Abstract
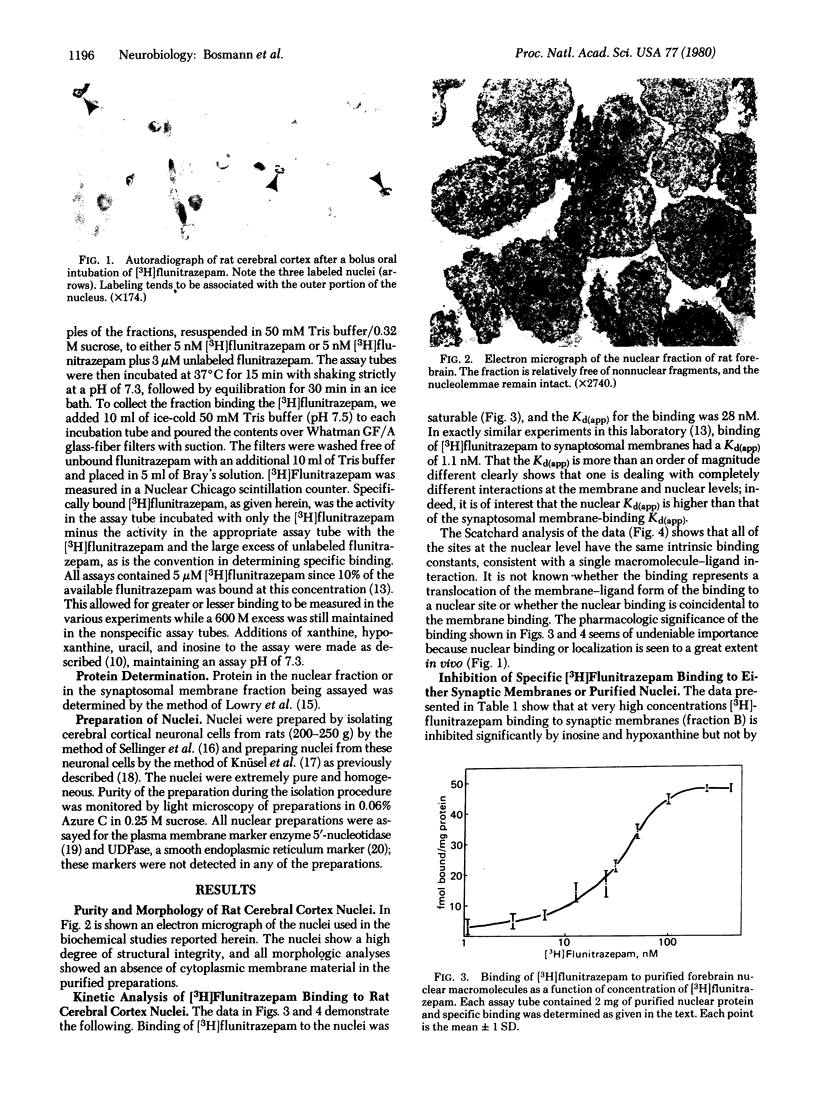
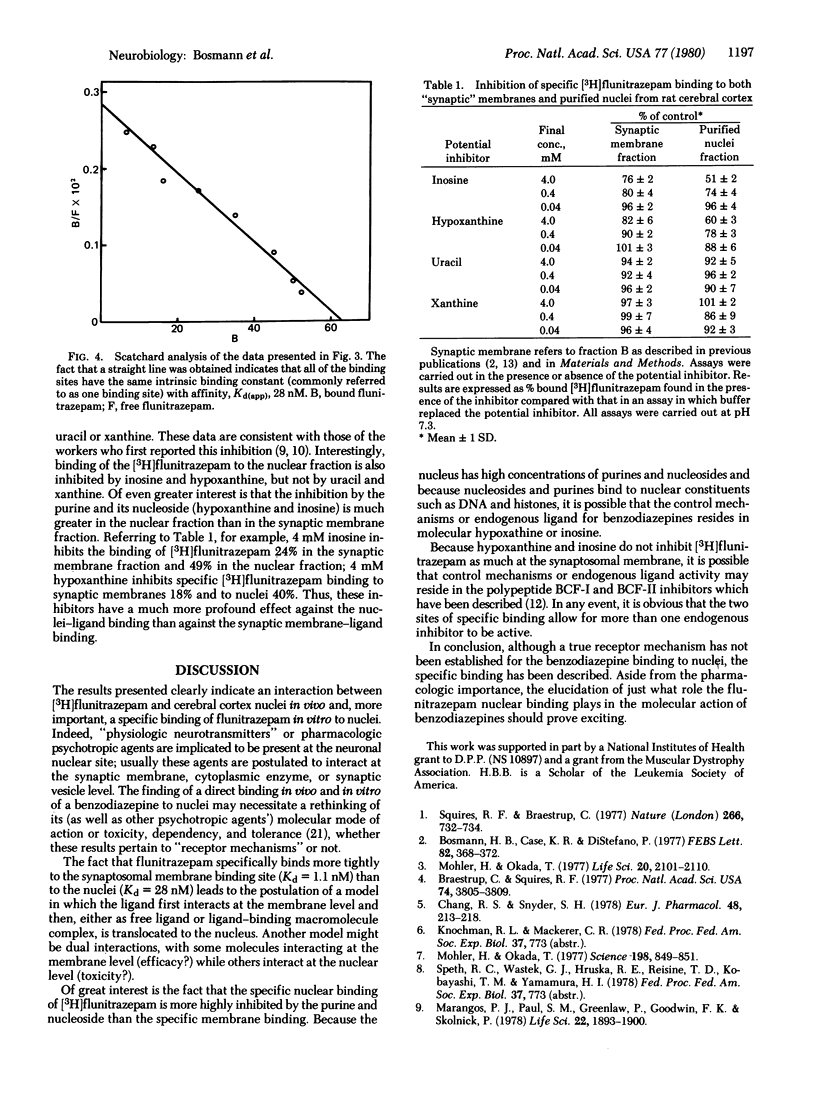
Autoradiographic localization of [3H]flunitrazepam in nuclei of the rat cerebral cortex was further confirmed by biochemical analysis of specific nuclear binding. Highly purified rat cerebral cortex nuclei were shown to bind [3H]flunitrazepam specifically. The Kd(app) for nuclear binding was 28 nM for the nuclei compared with a Kd(app) of 1.1 nM for binding of [3H] flunitrazepam to synaptosomal membrane fractions of the same tissue. Inhibition of the nuclear binding with inosine and hypoxanthine was greater than inhibition of the synaptic membrane fractions. These results lead to to conclude that specific binding may occur at both the synaptic membrane and the nuclear levels and that different endogenous ligands may compete at each site for binding. Furthermore, the possibility exists for translocation and alteration of the bound ligand complex from membrane site to nuclear site.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosmann H. B., Case K. R., DiStefano P. Diazepam receptor characterization: specific binding of a benzodiazepine to macromolecules in various areas of rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80623-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Case K. R. Properties of rat cerebral cortex neuronal nuclear surfaces: electrokinetic parameters. Neurobiology. 1975 Mar;5(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B. Isolation and characterization of a UDPase from cerebellum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 16;220(3):560–568. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90286-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Penney D. P., Case K. R., DiStefano P., Averill K. Diazepam receptor: specific binding of [3H] diazepam and [3H] flunitrazepam to rat brain subfractions. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Pike G. Z. Membrane marker enzymes: isolation, purification, and properties of 5'-nucleotidase from rat cerebellum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 10;227(2):402–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Snyder S. H. Benzodiazepine receptors: labeling in intact animals with [3H] flunitrazepam. