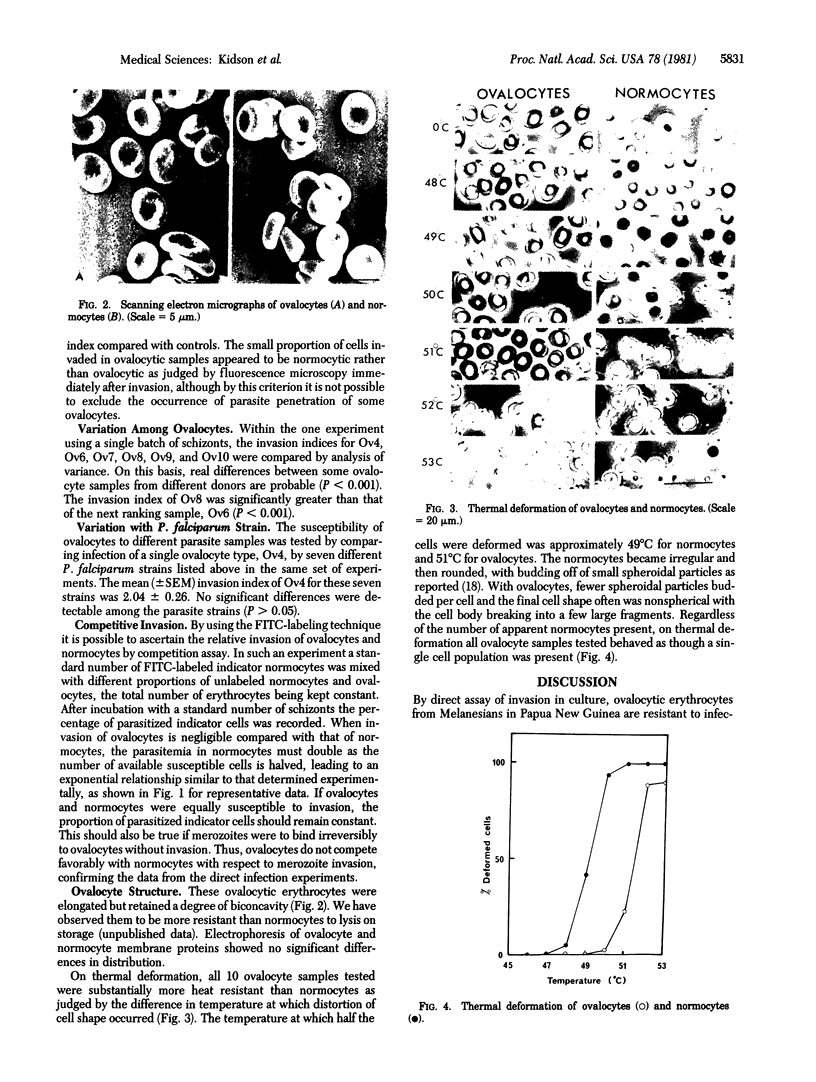
Abstract
Ovalocytic erythrocytes from Melanesians in Papua New Guinea have been demonstrated to be resistant to infection by malaria parasites (Plasmodium falciparum) in culture by using a double-label fluorescence assay of merozoite invasion. That merozoites do not bind irreversibly to ovalocytes has been demonstrated by an assay that measures competition between ovalocytes and normocytes. Analysis of behavior on thermal deformation has demonstrated that ovalocytes are more more thermostable than normocytes, suggesting that there is a major difference in cytoskeletal structure. These findings with P. falciparum and epidemiological data demonstrating clinical resistance to P. vivax and P. malariae suggest that the membrane alterations(s) in these ovalocytes affect(s) invasion step(s) common to all three species of malaria parasite.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amato D., Booth P. B. Hereditary ovalocytosis in Melanesians. P N G Med J. 1977 Mar;20(1):26–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth P. B., Serjeantson S., Woodfield D. G., Amato D. Selective depression of blood group antigens associated with hereditary ovalocytosis among melanesians. Vox Sang. 1977;32(2):99–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1977.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. A., Mitchell G. H., Cohen S. Letter: Mechanism of host specificity in malarial infection. Nature. 1973 Jul 6;244(5410):40–41. doi: 10.1038/244040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K., Williamson J. R., Zarkowsky H. S. Effect of heat on the circular dichroism of spectrin in hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):326–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI109456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Lamont G., Elliott T., Kidson C., Brown G., Mitchell G., Stace J., Alpers M. Plasmodium falciparum strains from Papua New Guinea: culture characteristics and drug sensitivity. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1980 Dec;11(4):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A., Miller L. H., Whitehouse W. C., Shiroishi T. Invasion of erythrocytes by malaria merozoites. Science. 1975 Feb 28;187(4178):748–750. doi: 10.1126/science.803712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler V., Branton D. Lateral mobility of human erythrocyte integral membrane proteins. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):23–26. doi: 10.1038/268023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. J. Erythrocytic mechanism of sickle cell resistance to malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1994–1997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. J. Oxidant damage mediates variant red cell resistance to malaria. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):245–247. doi: 10.1038/280245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. J., Roth E. F., Nagel R. L., Trager W. The role of hemoglobins C, S, and Nbalt in the inhibition of malaria parasite development in vitro. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 Sep;28(5):777–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golan D. E., Veatch W. Lateral mobility of band 3 in the human erythrocyte membrane studied by fluorescence photobleaching recovery: evidence for control by cytoskeletal interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2537–2541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison K. L., Collins K. A., McKenna H. W. Hereditary elliptical stomatocytosis: a case report. Pathology. 1976 Oct;8(4):307–311. doi: 10.3109/00313027609101493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B. Concentration from continuous culture of erythrocytes infected with trophozoites and schizonts of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1274–1276. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont G., Saul A., Kidson C. Plasmodium falciparum: assay of invasion of erythrocytes. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Feb;51(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E. Spectrin-actin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal red blood cells. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jan;16(1):21–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L. Genetics of red cells and susceptibility to malaria. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):961–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGHEE R. B. The infection by Plasmodium lophurae of duck erythrocytes in the chicken embryo. J Exp Med. 1953 Jun;97(6):773–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.6.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Johnson J. G., Shiroishi T. Interaction between cytochalasin B-treated malarial parasites and erythrocytes. Attachment and junction formation. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):172–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Haynes J. D., McAuliffe F. M., Shiroishi T., Durocher J. R., McGinniss M. H. Evidence for differences in erythrocyte surface receptors for the malarial parasites, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium knowlesi. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):277–281. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Mason S. J., Dvorak J. A., McGinniss M. H., Rothman I. K. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):561–563. doi: 10.1126/science.1145213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., McAuliffe F. M., Mason S. J. Erythrocyte receptors for malaria merozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):204–208. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Painter R. G. Anionic sites of human erythrocyte membranes. II. Antispectrin-induced transmembrane aggregation of the binding sites for positively charged colloidal particles. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONDER E. Shape and shape transformations of heated human red cells. J Exp Biol. 1949 May;26(1):35–45. doi: 10.1242/jeb.26.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S., Bryson K., Amato D., Babona D. Malaria and hereditary ovalocytosis. Hum Genet. 1977 Jun 30;37(2):161–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00393579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]