Abstract
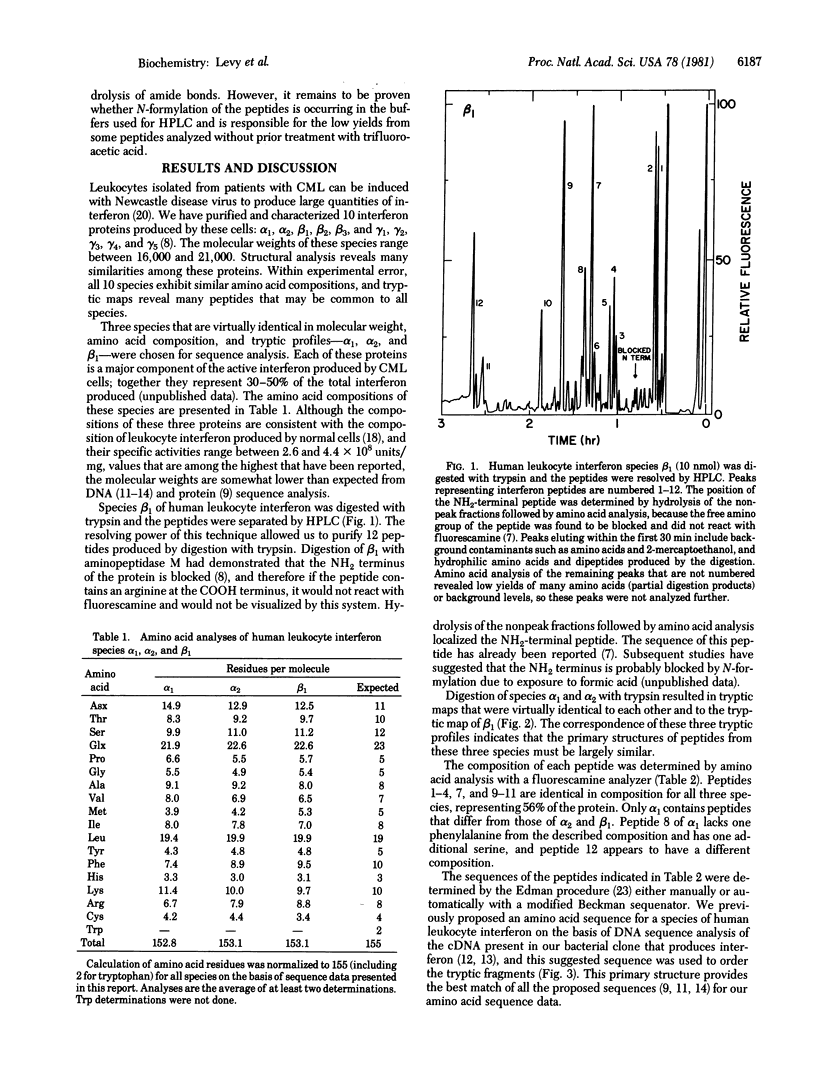
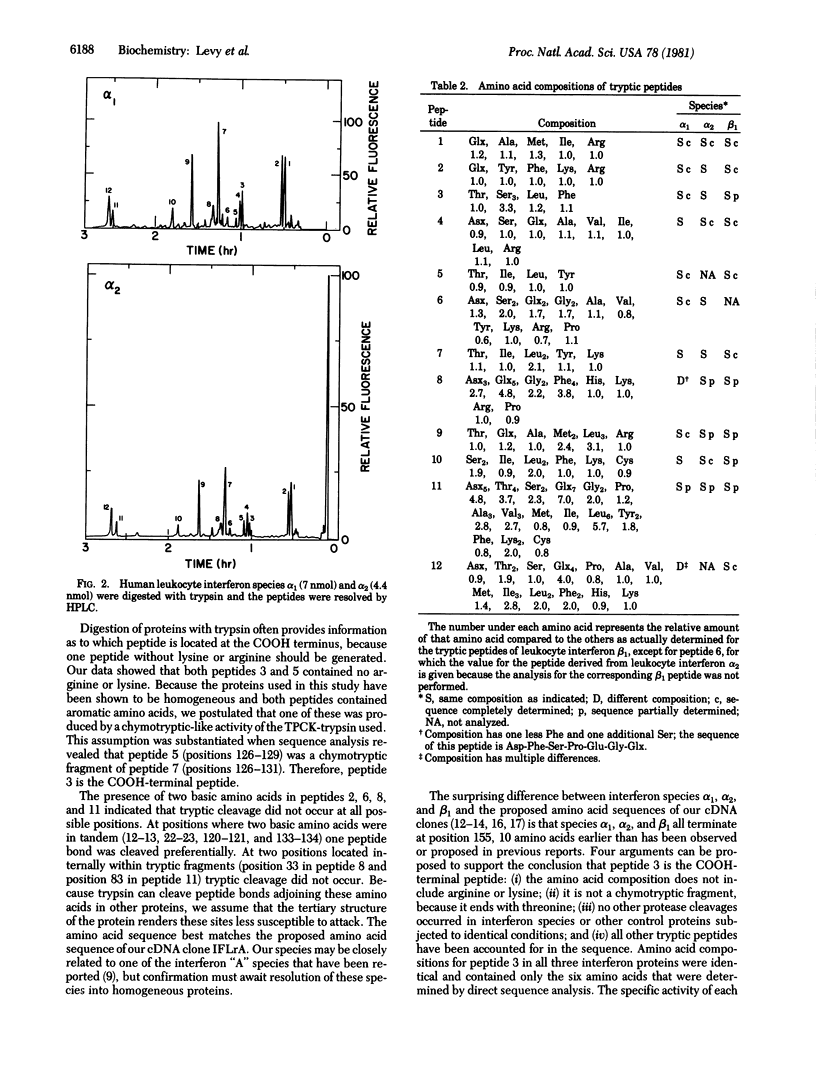
The primary structures of three major species of human leukocyte interferon differ from the structure predicted from the DNA sequence of recombinants containing leukocyte interferon-coding regions. Compared to the recombinant interferon produced in bacteria, three of the purified natural proteins isolated from leukocytes lack the 10 COOH-terminal amino acids suggested by the DNA sequence.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen G., Fantes K. H. A family of structural genes for human lymphoblastoid (leukocyte-type) interferon. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):408–411. doi: 10.1038/287408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Stone J., Udenfriend S. Automatic Monitoring of primary amines in preparative column effluents with fluorescamine. Anal Biochem. 1975 Aug;67(2):438–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson N. A., Brewer H. B., Anderson W. F. Hemoglobin switching in sheep and goats. 3. Cell-free initiation of sheep globin synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5227–5235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yelverton E., Ullrich A., Heyneker H. L., Miozzari G., Holmes W., Seeburg P. H., Dull T., May L., Stebbing N. Human leukocyte interferon produced by E. coli is biologically active. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):411–416. doi: 10.1038/287411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobb D. S., Moschera J. A., Levy W. P., Pestka S. Purification of interferon produced in a culture of human granulocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):472–481. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Direct microsequence analysis of polypeptides using an improved sequenator, a nonprotein carrier (polybrene), and high pressure liquid chromatography. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2124–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. New protein sequenator with increased sensitivity. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):523–525. doi: 10.1126/science.7352258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., LINDENMANN J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 Sep 12;147(927):258–267. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y. Regeneration of amino acids from anilinothiazolinones. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:369–373. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W. P. Manual Edman sequencing techniques for proteins and peptides at the nanomole level. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):27–31. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W. P., Shively J., Rubinstein M., Del Valle U., Pestka S. Amino-terminal amino acid sequence of human leukocyte interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5102–5104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., McCandliss R., Gross M., Sloma A., Familletti P. C., Tabor J. M., Evinger M., Levy W. P., Pestka S. Construction and identification of bacterial plasmids containing nucleotide sequence for human leukocyte interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7010–7013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Schwarzstein M., Streuli M., Panem S., Nagata S., Weissmann C. The nucleotide sequence of a cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNA. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. The structure of one of the eight or more distinct chromosomal genes for human interferon-alpha. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):401–408. doi: 10.1038/287401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Taira H., Hall A., Johnsrud L., Streuli M., Ecsödi J., Boll W., Cantell K., Weissmann C. Synthesis in E. coli of a polypeptide with human leukocyte interferon activity. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):316–320. doi: 10.1038/284316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Levy W. P., Moschera J. A., Lai C. Y., Hershberg R. D., Bartlett R. T., Pestka S. Human leukocyte interferon: isolation and characterization of several molecular forms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Aug;210(1):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Gross M. S., Miller R. S., Waldman A. A., Pestka S. Human leukocyte interferon purified to homogeneity. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1289–1290. doi: 10.1126/science.725605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Miller R. S., Waldman A. A., Pestka S. Human leukocyte interferon: production, purification to homogeneity, and initial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):640–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Hobbs D. S., Kung H., Pestka S. Purification of recombinant human leukocyte interferon (IFLrA) with monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Böhlen P., Stone J., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Amino acid analysis with fluorescamine at the picomole level. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):202–212. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Nagata S., Weissmann C. At least three human type alpha interferons: structure of alpha 2. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1343–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.6158094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. E. Improved manual sequencing methods. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:335–357. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B. Amino acid sequence studies on ten ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli with an improved sequenator equipped with an automatic conversion device. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Oct-Nov;354(10-11):1415–1431. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.2.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B., Graffunder H., Kohls H. A device coupled to a modified sequenator for the automated conversion of anilinothiazolinones into PTH amino acids. Anal Biochem. 1976 Oct;75(2):621–633. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman C. L., Appella E., Pisano J. J. Rapid analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1977 Feb;77(2):569–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Smith M. E., Bridgen P. J., Anfinsen C. B., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Amino terminal sequence of the major component of human lymphoblastoid interferon. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):527–528. doi: 10.1126/science.7352260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


