Abstract
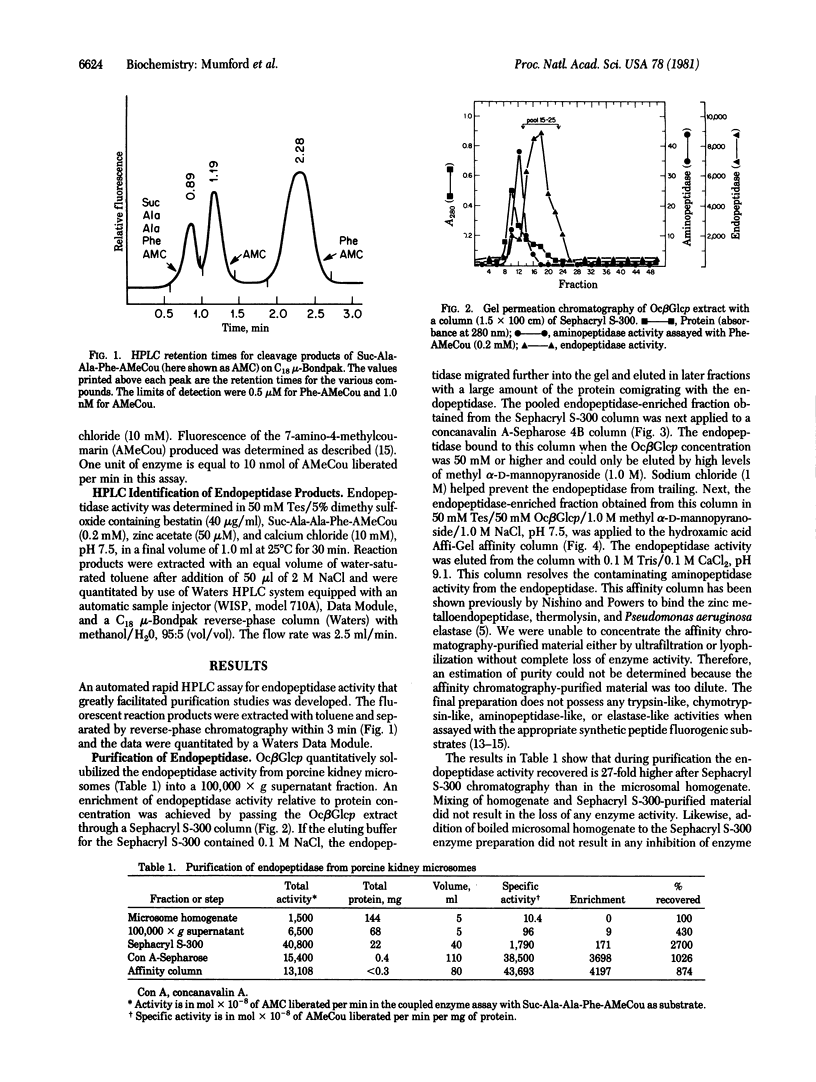
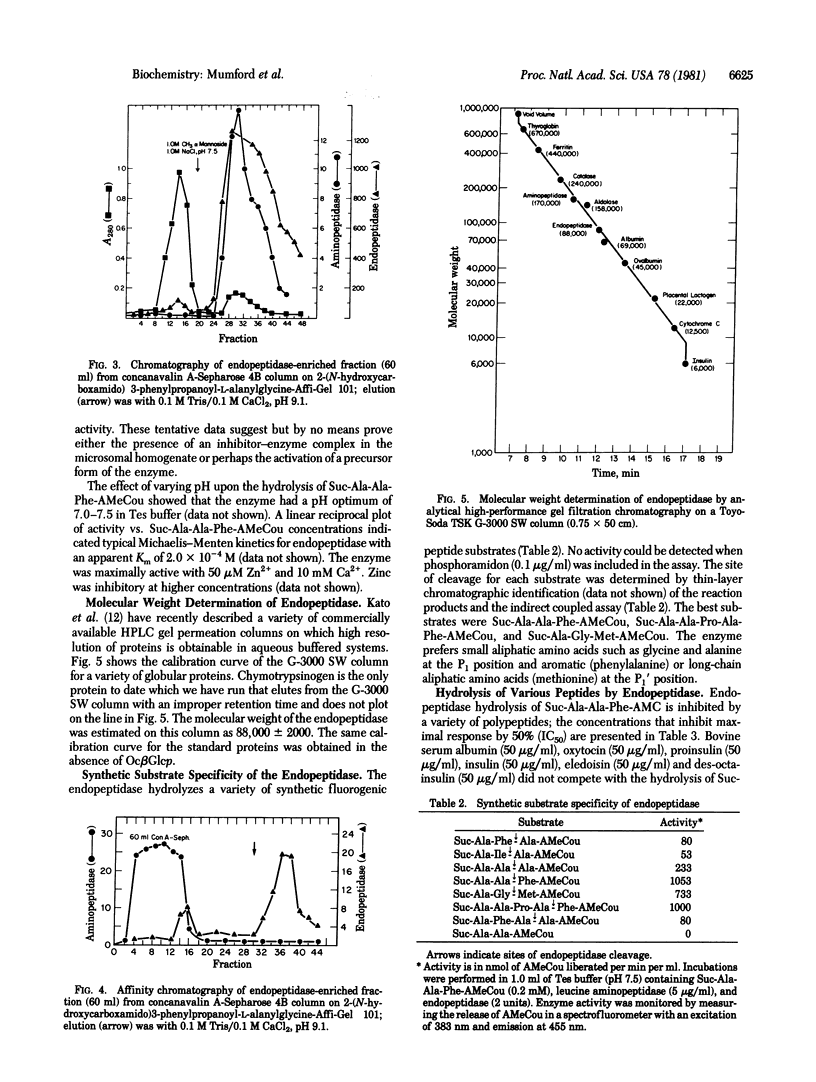
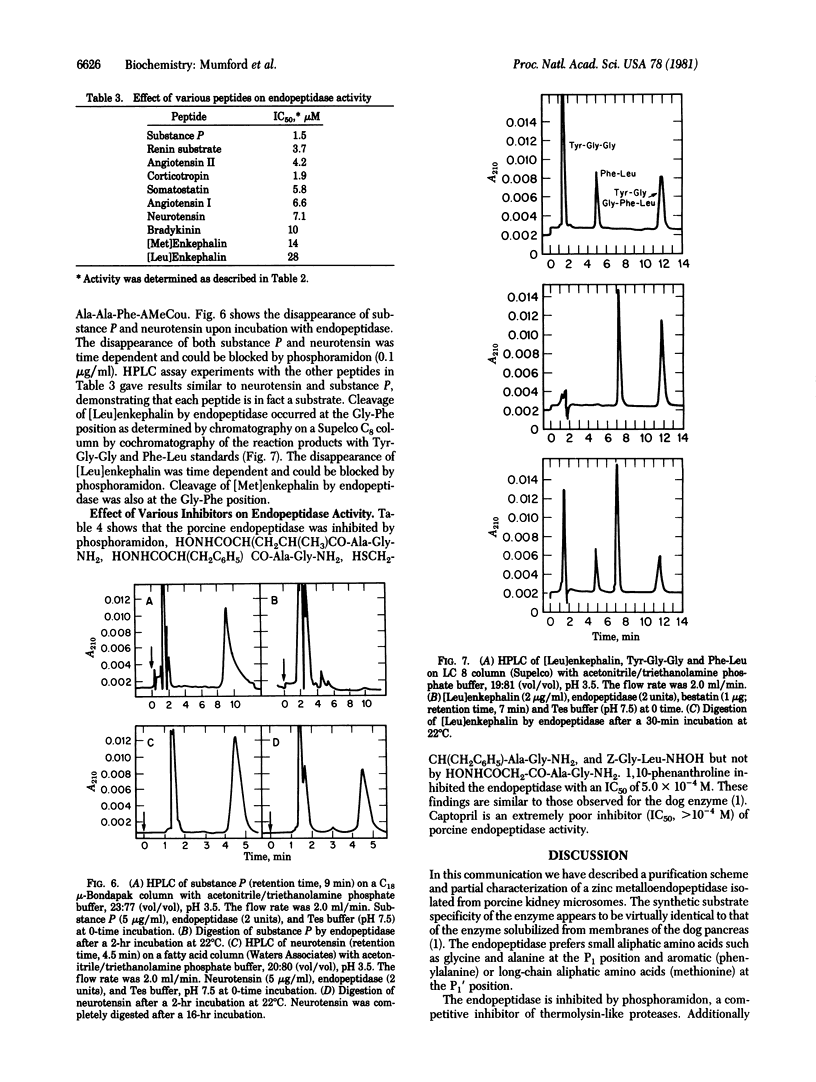
A porcine kidney microsomal metalloendopeptidase has been enriched 3900-fold. Gel filtration on a calibrated Toyo-Soda G-3000 SW column indicated an appropriate molecular weight for the endopeptidase of 88,000 +/- 2000. The purified enzyme is inhibited by a number of synthetic inhibitors of thermolysin. The endopeptidase hydrolyzes the succinyl (Suc)-containing fluorogenic peptide substrate Suc-Ala-Ala-Phe-(7-amino-4-methylcoumarin) at the Ala-Phe position with a Km of 2.9 X 10(-4) M. The endopeptidase also hydrolyzes a variety of peptides including corticotropin, substance P, angiotensin I and II, neurotensin, somatostatin, bradykinin, and the renin tetradecapeptide substrate. The endopeptidase hydrolyzes both [Leu]- and [Met]enkephalin at the Gly-Phe bond.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakhle Y. S. Pulmonary metabolism of bradykinin analogues and the contribution of angiotensin converting enzyme to bradykinin inactivation in isolated lungs. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;59(1):123–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb06985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benuck M., Marks N. Co-identity of brain angiotensin converting enzyme with a membrane bound dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase inactivating Met - enkephalin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 14;88(1):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91718-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. C., Smithwick E. L., Shuman R., Bemis K. G. Metkephamid, a systemically active analog of methionine enkephalin with potent opioid alpha-receptor activity. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):603–605. doi: 10.1126/science.6256856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Snyder S. H. Two distinct enkephalinases: solubilization, partial purification and separation from angiotensin converting enzyme. Life Sci. 1979 Dec 10;25(24-25):2065–2070. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Seals J. R. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activation in adipocyte mitochondria by an insulin-generated mediator from muscle. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1407–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.505013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The molecular weight and properties of a neutral metallo-endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):489–495. doi: 10.1042/bj1370489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Hartmann J. F., Ashe B. M., Zimmerman M. Proteinase activities of the golden hamster eggs and cells of the cumulus oophorus. Dev Biol. 1981 Jan 30;81(2):332–335. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Strauss A. W., Powers J. C., Pierzchala P. A., Nishino N., Zimmerman M. A zinc metalloendopeptidase associated with dog pancreatic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2227–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino N., Powers J. C. Design of potent reversible inhibitors for thermolysin. Peptides containing zinc coordinating ligands and their use in affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4340–4347. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierzchala P. A., Dorn C. P., Zimmerman M. A new fluorogenic substrate for plasmin. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):555–559. doi: 10.1042/bj1830555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Czech M. P. Evidence that insulin activates an intrinsic plasma membrane protease in generating a secondary chemical mediator. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6529–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Jarett L. Activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by direct addition of insulin to an isolated plasma membrane/mitochondria mixture: evidence for generated of insulin's second messenger in a subcellular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss A. W., Zimmerman M., Boime I., Ashe B., Mumford R. A., Alberts A. W. Characterization of an endopeptidase involved in pre-protein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4225–4229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss A. W., Zimmerman M., Mumford R. A., Alberts A. W. Processing of pre-proalbumin and pre-placental lactogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:168–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Shroyer L. A. A rat kidney neutral peptidase that degrades B chain of insulin, glucagon, and ACTH: purification by affinity chromatography and some properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 May;181(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90486-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veber D. F., Holly F. W., Paleveda W. J., Nutt R. F., Bergstrand S. J., Torchiana M., Glitzer M. S., Saperstein R., Hirschmann R. Conformationally restricted bicyclic analogs of somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2636–2640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Ashe B., Yurewicz E. C., Patel G. Sensitive assays for trypsin, elastase, and chymotrypsin using new fluorogenic substrates. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Quigley J. P., Ashe B., Dorn C., Goldfarb R., Troll W. Direct fluorescent assay of urokinase and plasminogen activators of normal and malignant cells: kinetics and inhibitor profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):750–753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


