Abstract
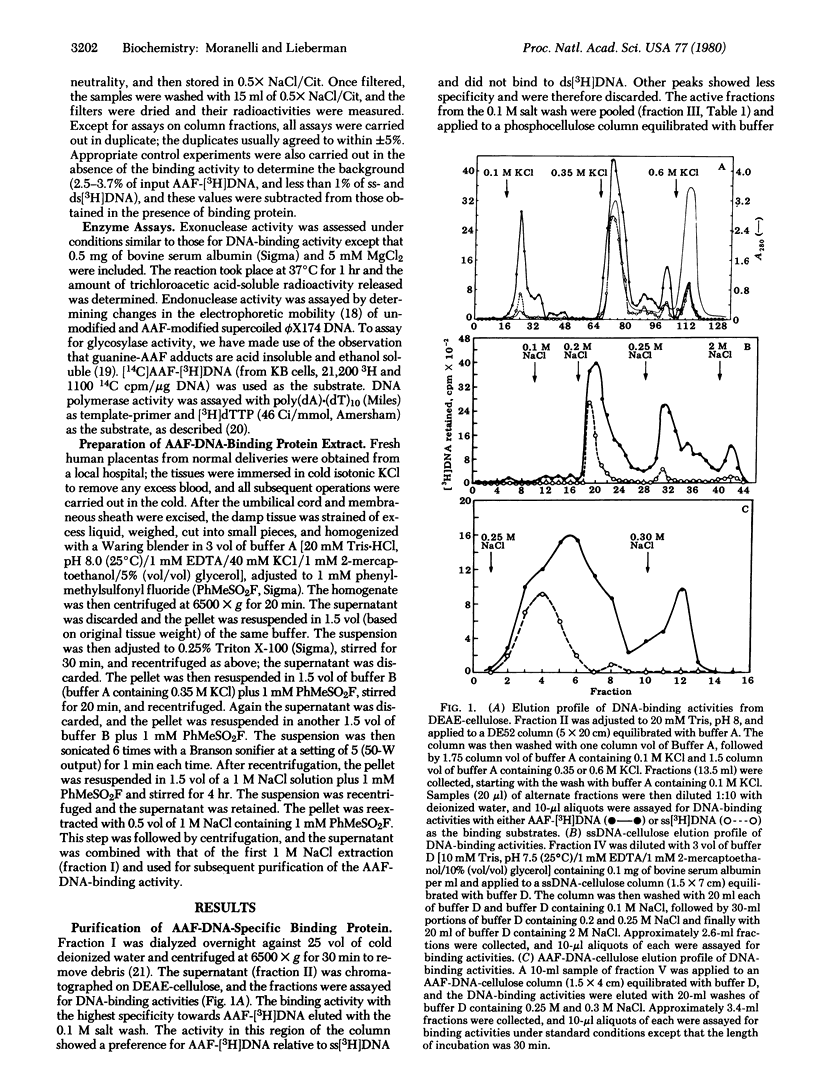
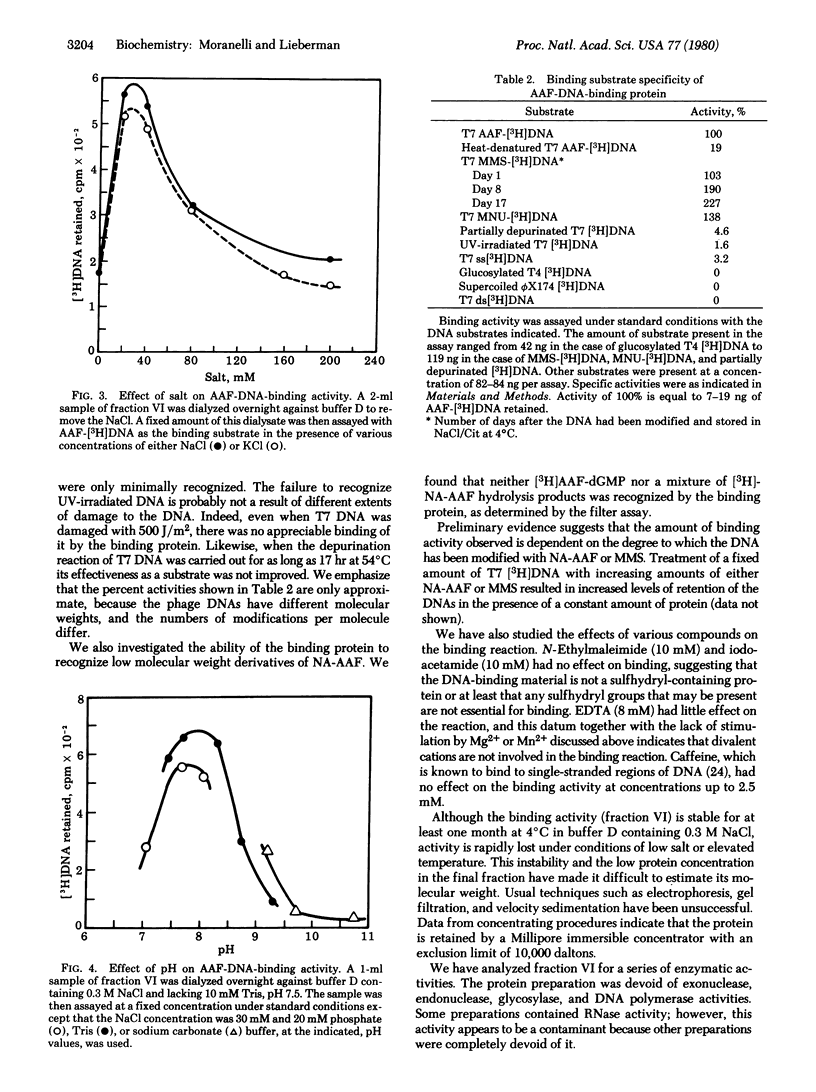
Using a filter binding assay, we have detected and partially purified a protein from human placenta that has a high affinity for N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene-modified double-stranded DNA (AAF-[3H]DNA) of bacteriophage T7. This protein has been partially purified from a 1 M NaCl extract of a crude nuclear fraction by a combination of ion-exchange and nucleic acid affinity chromatography. With AAF-[3H]DNA as the substrate, the binding reaction reached equlibrium within 1 hr at 4 degrees C, and the extent of binding ws proportional to the amount of protein added. Complex formation was dependent on both pH and salt concentration and was unaffected by the presence of sulfhydryl-blocking agents. The purest protein fraction also recognizes DNA modified with methylmethane-sulfonate or methylnitrosourea. It shows little or no recognition of single-stranded DNA, double-stranded DNA, supercoiled bacteriophage phiX174 DNA, partially depurinated DNA, glucosylated bacteriophage T4DNA, or UV-irradiated DNA. No endo- or exonuclease activity, DNA polymerase activity, or glucosylase activity for AAF-DNA was detectable in the preparation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed F. E., Setlow R. B. Different rate-limiting steps in excision repair of ultraviolet- and N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene-damaged DNA in normal human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1548–1552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amacher D. E., Elliott J. A., Lieberman M. W. Differences in removal of acetylaminofluorene and pyrimidine dimers from the DNA of cultured mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibor V., Verly W. G. Purification and properties of the endonuclease specific for apurinic sites of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):850–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo A., Zupi G., Clanciulli A. Isolation of endonuclease from mammalian cells by DNA - cellulose chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jun;2(6):905–913. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.6.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chetsanga C. J., Lindahl T. Release of 7-methylguanine residues whose imidazole rings have been opened from damaged DNA by a DNA glycosylase from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3673–3684. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch W. A., Linn S. DNA binding activity from cultured human fibrolasts that is specific for partially depurinated DNA and that inserts purines into apurinic sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):141–144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domon M., Barton B., Porte A., Rauth A. M. The interaction of caffeine with ultra-violet-light-irradiated DNA. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1970;17(4):395–399. doi: 10.1080/09553007014550481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg R. S., Grossman L. A DNA binding protein from human placenta specific for ultraviolet damaged DNA. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2402–2408. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. O., Pardee A. B. Proteins made in the mammalian cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6159–6165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Daune M. Physical studies on deoxyribonucleic acid after covalent binding of a carcinogen. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2659–2666. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvan D. J., Hass J. R., Lieberman M. W. Adduct formation between the carcinogen N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene and synthetic polydeoxyribonucleotides. Chem Biol Interact. 1977 May;17(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(77)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriek E. Carcinogenesis by aromatic amines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 9;355(2):177–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(74)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriek E., Miller J. A., Juhl U., Miller E. C. 8-(N-2-fluorenylacetamido)guanosine, an arylamidation reaction product of guanosine and the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-fluorenylacetamide in neutral solution. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):177–182. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto B., Baynes M., Knippers R. A single-strand-specific DNA-binding protein from mouse cells that stimulates DNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Crine P., Verly W. G. Properties of the endonuclease for depurinated DNA from Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(11):1199–1209. doi: 10.1139/o72-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker V. P., Lieberman M. W. Levels of DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma in control and repair-deficient human diploid fibroblasts 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):2029–2037. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Lieberman M. W. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair synthesis in permeable human fibroblasts exposed to ultraviolet radiation and N-acetoxy-2-(acetylamino)fluorene. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4499–4505. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarrif A. M., McCarthy K. L., Nesnow S., Heidelberger C. Separation of glutathione S-transferase activities with epoxides from the mouse liver h-protein, a major polycyclic hydrocarbon-binding protein. Cancer Res. 1978 May;38(5):1438–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. N-nitroso alkylating agents: formation and persistence of alkyl derivatives in mammalian nucleic acids as contributing factors in carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jun;62(6):1329–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S., Litwack G. Identity of corticosteroid binder I with the macromolecule binding 3-methylcholanthrene in liver cytosol in vivo. Cancer Res. 1971 Oct;31(10):1364–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorof S., Young E. M., Coffey C. B., Morris H. P. On protein binding of fluorenyl carcinogens by minimal deviation hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1966 Jan;26(1):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verly W. G., Paquette Y. An endonuclease for depurinated DNA in rat liver. Can J Biochem. 1973 Jul;51(7):1003–1009. doi: 10.1139/o73-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


