Abstract
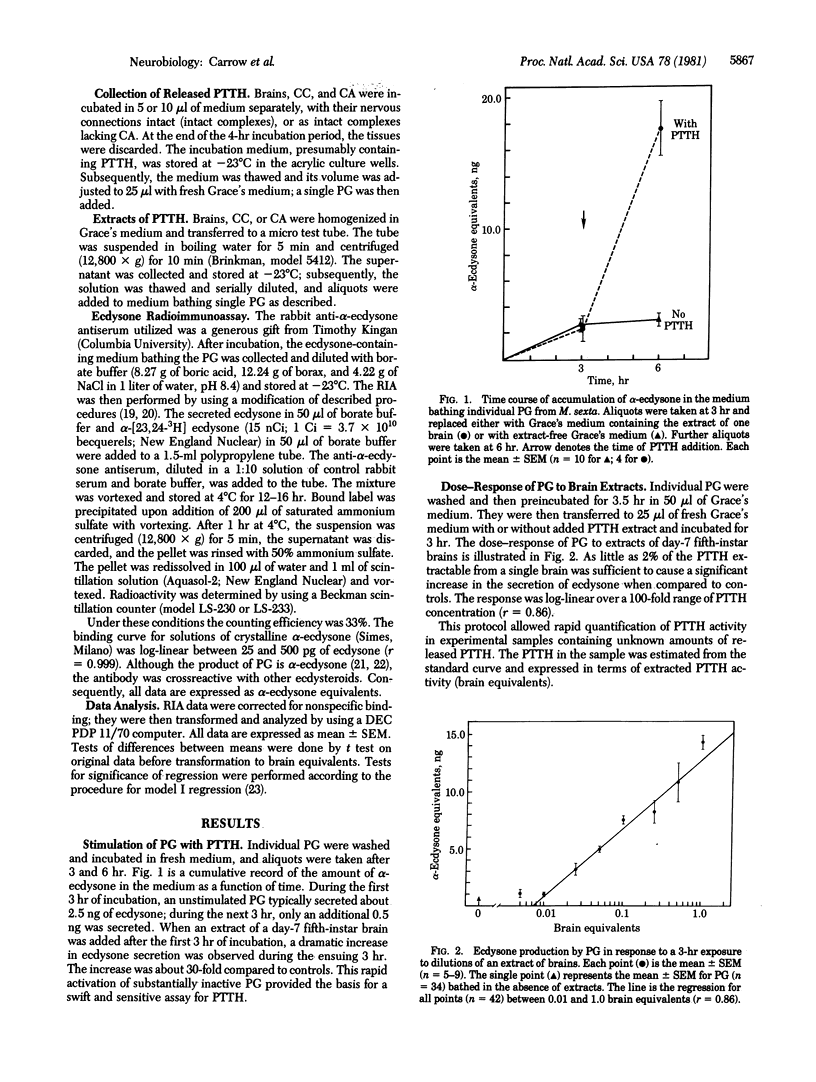
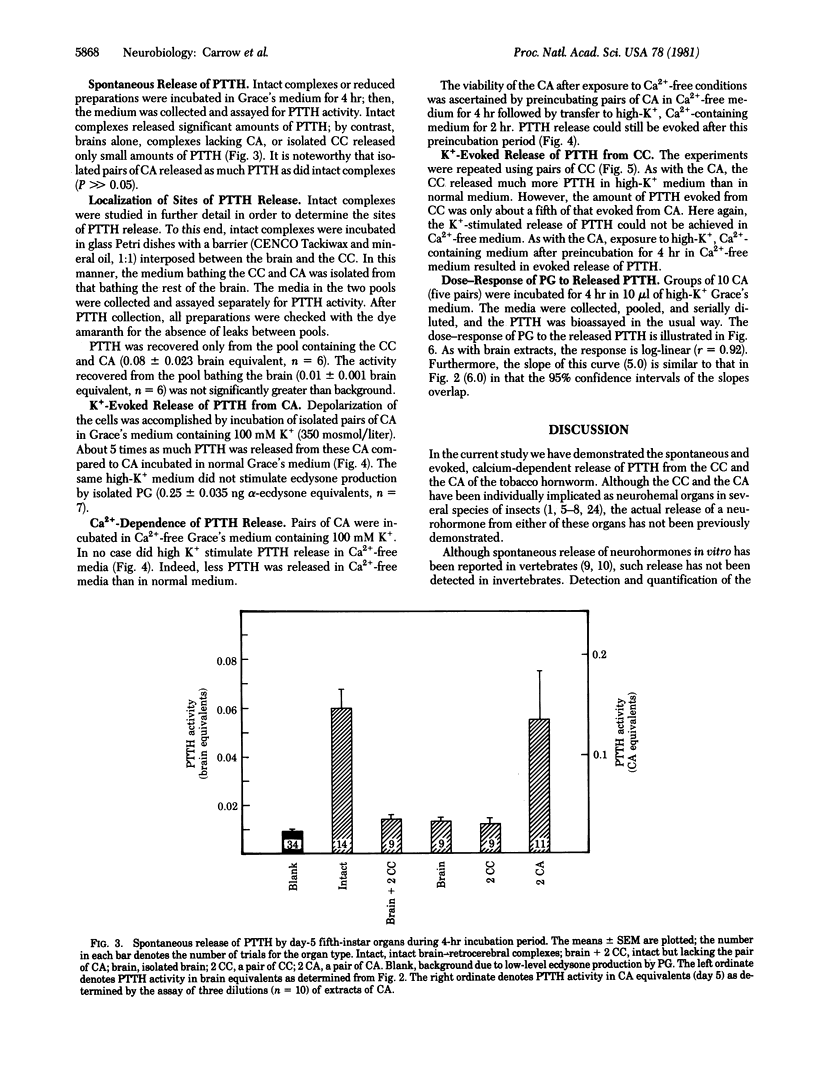
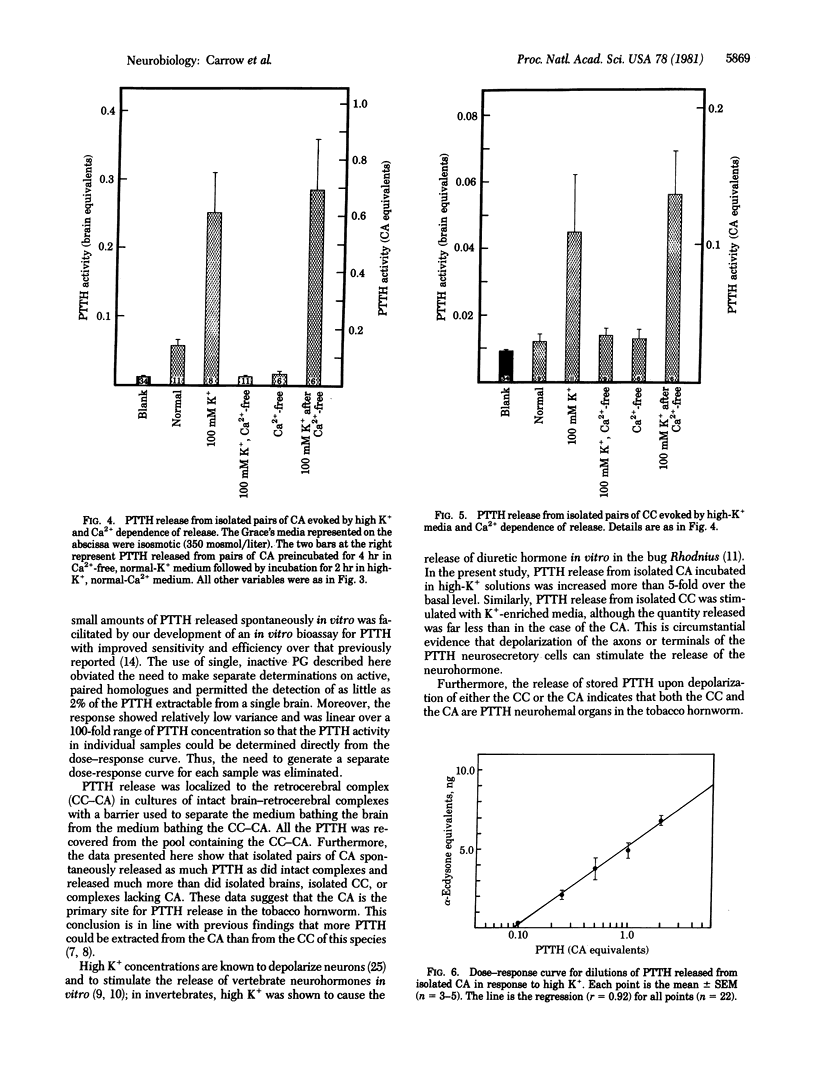
Release of neurohormone from putative cephalic neurohemal organs was directly demonstrated in an insect. The prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, was measured indirectly by its ability to stimulate the secretion of α-ecdysone by inactive prothoracic glands; the ecdysone was measured by radioimmunoassay. The PTTH released spontaneously from intact brain-retrocerebral complexes was localized to the retrocerebral complex by placing a waxy barrier across the nerves connecting the corpora cardiaca to the brain. Isolated corpora allata spontaneously released much more PTTH than did either isolated corpora cardiaca or isolated brains. Media containing 100 mM potassium stimulated PTTH release from both isolated corpora allata and isolated corpora cardiaca. In calcium-free media, spontaneous PTTH release was diminished and release could not be stimulated by high potassium. These results indicate that depolarization of the neurosecretory cells is correlated with calcium-dependent neurohormone release and that there are multiple neurohemal organs for PTTH. The biological activities of stored and circulating PTTH are compared.
Keywords: in vitro neurosecretion, brain, corpora cardiaca, corpora allata, prothoracic glands
