Abstract
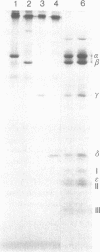
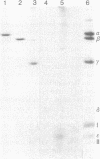
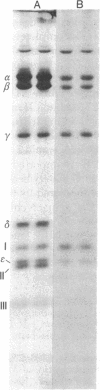
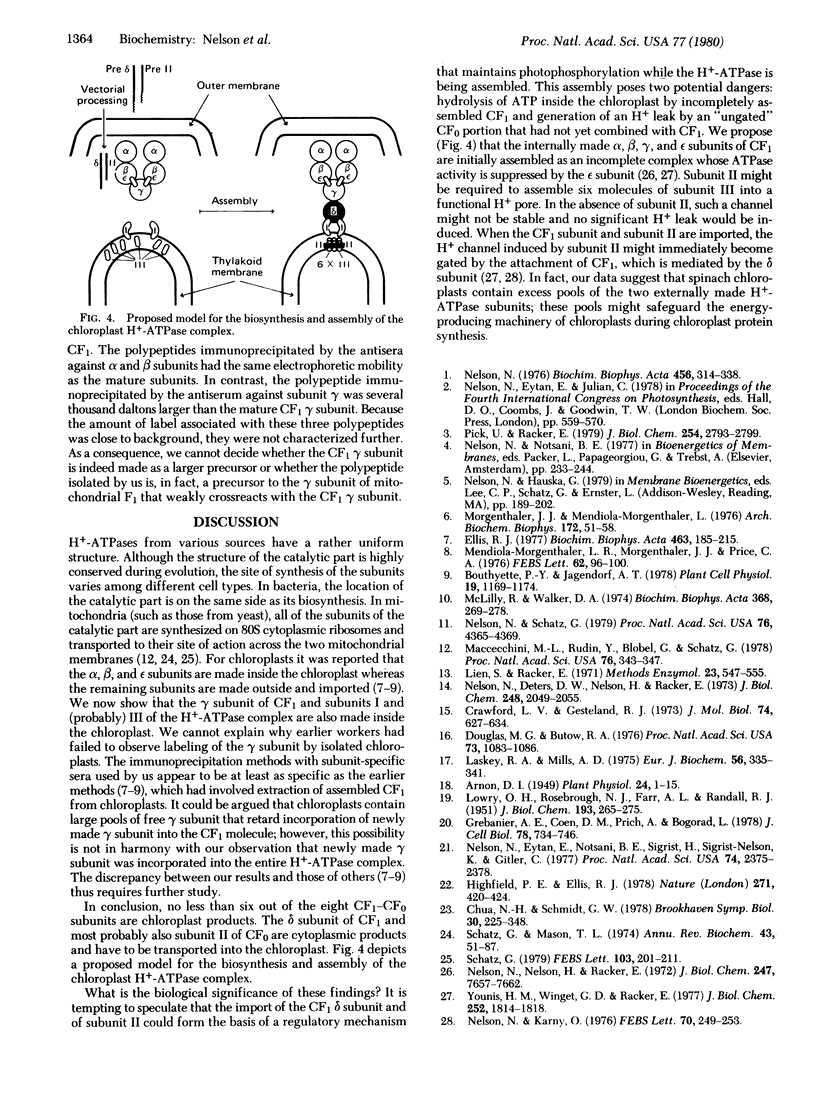
The H+-translocating ATPase complex of chloroplasts consists of at least eight nonidentical subunits. Five of these (α, β, γ, δ, and ε subunits) collectively constitute the globular extramembranous CF1 portion of the complex. The remaining three subunits (I-III) represent the membrane-embedded portion. Biosynthesis and assembly of these subunits were studied by pulse-labeling isolated spinach chloroplasts in the presence of cycloheximide or chloramphenicol and by translating total leaf RNA in a rabbit reticulocyte system. The labeled products were analyzed by immunoprecipitation with subunit-specific antisera or by isolating the entire H+-translocating ATPase complex in a nearly pure state. We found that chloroplasts synthesize the α, β, γ, and ε subunits of CF1, the membrane-embedded subunit I, and probably also the membrane-embedded subunit III. The δ subunit (and probably also subunit II) are imported from the cytoplasm via larger precursor forms. After isolated chloroplasts are labeled in the presence of cycloheximide, the chloroplast-made H+-ATPase subunits are assembled into a complex that is indistinguishable from the authentic H+-ATPase complex. This assembly indicates that isolated chloroplasts contain excess pools of the cytoplasmically made subunits.
Keywords: coupling factor, immunoprecipitation, in vitro synthesis, precursors, assembly
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Gesteland R. F. Synthesis of polyoma proteins in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):627–634. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., Butow R. A. Variant forms of mitochondrial translation products in yeast: evidence for location of determinants on mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1083–1086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebanier A. E., Coen D. M., Rich A., Bogorad L. Membrane proteins synthesized but not processed by isolated maize chloroplasts. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):734–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Walker D. A. The reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate by reconstituted chloroplasts and by chloroplast extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 19;368(3):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maccecchini M. L., Rudin Y., Blobel G., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria: precursor forms of the extramitochondrially made F1-ATPase subunits in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):343–347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenthaler J. J., Mendiola-Morgenthaler L. Synthesis of soluble, thylakoid, and envelope membrane proteins by spinach chloroplasts purified from gradients. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Deters D. W., Nelson H., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing photophosphorylation. 8. Properties of isolated subunits of coupling factor 1 from spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2049–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Eytan E., Notsani B. E., Sigrist H., Sigrist-Nelson K., Gitler C. Isolation of a chloroplast N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding proteolipid, active in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2375–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Karny O. The role of delta subunit in the coupling activity of chloroplast coupling factor 1. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80768-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Nelson H., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing photophosphorylation. XII. Purification and properties of an inhibitor isolated from chloroplast coupling factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7657–7662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Schatz G. Energy-dependent processing of cytoplasmically made precursors to mitochondrial proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4365–4369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure and function of chloroplast ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 30;456(3-4):314–338. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(76)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Racker E. Purification and reconstitution of the N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive ATPase complex from spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2793–2799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz G. How mitochondria import proteins from the cytoplasm. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81328-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younis H. M., Winget G. D., Racker E. Requirement of the delta subunit of chloroplast coupling factor 1 for photophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1814–1818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]