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;48(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colello G. D., Hockenbery D. M., Bosmann H. B., Fuchs S., Folkers K. Competitive inhibition of benzodiazepine binding by fractions from porcine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6319–6323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano P., Case K. R., Colello G. D., Bosmann H. B. Increased specific binding of [3H]diazepam in rat brain following chronic diazepam administration. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1979 Mar;3(2):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(79)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel A., Lehner B., Kuenzle C. C., Kistler G. S. Isolation of neuronal nuclei from rat brain cortex. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):762–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Paul S. M., Greenlaw P., Goodwin F. K., Skolnick P. Demonstration of an endogenous, competitive inhibitor(s) of [3H] diazepam binding in bovine brain. Life Sci. 1978 Jun 5;22(21):1893–1900. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Properties of 3H-diazepam binding to benzodiazepine receptors in rat cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 1977 Jun 15;20(12):2101–2110. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Gredal O., Braestrup C. Some properties of 3H-diazepam displacing activity from human urine. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 20;25(8):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellinger O. Z., Azcurra J. M., Johnson D. E., Ohlsson W. G., Lodin Z. Independence of protein synthesis and drug uptake in nerve cell bodies and glial cells isolated by a new technique. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 21;230(16):253–256. doi: 10.1038/newbio230253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick P., Marangos P. J., Goodwin F. K., Edwards M., Paul S. Identification of inosine and hypoxanthine as endogenous inhibitors of [3H] diazepam binding in the central nervous system. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 9;23(14):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




