Abstract
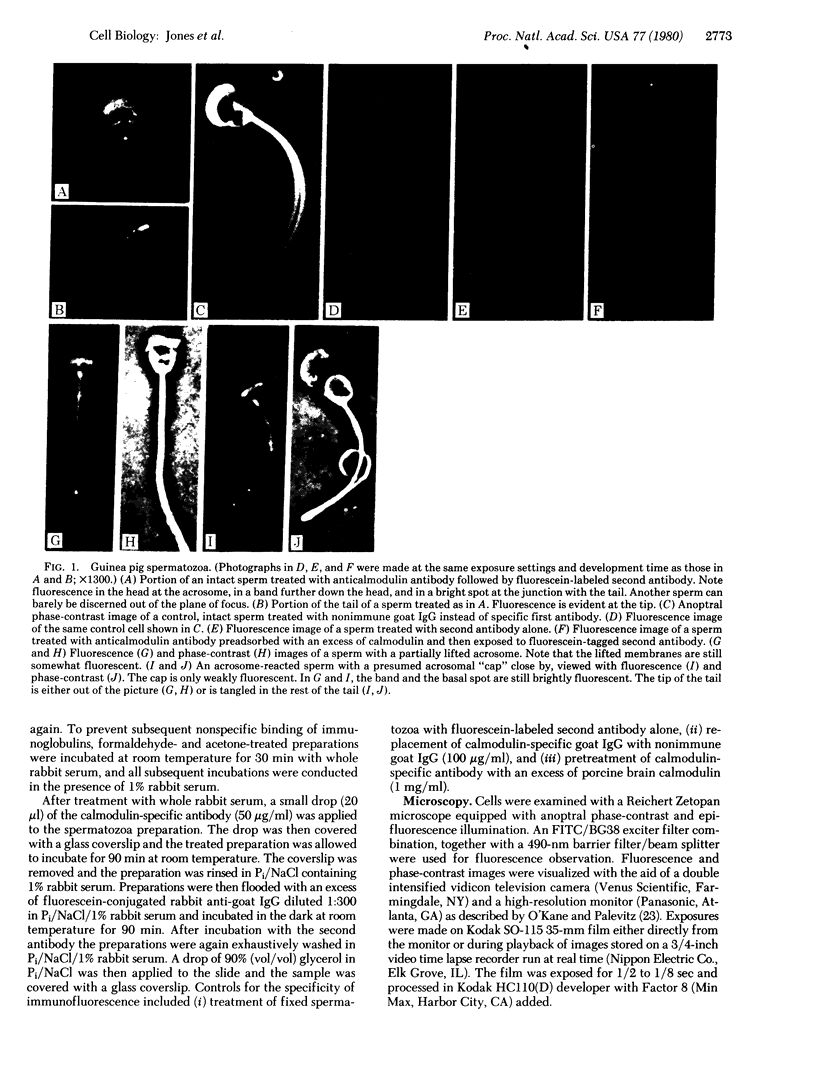
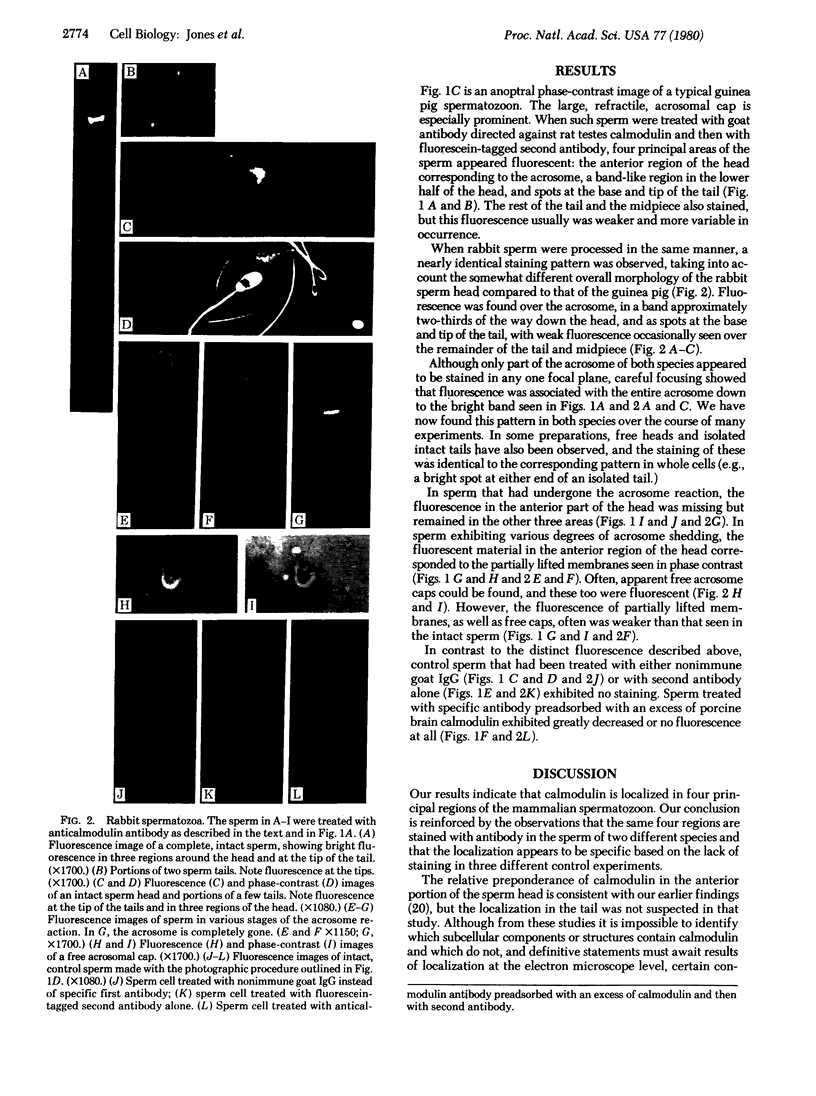
The location of calmodulin in rabbit and guinea pig spermatozoa was determined by indirect immunofluorescence techniques. Spermatozoa that had not undergone the acrosome reaction exhibited four distinct regions of calmodulin-specific immunofluorescence: around the acrosome, in a band across the lower third of the head, and in two localized areas at the base and tip of the flagellum. In contrast, after the acrosome reaction, although other features of calmodulin distribution remained the same, the fluorescence associated with the anterior half of the head was notably absent. Instead, fluorescence was associated with the membranes that had separated from the sperm head. These findings suggest a potential role for calmodulin in the Ca2+-dependent control of sperm activation, in sperm-egg fusion, and in microtubule disassembly processes in the flagellum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Cormier M. J. Calcium-dependent regulation of NAD kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90747-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barros C., Franklin L. E. Behavior of the gamete membranes during sperm entry into the mammalian egg. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):C13–C18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.c13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G. Polarity of microtubules of the mitotic spindle. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Cormier M. J. Purification of plant calmodulin by fluphenazine-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91931-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Demonstration of an activator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 6;38(3):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90747-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Sherry J. M., Aromatorio D. K., Hartshorne D. J. Modulator protein as a component of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):253–258. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J., Freedman S. D., Yohe W. B., Maurer S. C. Stimulation of Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release and presynaptic nerve terminal protein phosphorylation by calmodulin and a calmodulin-like protein isolated from synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1838–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman J. R., Welsh M. J., Means A. R. Ca2+-dependent regulator. Production and characterization of a monospecific antibody. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7515–7521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in Chlamydomonas. III. structures attached to the tips of flagellar microtubules and their relationship to the directionality of flagellar microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):747–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W. The mammalian spermatozoon. Dev Biol. 1975 Jun;44(2):394–436. