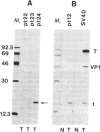
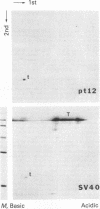
Abstract
With the premise that mRNAs transcribed in Escherichia coli from cloned eukaryotic DNA inserts do not possess the necessary regulatory signals for recognition by prokaryotic ribosomes, we have constructed a general plasmid vector carrying a chemically synthesized prokaryotic ribosome binding site that will ensure the efficient expression of eukaryotic proteins in E. coli. In addition to the regulatory signals necessary for ribosome recognition, the synthetic segment contains, at one end, a Pst I cleavage site which will direct its insertion to pBR322 DNA and, at the other end, a HindIII site to facilitate attachment of the passenger eukaryotic gene. Using simian virus 40 (SV40) tumor (t) antigen as a model system, we have ligated the SV40 DNA fragment containing the entire t antigen gene in tandem with the synthetic ribosome binding site to pBR322 DNA at the Pst I site, which lies within the coding sequence of the beta-lactamase gene. Initiation of transcription at the beta-lactamase promoter would produce a chimeric mRNA with the synthetic ribosome binding signals and the SV40 sequence flanked by beta-lactamase coding sequences. Utilization of the synthetic regulatory signals for initiation of translation is demonstrated by the efficient synthesis, in bacterial transformants, of authentic SV40 t antigen. Excision of the entire SV40 insert by HindIII from those clones that have retained intact HindIII sites at the junction between the ribosome binding site and the SV40 sequence would allow insertion of other heterologous DNAs by using HindIII linkers. The efficient expression of any DNA insert would require that the entire coding sequence be contiguous and that its termini be randomized by treatment with exonuclease III and nuclease S1 to vary the distance between the translational initiation codon and the synthetic ribosome binding site.
Full text
PDF



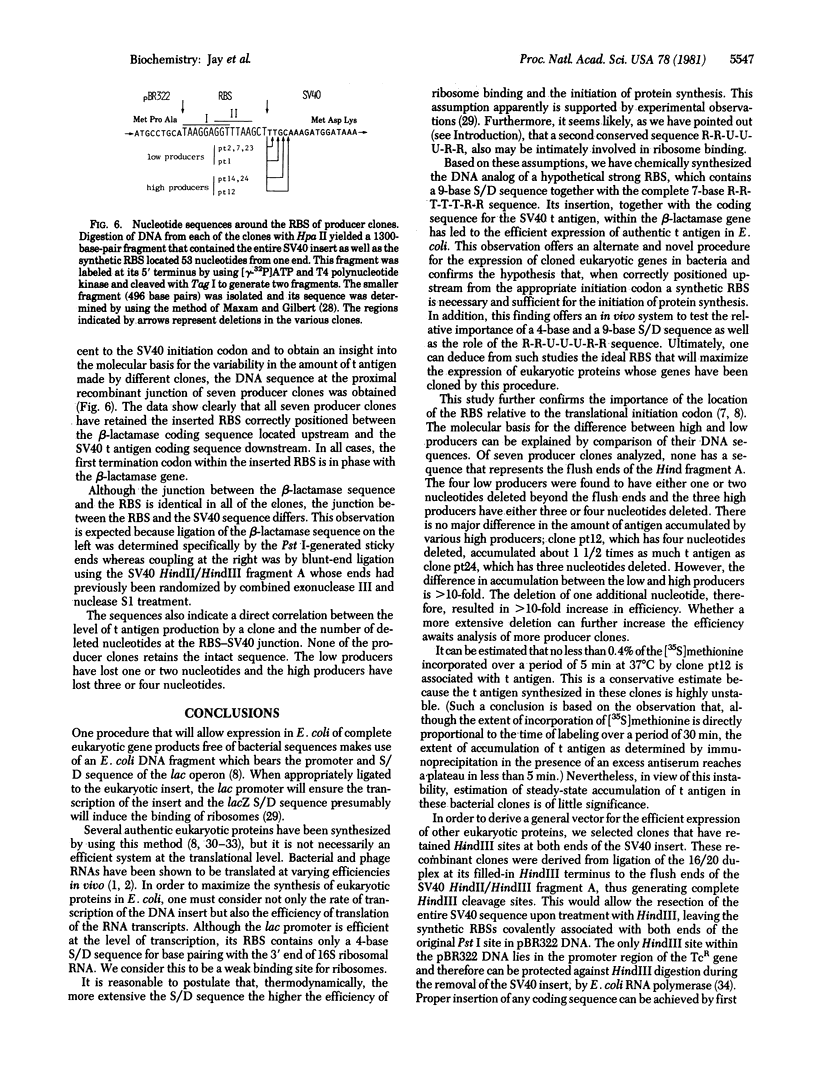

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baralle F. E., Brownlee G. G. AUG is the only recognisable signal sequence in the 5' non-coding regions of eukaryotic mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):84–87. doi: 10.1038/274084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Cole C. N., Smith A. E., Paucha E., Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Berg P. Organization and expression of early genes of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):117–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Buzash-Pollert E., Studier F. W. Mutations of bacteriophage T7 that affect initiation of synthesis of the gene 0.3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2741–2745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L., Hozumi T., Arentzen R., Itakura K., Yansura D. G., Ross M. J., Miozzari G., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. Direct expression in Escherichia coli of a DNA sequence coding for human growth hormone. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):544–548. doi: 10.1038/281544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberg-Manago M., Gros F. Initiation mechanisms of protein syntehesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1977;20:209–284. