Abstract
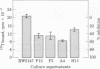
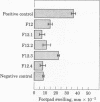
By using polyethylene glycol 1540, BW5147 AKR T lymphoma cells were fused with splenocytes from A/J mice treated so as to induce suppressor T cells specific for azobenzenearsonate (ABA). Of 576 microwells originally seeded, 132 demonstrated growing cell clones, 4 of which produced an ABA-binding supernatant factor. When tested in vivo for suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity to ABA, two of these cell lines, A4 and F12, were shown to produce suppressive supernatant factors. Fluorescence analysis of the F12 cells with appropriate antisera demonstrated this T cell hybrid to be Thy 1.2+, Lyt 1+,2-, and surface immunoglobulin negative, the surface marker phenotype of conventional ABA-specific suppressor T cells. This cloned suppressor cell line, F12, produces a culture supernatant factor that is suppressive at dilutions up to 1:100 and has provided material for genetic and immunochemical analysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach B. A., Sherman L., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Mechanisms of regulation of cell-mediated immunity. II. Induction and suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity to azobenzenearsonate-coupled syngeneic cells. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1460–1468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz M. H., Sy M. S., Benacerraf B., Nisonoff A., Greene M. I., Germain R. N. Antigen- and receptor-driven regulatory mechanisms. VII. H-2-restricted anti-idiotypic suppressor factor from efferent suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):450–463. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz M. H., Sy M. S., Greene M. I., Nisonoff A., Benacerraf B., Germain R. N. Antigen and receptor-driven regulatory mechanisms. VI. Demonstration of cross-reactive idiotypic determinants on azobenzenearsonate-specific antigen-binding suppressor T cells producing soluble suppressor factor(s). J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2374–2379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Benacerraf B. Helper and suppressor T cell factors. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 May;3(1):93–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00199927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. W., Lewis G. K., Primi D., Hornbeck P., Ruddle N. H. Antigen-specific molecules from murine T lymphocytes and T cell hybridomas. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jul;17(7):933–945. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene M. I., Fujimoto S., Sehon A. H. Regulation of the immune response to tumor antigens. III. Characterization of thymic suppressor factor(s) produced by tumor-bearing hosts. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):757–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström K. E., Hellström I., Nepom J. T. Specific blocking factors--are they important? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 23;473(2):121–148. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Araneo B. A., Clevinger B. L. Suppression of antibody and T cell proliferative responses to L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 by a specific monoclonal T cell factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):235–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoyi E., Estess P., Capra J. D., Nisonoff A. Heterogeneity of an intrastrain cross-reactive idiotype associated with anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies of A/J mice. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2834–2840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Cory J., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. T-T hybridoma product specifically suppresses tumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2866–2870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifico A., Capra J. D. T cell hybrids with arsonate specificity. I. Initial characterization of antigen-specific T cell products that bear a cross-reactive idiotype and determinants encoded by the murine major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1289–1301. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. L., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Regulation of the immune response to tumor antigen. IV. Tumor antigen-specific suppressor factor(s) bear I-J determinants and induce suppressor T cells in vivo. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2144–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A. Regulation of immune responses by suppressor T cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1976;5:91–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Beezley B. B., Eardley D. D. Regulation of self-recognition by T-cell hybrids. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 15;55(1):42–55. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Beezley B., Lewis G. K., Goodman J. W. Antigen specific T cell hybrids--II. T cell hybrids which bind azobenzenearsonate. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jul;17(7):925–931. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H. T cell hybrids with specificity for individual antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:203–211. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Dietz M. H., Germain R. N., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Antigen- and receptor-driven regulatory mechanisms. IV. Idiotype-bearing I-J+ suppressor T cell factors induce second-order suppressor T cells which express anti-idiotypic receptors. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1183–1195. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., Takemori T. Properties of primed suppressor T cells and their products. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:106–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Miller J. F. Specific suppressive factors produced by hybridomas derived from the fusion of enriched suppressor T cells and a T lymphoma cell line. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):373–382. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J., Corvalan J. R., Binns R. M., Holliman A. Production of an H--2-related suppressor factor by a hybrid T-cell line. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):305–308. doi: 10.1038/277305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Kimoto M., Maruyama S., Kishimoto T., Yamamura Y. Regulation of antibody response in different immunoglobulin classes. V. Establishment of T hybrid cell line secreting IgE class-specific suppressor factor. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2113–2117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J. Z., Germain R. N., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Hapten-specific T cell responses to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl. V. Role of idiotypes in the suppressor pathway. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):161–169. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker R. B., Ruddle N. H. Antigen-specific T-cell hybrids. I. Ovalbumin binding T-cell hybrid. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 15;55(1):56–65. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]