Abstract
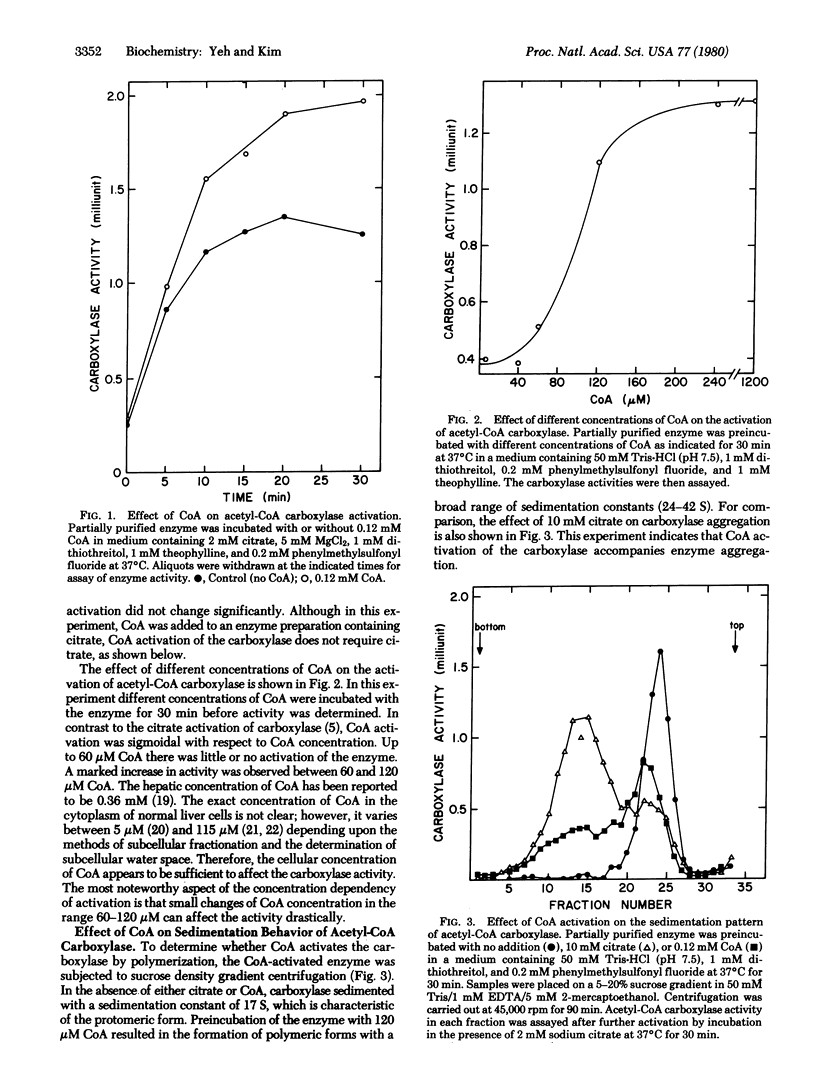
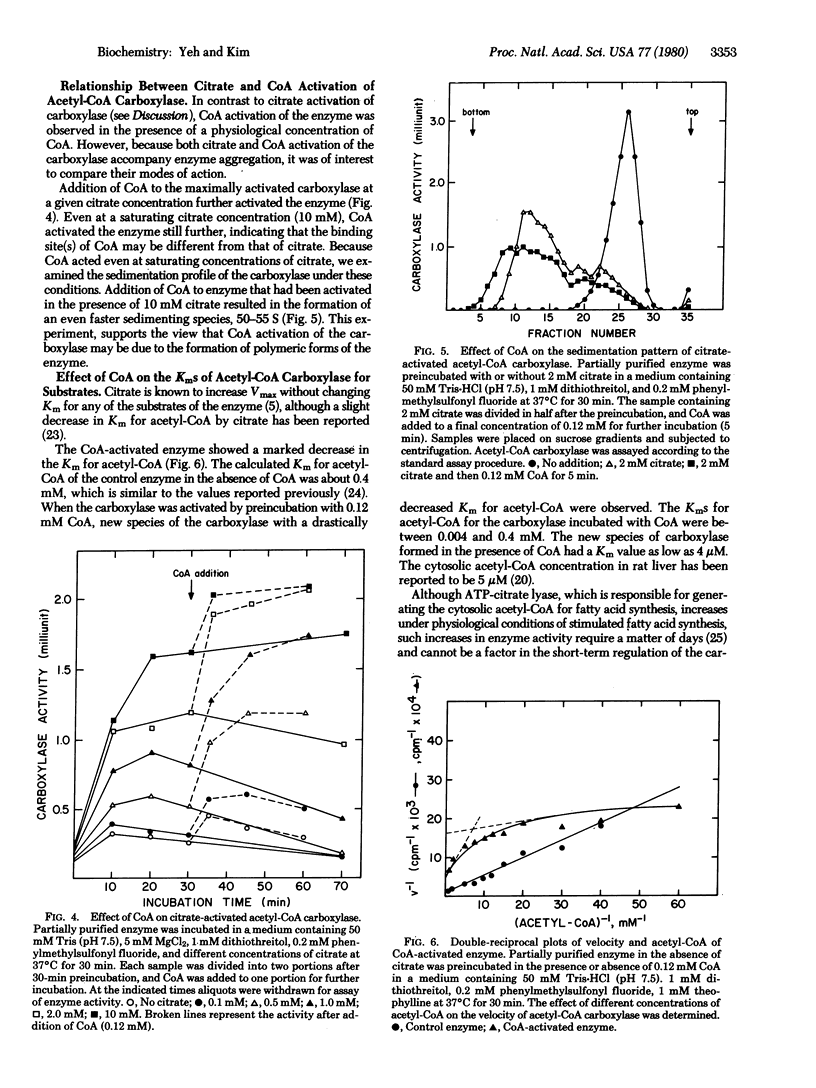
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase [acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming), EC 6.4.1.2] is activated by physiological concentrations of CoA. The CoA concentration dependency of this activation is sigmoidal; below 60 microM there is little or no activation, but the activation observed between 60 and 120 microM indicates that small changes in the concentration of CoA can cause significant changes in carboxylase activity. CoA activation of acetyl-CoA crboxylase accompanies polymerization of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. However, the binding site for CoA appears to be different from that of citrate. In contrast to citrate activation, which changes only the Vmax of the reaction, CoA activation of carboxylase results in polymeric forms with a lower Km for acetyl-CoA. The Km for acetyl-CoA is 0.4 mM in the control enzyme, whereas that of the CoA-activated enzyme is as low as 4 microM. The Km for ATP was not changed. Derivatives of CoA were not effective in activating the carboxylase, indicating that the CoA effect is specific. Arguments are presented that CoA could be a physiologically significant positive effector of the carboxylase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlson C. A., Kim K. H. Differential effects of metabolites on the active and inactive forms of hepatic acetyl CoA carboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):490–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. A., Kim K. H. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):478–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. A., Kim K. H. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):378–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. D., Watkins P. A., Lane M. D. Acute control of fatty acid synthesis by cyclic AMP in the chick liver cell: possible site of inhibition of citrate formation. J Lipid Res. 1979 Nov;20(8):974–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. A., Nielsen R. C., Hawkins R. A., Mehlman M. A., Lakshmanan M. R., Veech R. L. Effect of glucagon on hepatic malonyl coenzyme A concentration and on lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4421–4424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbridge A. G. Regulation of fatty acid synthesis in the liver of prenatal and early postnatal chicks. Hepatic concentrations of individual free fatty acids and other metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):1939–1945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum A. L., Gumaa K. A., McLean P. The distribution of hepatic metabolites and the control of the pathways of carbohydrate metabolism in animals of different dietary and hormonal status. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Apr;143(2):617–663. