Abstract
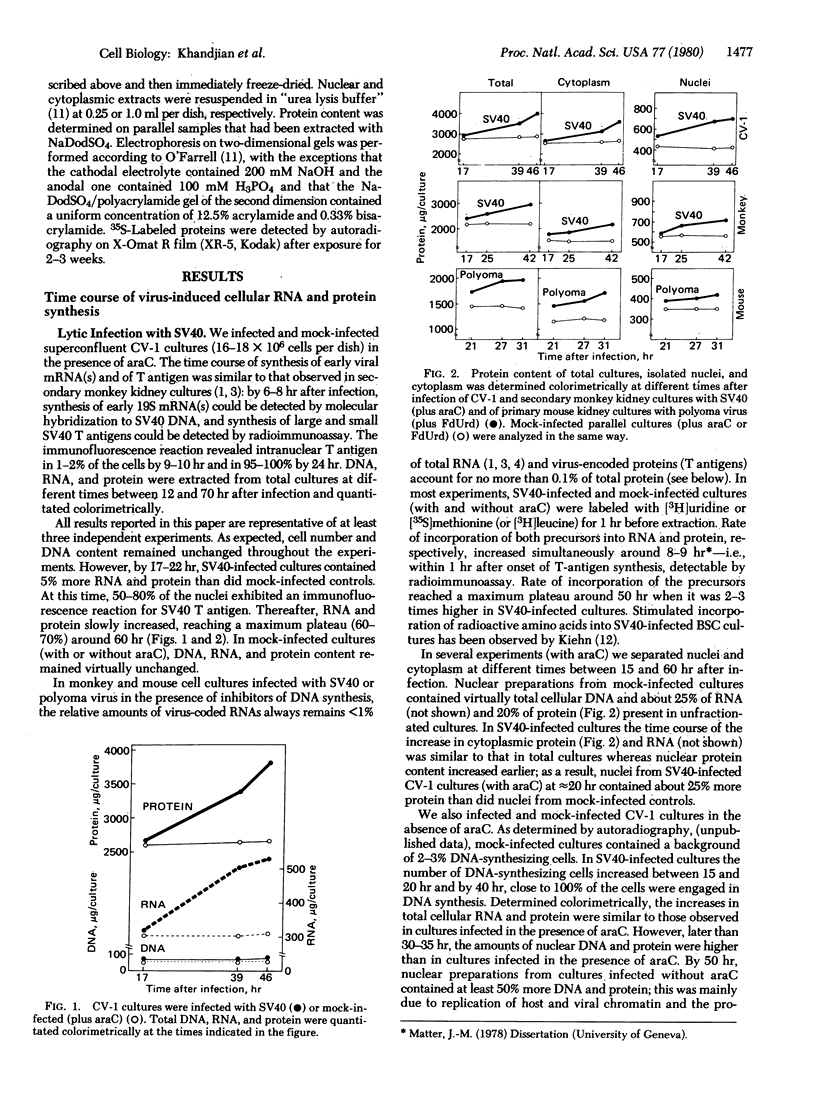
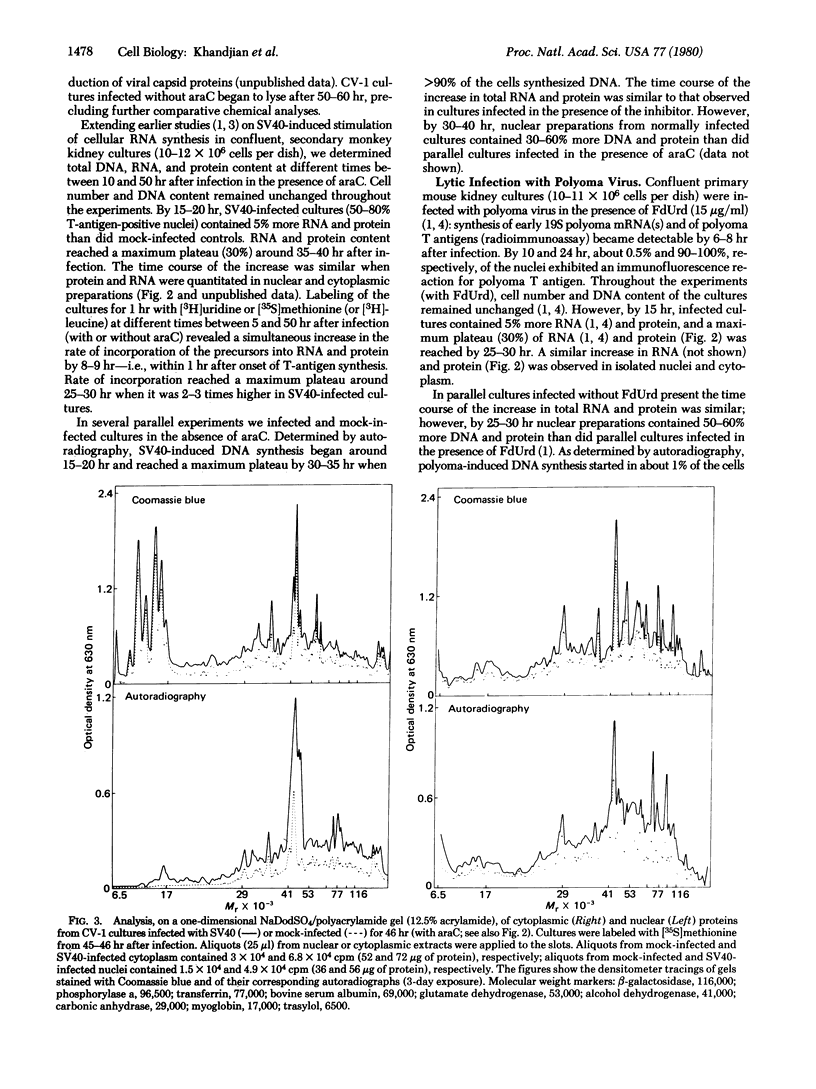
In lytic infection with simian virus 40 and polyoma virus of monkey and mouse cells in tissue culture, synthesis of the viral tumor (T) antigens (T antigens) is rapidly followed by a mitogenic response of the host cell. The latter begins with virus-induced stimulation of overall cellular RNA and protein synthesis, leading to a substantial increase in cytoplasmic and nuclear RNA and protein. Stimulation begins within 1 hr after onset of T-antigen synthesis and also occurs if virus-induced DNA synthesis is blocked by metabolic inhibitors. The broad spectrum of biological and molecular effects induced by simian virus 40 and polyoma virus is, at least phenotypically, reminescent of the pleiotropic impact exerted on target cells by nonviral mitogens and by certain growth-promoting steroid and polypeptide hormones.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad-Zadeh C., Allet B., Greenblatt J., Weil R. Two forms of simian-virus-40-specific T-antigen in abortive and lytic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1097–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R., Ide T., Whelly S. Stimulation of ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei and nucleoli by partially purified preparations of SV40 T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):685–691. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn E. D. Protein metabolism in SV40-infected cells. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):313–333. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M. Resolution of simian virus 40 proteins in whole cell extracts by two-dimensional electrophoresis: heterogeneity of the major capsid protein. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malkey B. W., Woo S. L., Harris S. E., Rosen J. M., Means A. R. Steroid hormone regulation of specific messenger RNA and protein synthesis in eucaryotic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Apr;85(2 Pt 2 Suppl 1):343–356. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal L. J., Brown M. The control of SV40 transcription during a lytic infection: late RNA synthesis in the presence of inhibitors of DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Mar;4(3):551–565. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon C., Türler H., Weil R. Polyoma-induced stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis is paralleled by changed expression of the viral genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1483–1503. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer R. ACTH: a short introductory review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Oct 28;297:3–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb41843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R. Viral 'tumor antigens': A novel type of mammalian regulator protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):301–388. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M. Steroid receptors: elements for modulation of eukaryotic transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:721–746. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]