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath R. M., Vincenzi F. F. Phosphodiesterase protein activator mimics red blood cell cytoplasmic activator of (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1203–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Cheung W. Y., Wallace R. W., Huang H. L., Levine S. N., Steiner A. L. Localization of calmodulin in rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett H. W., Penniston J. T. Partial purification of the Ca2+-Mg2+ ATPase activator from human erythrocytes: its similarity to the activator of 3':5' - cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1210–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. P., Bradford M. M., McRorie R. A., Cormier M. J. High levels of a calcium-dependent modulator protein in spermatozoa and its similarity to brain modulator protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1264–1272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Yamazaki R., Teshima Y., Uenishi K., Yasuda S., Kashiba A., Sobue K., Ohshima M., Nakajima T. Membrane-bound protein modulator and phosphodiesterase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. K. The mammalian sperm surface: studies with specific labeling techniques. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;54:73–108. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. M., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Control of microtubule assembly-disassembly by calcium-dependent regulator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3771–3775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Opposite end assembly and disassembly of microtubules at steady state in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Greengard P. Ca2+-dependent protein phosphorylation system in membranes from various tissues, and its activation by "calcium-dependent regulator". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5432–5436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J. P., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Increased calcium-ion influx is a component of capacitation of spermatozoa. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 15;172(3):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj1720549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers K., Kirschner M. W. Characteristics of the polar assembly and disassembly of microtubules observed in vitro by darkfield light microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):205–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D. M., Singh T. J., Wang J. H. The modulator-dependent protein kinase. A multifunctional protein kinase activatable by the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein of the cyclic nucleotide system. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3387–3390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Tubulin and calmodulin. Effects of microtubule and microfilament inhibitors on localization in the mitotic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):624–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin stimulates human platelet phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Wallace R. W., Whitaker J. N., Cheung W. Y. Immunocytochemical localization of calmodulin and a heat-labile calmodulin-binding protein (CaM-BP80) in basal ganglia of mouse brain. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):66–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagimachi R. Calcium requirement for sperm-egg fusion in mammals. Biol Reprod. 1978 Dec;19(5):949–958. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod19.5.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagimachi R., Usui N. Calcium dependence of the acrosome reaction and activation of guinea pig spermatozoa. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Nov;89(1):161–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]