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregolin C., Ryder E., Kleinschmidt A. K., Warner R. C., Lane M. D. Molecular characteristics of liver acetyl CoA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):148–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregolin C., Ryder E., Warner R. C., Kleinschmidt A. K., Lane M. D. Liver acetyl coa carboxylase: the dissociation-reassociation process and its relation to catalytic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1751–1758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guynn R. W., Veloso D., Veech R. L. The concentration of malonyl-coenzyme A and the control of fatty acid synthesis in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7325–7331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Hormonal regulation of adipose-tissue acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase by changes in the polymeric state of the enzyme. The role of long-chain fatty acyl-Coenzyme A thioesters and citrate. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):365–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1420365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. The regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis: simple procedure for the purification of acetyl CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland, and its phosphorylation by endogenous cyclic AMP-dependent and -independent protein kinase activities. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 1;91(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Numa S. Kinetic studies on the reaction mechanism and the citrate activation of liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb 1;18(3):319–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Lowenstein J. M. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase from rat liver. Purification and demonstration of different subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4825–4832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. D., Moss J., Polakis S. E. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):139–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Regulation of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Evidence for interconversion between active and inactive forms of enzyme by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1748–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Regulation of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Evidence for interconversion between active and inactive forms of enzyme by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1748–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Stark M. J., Srere P. A. Coenzyme A is required for rat liver fatty acid synthetase activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1388–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein J. M. Citrate and the conversion of carbohydrate into fat. Biochem Soc Symp. 1968;27:61–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune S. A., Harris R. A. Mechanism responsible for 5-(tetradecyloxy)-2-furoic acid inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10095–10101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nomoto N., Yagi R., Oya N. Metabolic vitamin B complex deficiency due to the administration of glucocorticoid. J Vitaminol (Kyoto) 1970 Jun 10;16(2):89–98. doi: 10.5925/jnsv1954.16.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Numa S. Purification of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase and immunochemical studies on its synthesis and degradation. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):161–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S., Goto T., Ringelmann E., Riedel B. Studies on the relationship between activity and structure of liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Effects of magnesium ions, adenine nucleotides and acetyl-CoA. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(1):124–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S., Ringelmann E., Lynen F. Zur Hemmung der Acetyl-CoA-Carboxylase durch Fettsäure-Coenzym A-Verbindungen. Biochem Z. 1965 Dec 1;343(3):243–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiwara H., Tanabe T., Nikawa J., Numa S. Inhibition of rat-liver acetyl-coenzyme-A carboxylase by palmitoyl-coenzyme A. Formation of equimolar enzyme-inhibitor complex. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):33–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Wenger J. I., Neely J. R. Regulation of long chain fatty acid activation in heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess E. A., Brocks D. G., Wieland O. H. Subcellular distribution of key metabolites in isolated liver cells from fasted rats. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80701-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer A. F., Lowenstein J. M. Citrate content of liver and kidney of rat in various metabolic states and in fluoroacetate poisoning. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):342–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1030342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERWOOD A. H., NEWSHOLME E. A. PROPERTIES OF PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE FROM RAT LIVER AND THEIR RELATION TO THE CONTROL OF GLYCOLYSIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:868–875. doi: 10.1042/bj0950868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood A. H., Newsholme E. A. Some properties of phosphofructokinase from kidney cortex and their relation to glucose metabolism. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):296–299. doi: 10.1042/bj1040296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAGELOS P. R., ALBERTS A. W., MARTIN D. B. Studies on the mechnism of activation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by citrate. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Browning E. T., Scholz R. Control mechanisms of gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis. I. Effects of oleate on gluconeogenesis in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 10;244(17):4607–4616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Kowaloff E. M., Avruch J. Glucagon regulation of protein phosphorylation. Identification of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase as a substrate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Moriarity D., Martin D. B. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by insulin and glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6644–6649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh Y. Y., Leveille G. A. Studies on the relationship between lipogenesis and the level of coenzyme A derivatives, lactate and pyruvate in chick liver. J Nutr. 1971 Jul;101(7):911–918. doi: 10.1093/jn/101.7.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