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60474-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lauer G., Roberts T. M., Ptashne M. Improved methods for maximizing expression of a cloned gene: a bacterium that synthesizes rabbit beta-globin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90640-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Seth A. K., Jay G. Specific binding of a chemically synthesized prokaryotic ribosome recognition site. Prospect for molecular cloning and expression of eukaryotic genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3809–3812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Ferrini U., Robinson E. A., Khoury G., Appella E. Cell-free synthesis of mouse H-2 histocompatibility antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6562–6566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Jay F. T., Chang C., Friedman R. M., Levine A. S. Tumor-specific transplantation antigen: use of the Ad2+ND1 hybrid virus to identify the protein responsible for simian virus 40 tumor rejection and its genetic origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3055–3059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Shiu R. P., Jay F. T., Levine A. S., Pastan I. Identification of a transformation-specific protein induced by a Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Identification of features in 5' terminal fragments from reovirus mRNA which are important for ribosome binding. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Bikel I., Yocum R. R., Livingston D. M., Ptashne M. Synthesis of simian virus 40 t antigen in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5596–5600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Kacich R., Ptashne M. A general method for maximizing the expression of a cloned gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. L., West R. W., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Characterizing wild-type and mutant promoters of the tetracycline resistance gene in pBR313. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3267–3287. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., Walkinshaw M. D., Arnott S., Morré D. J. The ribosome binding sites recognized by E. coli ribosomes have regions with signal character in both the leader and protein coding segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3895–3907. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A. K., Jay E. A study of the efficiency and the problem of sulfonation of several condensing reagents and their mechanisms for the chemical synthesis of deoxyoligoribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5445–5459. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Goodman H. M., Heyneker H. L., Shine J., Boyer H. W., Cozzarelli N. R. Interaction of bacteriophage T4 RNA and DNA ligases in joining of duplex DNA at base-paired ends. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3987–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W., Hermoso J. M., Leffler S. Ribosomal protein S1 and polypeptide chain initiation in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2325–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., Aviram M., Kanarek A., Weiss A. Polyuridylic acid binding and translating by Escherichia coli ribosomes: stimulation by protein I, inhibition by aurintricarboxylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 27;281(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Guarente L., Roberts T. M., Kimelman D., Douhan J., 3rd, Ptashne M. Expression of the human fibroblast interferon gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5230–5233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burgess T. L., Tjian R. Properties of simian virus 40 small t antigen overproduced in bacteria. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):683–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.683-697.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]