Abstract
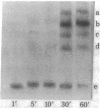
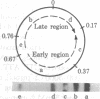
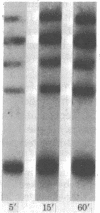
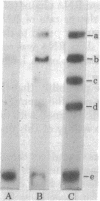
Short RNA chains initiating at the major promoter sites for simian virus 40 (SV40) late transcription are elongated to approximately 450 nucleotides in a molar ammount greater than that from any other region of the viral DNA. This conclusion is based on the following observations: (i) Transcriptional complexes isolated by Sarkosyl and by hypotonic leaching (minichromosomes) from nuclei of cells infected with SV40 as well as intact nuclei were pulse labeled in vitro with [alpha-32P]TUP and were observed to synthesize short RNA transcripts that hybridized predominantly to a SV40 DNA fragment spanning between 0.67 and 0.76 map units. (ii) In the presence of 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole (DRB), a drug known to accentuate premature transcriptional termination, accumulation of these short SV40 RNA chains was enhanced. When SV40-infected cells were pretreated with DRB and then labeled in vivo or in vitro, they synthesized short labeled viral RNAs that hydridized almost exclusively with the DNA fragment spanning between 0.67 and 0.76 map units. These observations suggest a mechanism in the regulation of SV40 late transcription.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Transcription during productive infection with polyoma virus and Simian virus 40. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y. Biogenesis and characterization of SV40 and polyoma RNAs in productively infected cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):165–178. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y., Dhar R., Khoury G. Methylation of nuclear simian virus 40 RNAs. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.52-60.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y., Dhar R., Laub O., Horowitz M., Khoury G. Novel mechanism for RNA maturation: the leader sequences of simian virus 40 mRNA are not transcribed adjacent to the coding sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. DNA sequence from the histidine operon control region: seven histidine codons in a row. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M., Thoren M., Salzman N., Thomspon J. A. Rapid sequence determination of late simian virus 40 16S mRNA leader by using inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratosin S., Horowitz M., Laub O., Aloni Y. Electron microscopic evidence for splicing of SV40 late mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Kahana C., Mukamel A., Groner Y. Sequence heterogeneity at the 5' termini of late simian virus 40 19S and 16S mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Blasi F., Di Lauro R., Frunzio R., Bruni C. B. Nucleotide sequence of the attenuator region of the histidine operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4276–4280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer C., Hausen P. Inhibition of mammalian RNA polymerase by 5,6-dichlororibofuranosylbenzimidazole (DRB) and DRB triphosphate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3325–3335. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Weber J., Ziff E., Darnell J. E. Premature termination during adenovirus transcription. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):367–370. doi: 10.1038/278367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinand F. J., Brown M., Khoury G. Synthesis and characterization of late lytic simian virus 40 RNA from transcriptional complexes. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):150–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Sehgal P. B., Darnell J. E. DRB-induced premature termination of late adenovirus transcription. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):590–593. doi: 10.1038/272590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Sehgal P. B., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple discrete sites for premature RNA chain termination late in adenovirus-2 infection: enhancement by 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2571–2575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Fiers W. Localization of the 5' terminus of late SV40 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2359–2371. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Laub O., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. Splicing of SV40 late mRNA is a post-transcriptional process. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):558–559. doi: 10.1038/275558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. T., Ford J. Sequence arrangement of the 5' ends of simian virus 40 16S and 19S mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4982–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Aloni Y. Isolation and characterization of various forms of simian virus 40 DNA-protein complexes. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub O., Aloni Y. Transcription of simian virus 40. V. Regulattion of simian virus 40 gene expression. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1171–1183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1171-1183.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub O., Aloni Y. Transcription of simian virus 40. VI. SV 40 DNA-RNA polymerase complex isolated from productively infected cells transcribed in vitro. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub O., Bratosin S., Horowitz M., Aloni Y. The initiation of transcription of SV40 DNA at late time after infection. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):310–323. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Groner Y. 5'-Terminal sequences and coding region of late simian virus 40 mRNAs are derived from noncontiguous segments of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5323–5327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Organization and transcription of the simian virus 40 genome. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;87:43–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67344-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Dobkin C., Kramer F. R. Template-determined, variable rate of RNA chain elongation. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Fraser N. W., Darnell J. E., Jr Early Ad-2 transcription units: only promoter-proximal RNA continues to be made in the presence of DRB. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Birkenmeier E., May E., Salzman N. P. Properties of simian virus 40 transcriptional intermediates isolated from nuclei of permissive cells. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):20–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.20-28.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., FOLKERS K., SHUNK C. H., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Inhibition of influenza virus multiplication by N-glycosides of benzimidazoles-N. J Exp Med. 1954 Mar;99(3):227–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm I. Definition of subclasses of nucleoplasmic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5011–5015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm I., Kikuchi T. Early termination of heterogeneous nuclear RNA transcripts in mammalian cells: accentuation by 5,6-dichloro 1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5750–5754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., White R. T., Berg P. Mutational alterations within the simian virus 40 leader segment generate altered 16S and 19S mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):209–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.209-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Föhring B., Chowdhury K., Gruss P., Sauer G. Origin of DNA replication in papovavirus chromatin is recognized by endogenous endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5964–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Brown K., Killingly D., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the leader region of the phenylalanine operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]