Abstract
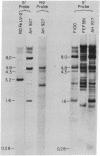
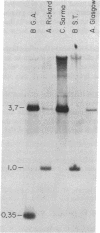
The presence and location of DNA sequences related to the U3 and U5 portions of the infectious exogenous feline leukemia virus (FeLV) long terminal repeat (LTR) in various cat DNAs have been determined by hybridization experiments. In uninfected cat DNAs, the U5 LTR segment from the Gardner-Arnstein strain B virus is present at approximately 150 copies per cell. This level is approximately 10-fold greater than that of endogenous internal FeLV sequences. The U5 sequences differ in copy number and, to some extent, in location from one animal to another. For any one animal, the sequence organization of the U5 segments is the same among different tissues, showing that the pattern is inherited through the germ line. Most importantly, the viral U3 LTR probe hybridizes only very weakly with uninfected cat DNAs. Both the U3 and the U5 regions of the LTR from the Gardner-Arnstein strain of virus cross-hybridize with DNA derived from four other infectious FeLVs representing A, B, and C subtypes. Thus, the C3 region may be used as a probe for studying the number and location of exogenously acquired FeLV proviruses in infected cat tissues. In some cases exogenously acquired proviruses are present in unique sites in the genome of virus-positive cat lymphosarcomas, indicating a monoclonal origin for the tumor. In other tumors, the proviral sequences are randomly distributed over many sites. Lymphosarcomas of virus-negative cats have no exogenous U3 sequences despite epidemiological evidence of an association of virus-negative leukemia with exposure to FeLV.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R. E., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: origin of feline leukemia virus. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):886–888. doi: 10.1126/science.52892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. D., Jr, McClelland A. J., Zuckerman E. E., Snyder H. W., Jr, MacEwen E. G., Francis D., Essex M. Development of virus non-producer lymphosarcomas in pet cats exposed to FeLv. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):90–92. doi: 10.1038/288090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Toyoshima K., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Organization of the endogenous proviruses of chickens: implications for origin and expression. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):189–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett W., Jarrett O., Mackey L., Laird H., Hardy W., Jr, Essex M. Horizontal transmission of leukemia virus and leukemia in the cat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Sep;51(3):833–841. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.3.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshy R., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Characterization of the endogenous feline leukemia virus-related DNA sequences in cats and attempts to identify exogenous viral sequences in tissues of virus-negative leukemic animals. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):434–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Casey J. W., Nicolson M. O., Burck K. B., Davidson N. Sequence arrangement and biological activity of cloned feline leukemia virus proviruses from a virus-productive human cell line. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):688–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.688-703.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Casey J. W., Nicolson M. O., Davidson N. Sequence organization of feline leukemia virus DNA in infected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3287–3305. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson M. O., Hariri F., Krempin H. M., McAllister R. M., Gilden R. V. Infectious proviral DNA in human cells infected with transformation-defective type C viruses. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Akhavi M., Gardner M. B., Stephenson J. R., Roy-Burman P. Differential expression of two distinct endogenous retrovisus genomes in developing tissues of the domestic cat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Mar;64(3):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe H., DuBuy J., Gilden R. V., Gardner M. B. A portion of the feline leukaemia virus genome is not endogenous in cat cells. Int J Cancer. 1978 Jul 15;22(1):70–78. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N., Rogers S. G. Plasmid pKC7: a vector containing ten restriction endonuclease sites suitable for cloning DNA segments. Gene. 1979 Sep;7(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Fedele L. A., Oskarsson M., Maizel J., Vande Woude G. Molecular cloning of Snyder-Theilen feline leukemia and sarcoma viruses: comparative studies of feline sarcoma virus with its natural helper virus and with Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):200–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.200-212.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]