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berlind A., Cooke I. M. Effect of calcium omission on neurosecretion and electrical activity of crab pericardial organs. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1968 Oct;11(2):458–463. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(68)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollenbacher W. E., Agui N., Granger N. A., Gilbert L. I. In vitro activation of insect prothoracic glands by the prothoracicotropic hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5148–5152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst D. W., O'Connor J. D. Trace analysis of ecdysones by gas-liquid chromatography, radioimmunoassay and bioassay. Steroids. 1974 Nov;24(5):637–656. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(74)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chino H., Sakurai S., Ohtaki T., Ikekawa N., Miyazaki H., Ishibashi M., Abuki H. Biosynthesis of agr-Ecdysone by Prothoracic Glands in vitro. Science. 1974 Feb 8;183(4124):529–530. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4124.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: variations on the theme of calcium-activated exocytosis involving cellular and extracellular sources of calcium. Ciba Found Symp. 1978;(54):61–90. doi: 10.1002/9780470720356.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs D., Riddiford L. M. Prothoracicotropic hormone in Manduca sexta: localization by a larval assay. J Exp Biol. 1977 Feb;66(1):255–266. doi: 10.1242/jeb.66.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Lee C. M., Gilbert R. F., Hunt S., Emson P. C. Regulation of neuropeptide release. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Oct 29;210(1178):91–111. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. S., Bollenbacher W. E., Borst D. W., Vedeckis W. V., O'connor J. D., Ittycheriah P. I., Gilbert L. I. The Secretion of alpha-Ecdysone by the Prothoracic Glands of Manduca sexta In Vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):793–796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddrell S. H., Gee J. D. Potassium-induced release of the diuretic hormones of Rhodnius prolixus and Glossina austeni: Ca dependence, time course and localization of neurohaemal areas. J Exp Biol. 1974 Aug;61(1):155–171. doi: 10.1242/jeb.61.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Zingg H. H., Dreifuss J. J. Calcium-dependent somatostatin secretion from rat neurohypophysis in vitro. Nature. 1977 Jun 30;267(5614):852–853. doi: 10.1038/267852a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAMOS M. H., LAVINE L. S., SHAMOS M. I. Piezoelectric effect in bone. Nature. 1963 Jan 5;197:81–81. doi: 10.1038/197081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truman J. W., Riddiford L. M. Physiology of insect rhythms. 3. The temporal organization of the endocrine events underlying pupation of the tobacco hornworm. J Exp Biol. 1974 Apr;60(2):371–382. doi: 10.1242/jeb.60.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weevers R. D. A lepidopteran saline: effects of inorganic cation concentrations on sensory, reflex and motor responses in a herbivorous insect. J Exp Biol. 1966 Feb;44(1):163–175. doi: 10.1242/jeb.44.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


