Abstract
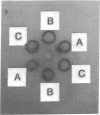
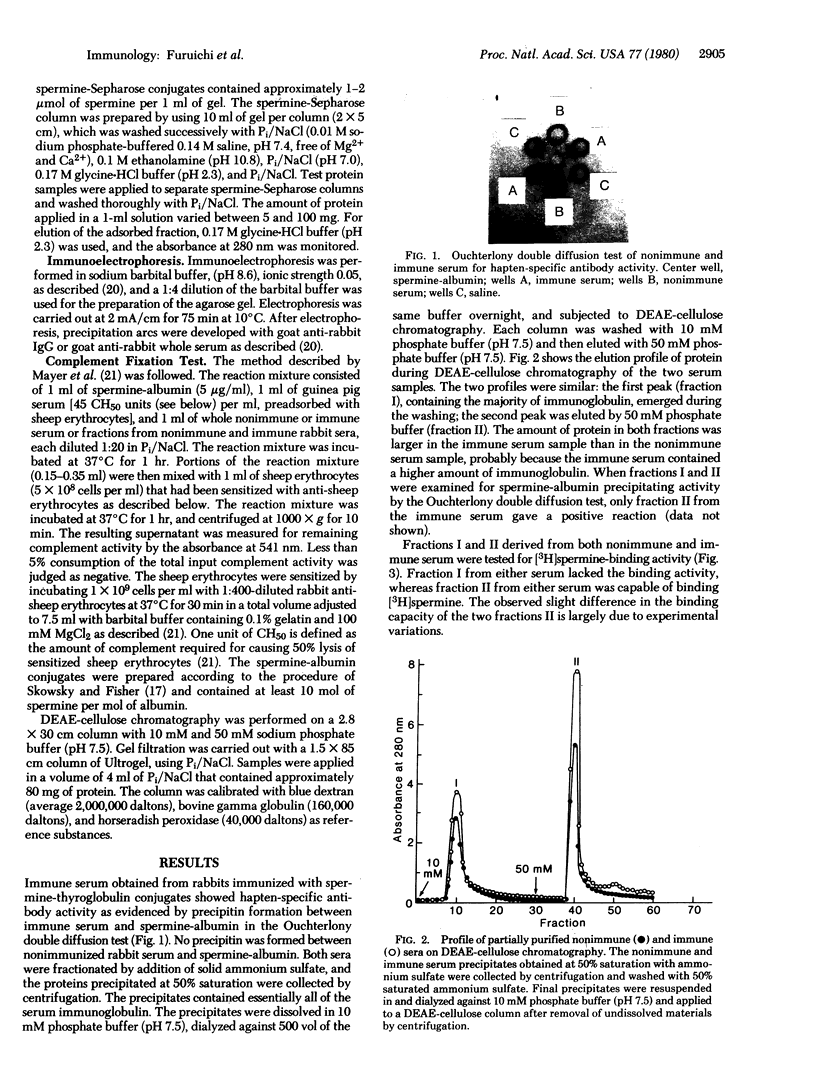
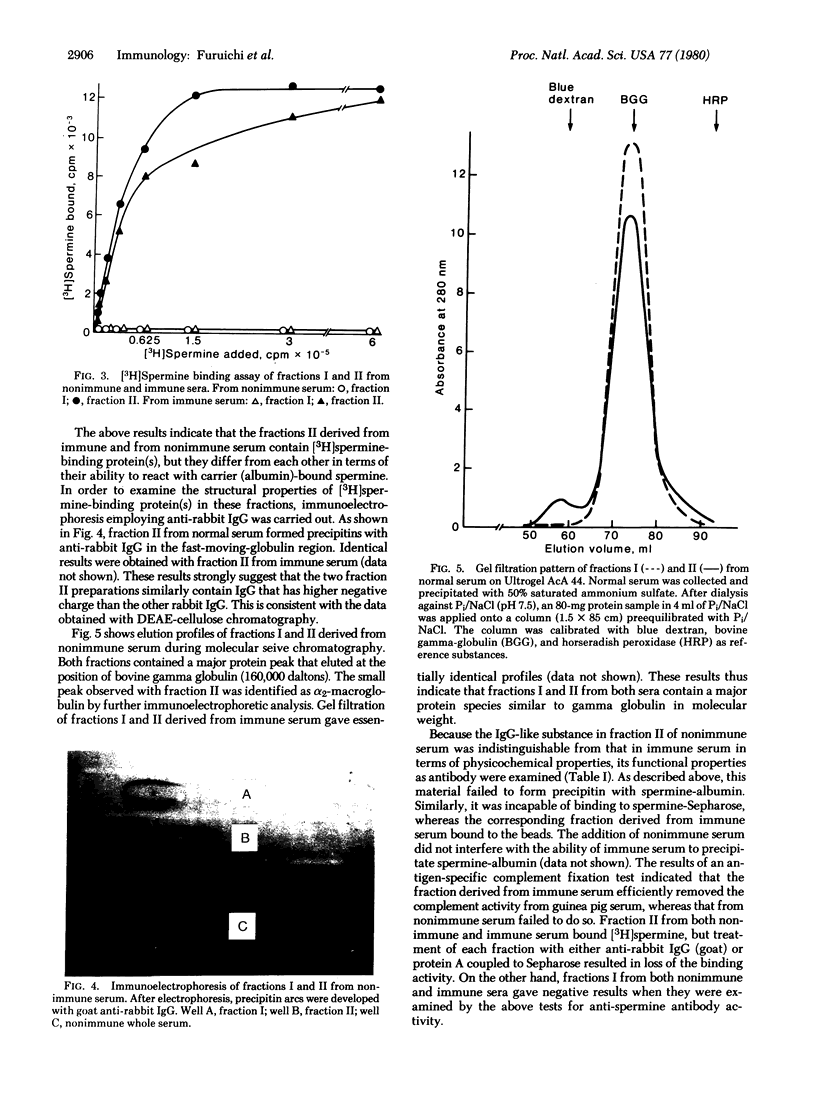
Normal rabbit serum contains an IgG-like component(s) that binds spermine as well as other polyamines. This molecule(s) has the same physicochemical properties as anti-spermine antibody obtained from rabbits immunized with spermine-thyroglobulin conjugates. However, the polyamines-binding IgG-like molecule(s), unlike anti-spermine antibody, is incapable either of precipitating a spermine-bovine serum albumin complex or of binding to a spermine-Sepharose column. These results suggest the existence of a naturally occurring anti-polyamine antibody that may have defective antibody functions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachrach U. Polyamines as chemical markers of malignancy. Ital J Biochem. 1976 Jan-Feb;25(1):77–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartos D., Campbell R. A., Bartos F., Grettie D. P. Direct determination of polyamines in human serum by radioimmunoassay. Cancer Res. 1975 Aug;35(8):2056–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. Y., Seale T. W., Shukla J. B., Rennert O. M. Polyamine conjugates and total polyamine concentrations in human amniotic fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Feb 1;91(3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Tan E. M., Dixon F. J. Presence of anti-Sm reactivity in autoimmune mouse strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):582–587. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonard J., Quash G., Wahl R. La spécificité des anticorps antipolyamines. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Oct 9;265(15):1099–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren D. W., Oka T. Alterations in polyamine levels in rat blood during pregnancy and lactation. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):E451–E456. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.5.E451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton L. J., Heby O., Levin V. A., Lubich W. P., Crafts D. C., Wilson C. B. The relationship of polyamines in cerebrospinal fluid to the presence of central nervous system tumors. Cancer Res. 1976 Mar;36(3):973–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notman D. D., Kurata N., Tan E. M. Profiles of antinuclear antibodies in systemic rheumatic diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Oct;83(4):464–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-4-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost T. T. Subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Mar;72(3):110–113. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12530348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina A., Jänne J. Physiology of the natural polyamines putrescine, spermidine and spermine. Med Biol. 1975 Jun;53(3):121–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch A. M., Quash G. A., Ripoll J. P., Saez S. Evidence for natural antibodies (IgG) to polyamines in human sera. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1979;67:56–62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81320-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H. Increased polyamine concentrations in the urine of human cancer patients. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):144–145. doi: 10.1038/newbio233144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrode J., Folk J. E. Transglutaminase-catalyzed cross-linking through diamines and polyamines. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4837–4840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale T. W., Chan W. Y., Shulka J., Rennert O. M. A polyamine-conjugated peptide isolated from human plasma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Nov;198(1):164–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowsky W. R., Fisher D. A. The use of thyroglobulin to induce antigenicity to small molecules. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jul;80(1):134–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. 1,4-Diaminobutane (putrescine), spermidine, and spermine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:285–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams-Ashman H. G., Canellakis Z. N. Polyamines in mammalian biology and medicine. Perspect Biol Med. 1979 Spring;22(3):421–453. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1979.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams-Ashman H. G., Wilson J., Beil R. E., Lorand L. Transglutaminase reactions associated with the rat semen clotting system: modulation by macromolecular polyanions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1192–1198. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]