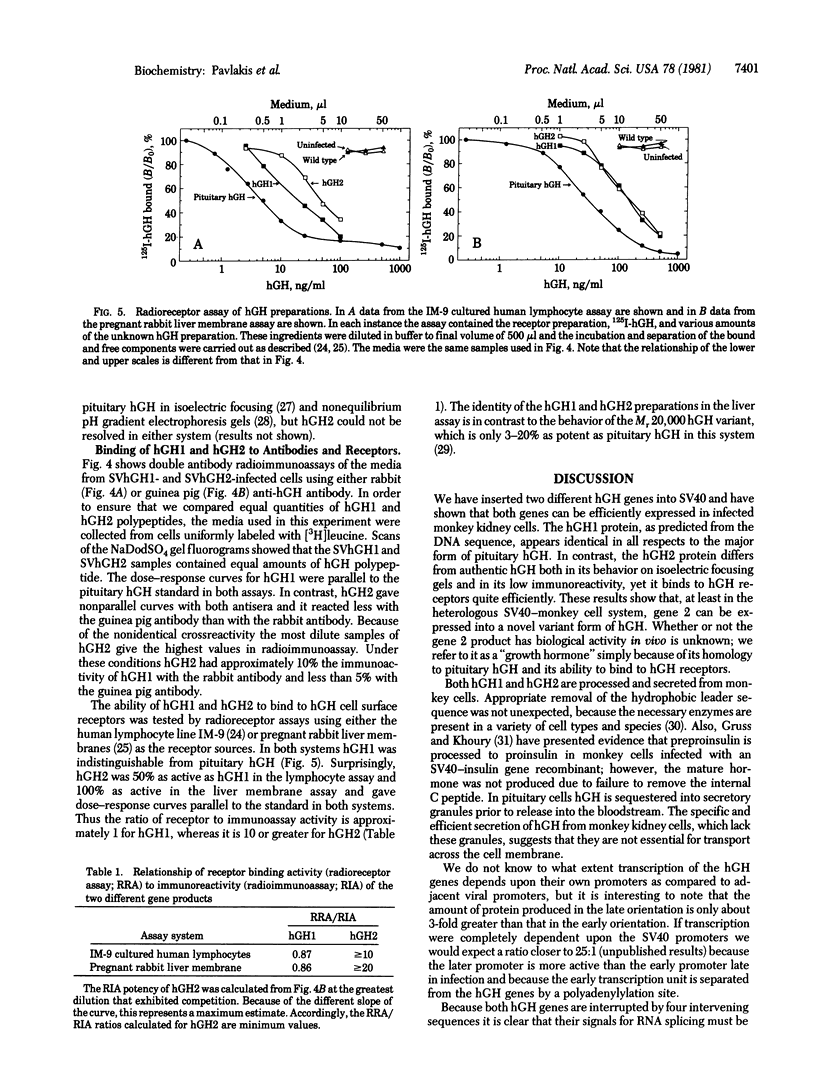
Abstract
We have constructed simian virus 40 recombinants carrying two different human growth hormone (hGH) genes. Monkey kidney cells infected with these recombinants synthesize, process, and secrete hGH. The product of gene 1, which has coding sequences identical to those of a cloned hGH complementary DNA, is indistinguishable from pituitary hGH by several criteria. The product of gene 2, which is predicted to encode a variant protein, is less immunoreactive than pituitary hGH but binds efficiently to hGH cell surface receptors. These results show that gene 2 has the potential to be expressed into a previously unidentified form of hGH. They also demonstrate that it is possible to produce a mature hormone by gene transfer in eukaryotic cells and indicate the utility of the simian virus 40-monkey cell system for producing and characterizing secreted animal cell proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Walter P., Chang C. N., Goldman B. M., Erickson A. H., Lingappa V. R. Translocation of proteins across membranes: the signal hypothesis and beyond. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1979;33:9–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheever E. V., Lewis U. J. Estimation of the molecular weights of the multiple components of growth hormone and prolactin. Endocrinology. 1969 Sep;85(3):465–473. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. Complementation analysis of simian virus 40 mutants. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1101–1109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1101-1109.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Yadley R. A., Ben-David M., Rodbard D. Isohormones of human growth hormone. I. Characterization by electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel. Endocrinology. 1973 Oct;93(4):848–857. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-4-848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman R. C., Lesniak M. A., Roth J., De Meyts P., Gorden P. Regulation of receptor by homologous hormone enhances sensitivity and broadens scope of radioreceptor assay for human growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Aug;49(2):262–268. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-2-262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Seeburg P. H., DeNoto F. M., Hallewell R. A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Structure of genes for human growth hormone and chorionic somatomammotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4294–4298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Given B. D., Mako M. E., Tager H. S., Baldwin D., Markese J., Rubenstein A. H., Olefsky J., Kobayashi M., Kolterman O., Poucher R. Diabetes due to secretion of an abnormal insulin. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 17;302(3):129–135. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001173020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman A. D., Tanenbaum R., Rabinowitz D. Existence of two forms of immunoreactive growth hormone in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Dec;35(6):868–878. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-6-868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Hendricks C. M., Roth J. Evidence for "big" and "little" components of human plasma and pituitary growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Jan;36(1):178–184. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-1-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Lesniak M. A., Eastman R., Hendricks C. M., Roth J. Evidence for higher proportion of "little" growth hormone with increased radioreceptor activity in acromegalic plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Aug;43(2):364–373. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-2-364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Khoury G. Expression of simian virus 40-rat preproinsulin recombinants in monkey kidney cells: use of preproinsulin RNA processing signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):133–137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Kaehler M., Leder P. A mouse globin gene promoter is functional in SV40. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowarski A. A., Schneider J., Ben-Galim E., Weldon V. V., Daughaday W. H. Growth failure with normal serum RIA-GH and low somatomedin activity: somatomedin restoration and growth acceleration after exogenous GH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Aug;47(2):461–464. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-2-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS U. J., CHEEVER E. V. EVIDENCE FOR TWO TYPES OF CONVERSION REACTIONS FOR PROLACTIN AND GROWTH HORMONE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:247–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., Roth J., Gavin J. R., 3rd Binding of 125I-human growth hormone to specific receptors in human cultured lymphocytes. Characterization of the interaction and a sensitive radioreceptor assay. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1661–1667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J., Bonewald L. F., Lewis L. J. The 20,000-dalton variant of human growth hormone: location of the amino acid deletions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):511–516. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J., Cheever E. V., Hopkins W. C. Kinetic study of the deamidation of growth hormone and prolactin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 29;214(3):498–508. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J., Dunn J. T., Bonewald L. F., Seavey B. K., Vanderlaan W. P. A naturally occurring structural variant of human growth hormone. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2679–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martial J. A., Hallewell R. A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Human growth hormone: complementary DNA cloning and expression in bacteria. Science. 1979 Aug 10;205(4406):602–607. doi: 10.1126/science.377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Kutner M. H., Goldsmith M. A., Kenny J., Jennings H., Bain R. P. Further observations on four subgroups of normal variant short stature. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Dec;51(6):1378–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-6-1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel M. B., Thorpe N. A., Kobrin M. S., Lewis U. J., Vanderlaan W. P. Binding characteristics of a biologically active variant of human growth hormone (20K) to growth hormone and lactogen receptors. Endocrinology. 1981 Apr;108(4):1600–1603. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-4-1600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Topp W. C., Hanich R., Sambrook J. F. Mutants of SV40 with an altered small t protein are reduced in their ability to transform cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman P. M., Tushinski R. J., Bancroft F. C. Pregrowth hormone: product of the translation in vitro of messenger RNA coding for growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):29–33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsushima T., Friesen H. G. Radioreceptor assay for growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Aug;37(2):334–337. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-2-334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis M. Growth hormone: deletions in the protein and introns in the gene. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):512–512. doi: 10.1038/284512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]