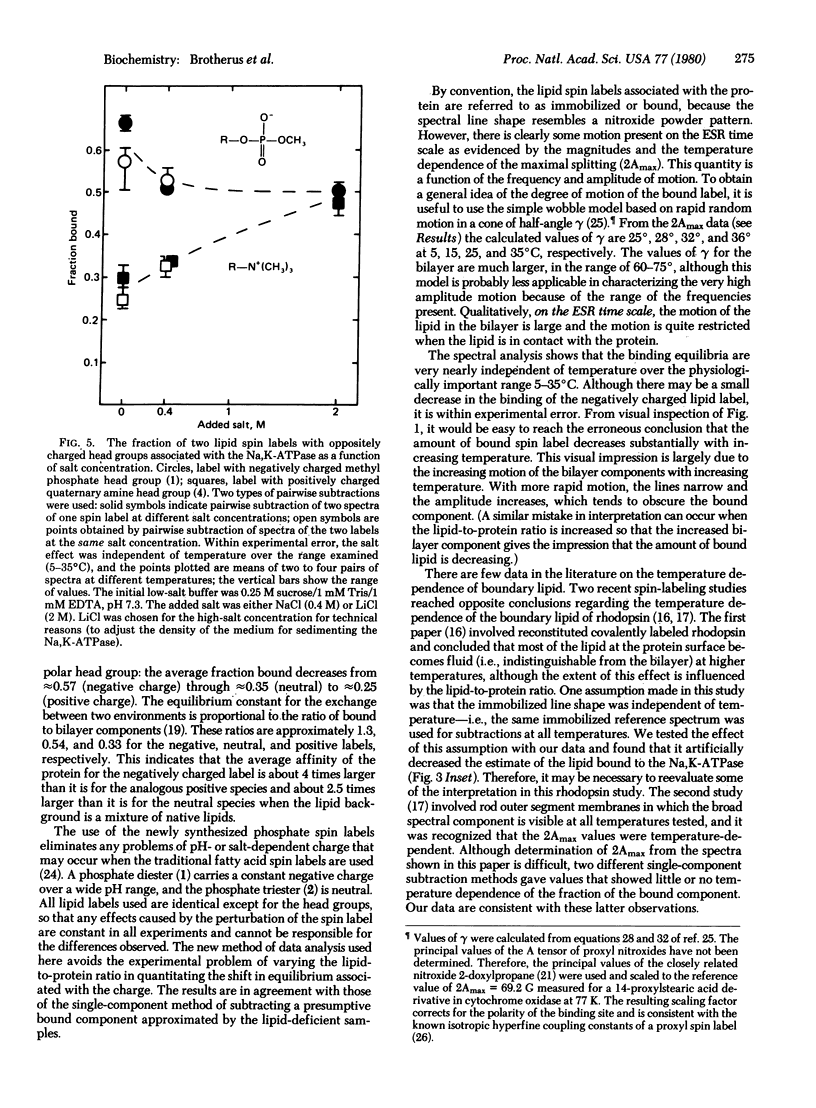
Abstract
Lipid interactions with the integral membrane protein Na,K-ATPase (ATP phosphohydrolase, EC 3.6.1.3) purified from the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus were studied by spin labeling. A protein-associated component (boundary layer) in equilibrium with the fluid bilayer is clearly evident in the electron spin resonance spectra. The influence of charge on this equilibrium was determined by varying the head group of the lipid while maintaining the chain length and the position of the label constant. The lipid spin labels were 14-proxylstearylmethyl phosphate and the corresponding dimethylphosphate, alcohol, and quaternary amine. By using a pairwise spectral analysis, as well as a conventional spectral analysis, the binding affinity was found to decrease in the order of negative greater than neutral greater than positive charges. The fraction bound decreased from about 0.57 for the negatively charged phosphate to 0.25 for the positively charged quaternary amine. The amount of each bound lipid was nearly constant over the temperature range investigated (5-35 degrees C). High salt concentrations reversibly abolished the selectivity between the labels, confirming the role of charge in the binding equilibria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbeck F., Beyreuther K., Köhler H., von Wettstein G., Braunitzer G. Virusproteine, IV. Die Konstitution des Hüllproteins des Phagen fd. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Sep;350(9):1047–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birrell G. B., Sistrom W. R., Griffith O. H. Lipid-protein associations in chromatophores from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 5;17(18):3768–3773. doi: 10.1021/bi00611a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse G., Steffens G. J. Studies on cytochrome c oxidase, II. The chemical constitution of a short polypeptide from the beef heart enzyme. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Aug;359(8):1005–1009. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davoust J., Schoot B. M., Devaux P. F. Physical modifications of rhodopsin boundary lipids in lecithin-rhodopsin complexes: a spin-label study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2755–2759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. A simple procedure for the preparation of highly purified (sodium + potassium) adenosinetriphosphatase from the rectal salt gland of Squalus acanthias and the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;86(2):378–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90761-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E., Hexum T. D. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Aug;151(2):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90521-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isern de Caldentey M., Wheeler K. P. Requirement for negatively charged dispersions of phospholipids for interaction with lipid-depleted adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):265–273. doi: 10.1042/bj1770265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Isolation and characterization of the components of the sodium pump. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 May;7(2):239–274. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H., Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. Evidence for boundary lipid in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):480–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H. The spin-labeling technique. Methods Enzymol. 1978;49:369–418. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)49019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Libertini L. J., Hebert V. C., Griffith O. H. Lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. A study of motion along fatty acid chains. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keana J. F., Lee T. D., Bernard E. M. Letter: Side-chain substituted 2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidone-N-oxyl (proxyl) nitroxides. A new series of lipid spin labels showing improved properties for the study of biological membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 May 12;98(10):3052–3053. doi: 10.1021/ja00426a082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K. Protein-liposome interactions and their relevance to the structure and function of cell membranes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Feb 25;10(3):171–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01731688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. R., Tinsley I. J. A simple, sensitive method for lipid phosphorus. Lipids. 1974 Jul;9(7):491–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02534277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandersloot J. G., Roelofsen B., de Gier J. Phosphatidylinositol as the endogenous activator of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in microsomes of rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 20;508(3):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima Y., Konigsberg W. Reinvestigation of a region of the fd bacteriophage coat protein sequence. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 25;88(3):598–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Gilmore R., Glaser M., Gutowsky H. S., Hshung J. C., Kang S. Y., King T. E., Meadows M., Rice D. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the effects of proteins and polypeptides on hydrocarbon chain order in model membrane systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4657–4660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatini P., Dabbeni-Sala F., Pitotti A., Bruni A., Mandersloot J. C. Activation of (Na+ + K+)-dependent ATPase by lipid vesicles of negative phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 1;466(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Sequence of the COOH-terminal hydrophilic region of histocompatibility antigens HLA-A2 and HLA-B7. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5319–5324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanson A., Ptak M., Rigaud J. L., Gary-Bobo C. M. An ESR study of the anchoring of spin-labeled stearic acid in lecithin multilayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1976 Nov;17(4):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(76)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. Lipid-protein interaction in reconstituted cytochrome c oxidase/phospholipid membranes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Dec;359(12):1747–1756. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R., Sakamoto T. Molecular structure in phospholipid essential to activate (Na+ K+ Mg2+)-dependent ATPase and (K+ Mg2+)-dependent phosphatase of bovine cerebral cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):384–393. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Primary structure of human erythrocyte glycophorin A. Isolation and characterization of peptides and complete amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4756–4770. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A., Volotovski I. D., Marsh D. Rhodopsin-lipid associations in bovine rod outer segment membranes. Identification of immobilized lipid by spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5006–5013. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


