Abstract
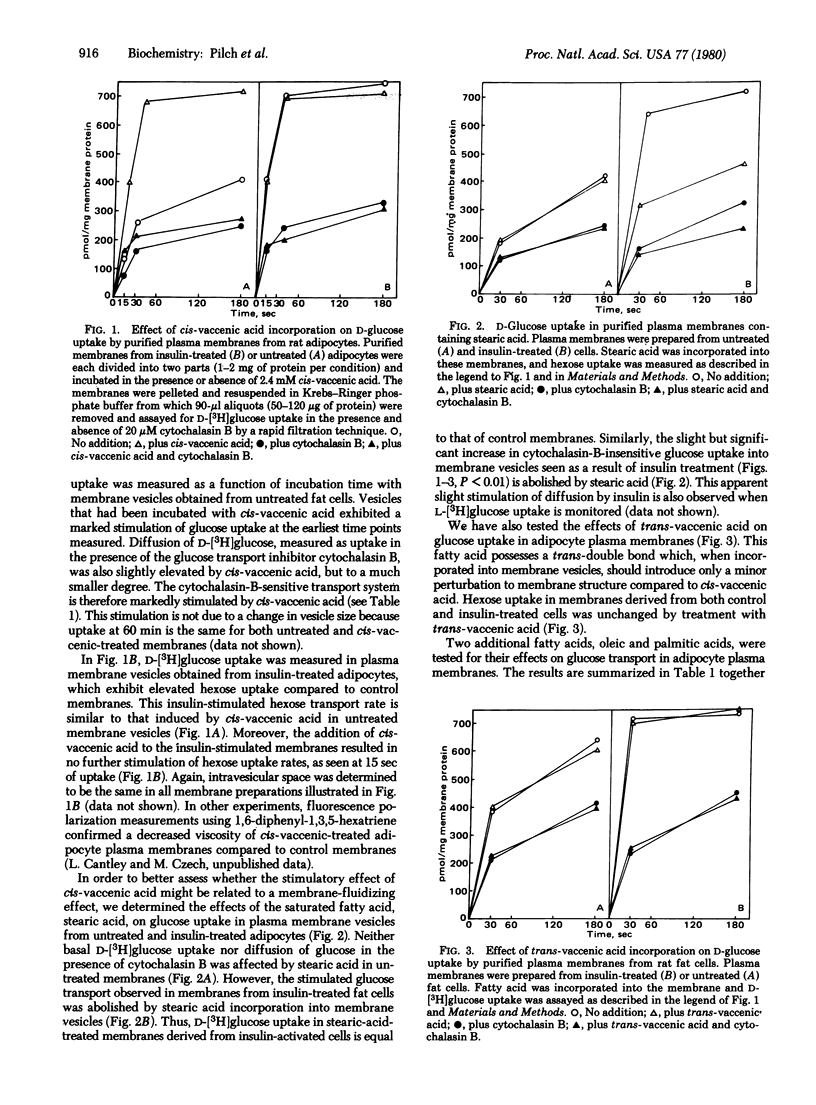
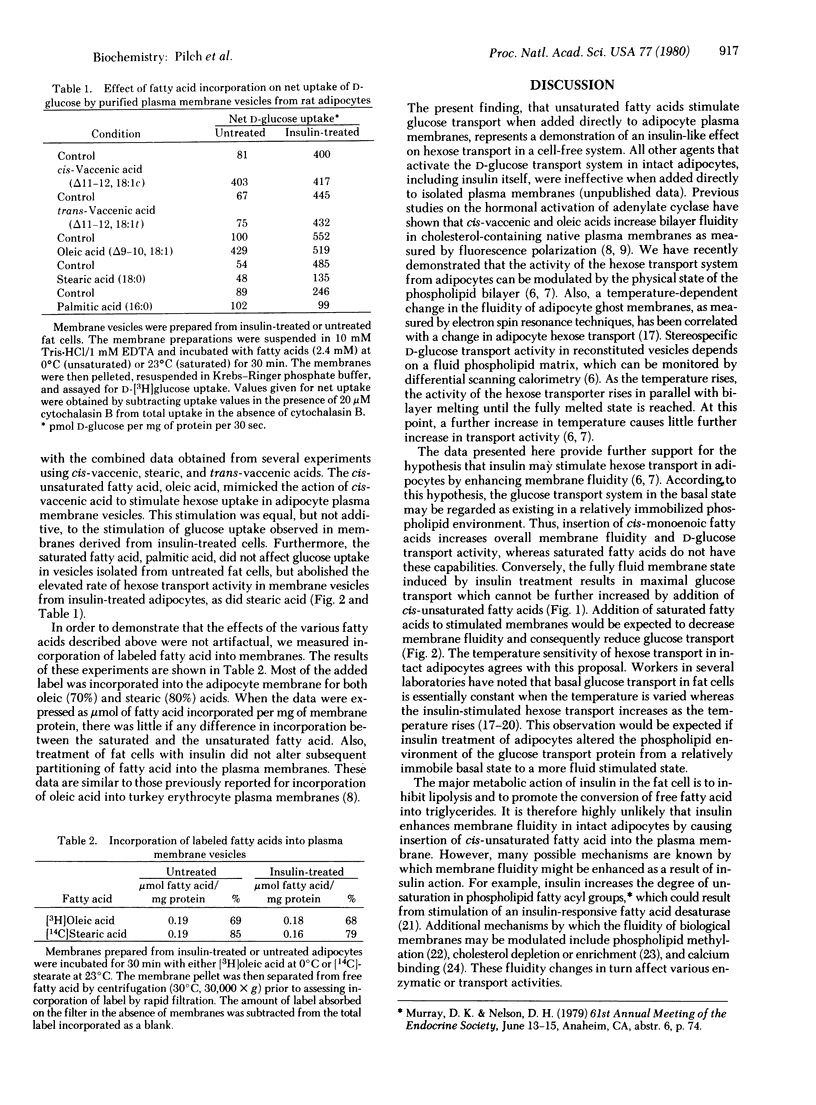
The cis-monoenoic fatty acids vaccenate and oleate stimulate D-glucose transport when partitioned into isolated plasma membranes from rat adipocytes. The magnitude of hexose transport stimulation due to these agents is equal to that observed in plasma membranes derived from insulin-treated adipocytes. Addition of cis-unsaturated fatty acids to plasma membranes derived from insulin-treated cells results in no further stimulation of glucose transport over that due to the hormone alone. In contrast, treatment of membranes exhibiting insulin-activated D-glucose transport activity with saturated fatty acids reduces transport activity to control levels. No effect of the saturated fatty acids was observed on D-glucose transport in control membranes. Because cis-unsaturated fatty acids fluidize plasma membranes under the conditions used in these experiments, these data demonstrate a positive correlation between membrane fluidity and adipocyte D-glucose transport system activity. In addition, the results suggest that enhanced bilayer fluidity or increased affinity of the glucose transporter for fluid microenvironments of the membrane may play a key role in transport regulation by insulin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda J. M., Finch E. D. Modulation of hexose uptake and insulin action by cell membrane fluidity. The effects of temperature on membrane fluidity, insulin action, and insulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2619–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Carter J. R., Martin D. B. Insulin-stimulated plasma membranes from rat adipocytes: their physiological and physicochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 23;288(1):27–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Leone G. R., Martin D. B. Identification and subcellular distribution of adipocyte peptides and phosphopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1505–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Tell G. P. Insulin-like activity of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin--direct interactions with insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lynn W. S. Stimulation of glucose metabolism by lectins in isolated white fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):368–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Regulation of the D-glucose transport system in isolated fat cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Mar 26;11(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01792833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Rimon G., Levitzki A. Adenylate cyclase activation by the beta-adrenergic receptors as a diffusion-controlled process. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):846–853. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Axelrod J. Enzymatic methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine increases erythrocyte membrane fluidity. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):219–220. doi: 10.1038/275219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Sarver J. A., Vega F. V., Pointer R. H. Actions of insulin in fat cells. Effects of low temperature, uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation, and respiratory inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2226–2233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luly P., Shinitzky M. Gross structural changes in isolated liver cell plasma membranes upon binding of insulin. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):445–450. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden T. D., Chapman D., Quinn P. J. Cholesterol modulates activity of calcium-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):538–541. doi: 10.1038/279538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior D. L., Czech M. P. Sensitivity of the adipocyte D-glucose transport system to membrane fluidity in reconstituted vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8744–8747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of the ability of insulin to activate the glucose-transport system in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):137–145. doi: 10.1042/bj1720137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Schramm M. Fatty acids as modulators of membrane functions: catecholamine-activated adenylate cyclase of the turkey erythrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillion D. J., Czech M. P. Antibodies against intrinsic adipocyte plasma membrane proteins activate D-glucose transport independent of interaction with insulin binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3761–3764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillion D. J., Shanahan M. F., Czech M. P. Retention of insulin-stimulated D-glucose transport activity by adipocyte plasma membranes following extraction of extrinsic proteins. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(3):269–277. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad M. R., Joshi V. C. Regulation of rat hepatic stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase. The roles of insulin and carbohydrate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):997–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puskin J. S., Martin T. Divalent cation binding to phospholipid veiscles. Dependence on temperature and lipid fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 23;552(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer B. E., Zadunaisky J. A. Stimulation of chloride transport by fatty acids in corneal epithelium and relation to changes in membrane fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 4;556(1):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F., Czech M. P. Partial purification of the D-glucose transport system in rat adipocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6554–6561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinten J. Cytochalasin B inhibition and temperature dependence of 3-O-methylglucose transport in fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 4;511(2):259–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Enhancement of the number of functional transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8002–8005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Gliemann J. Kinetic parameters of transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5276–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


