Abstract
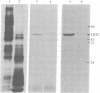
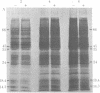
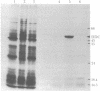
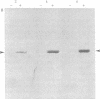
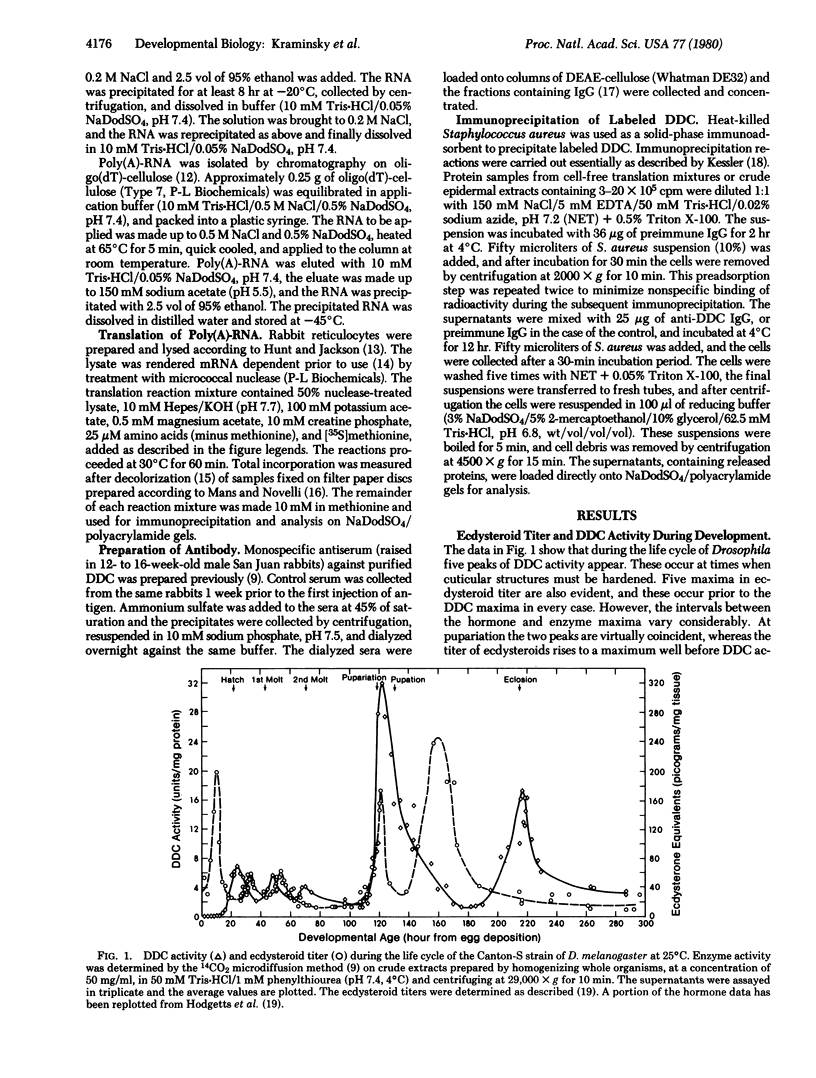
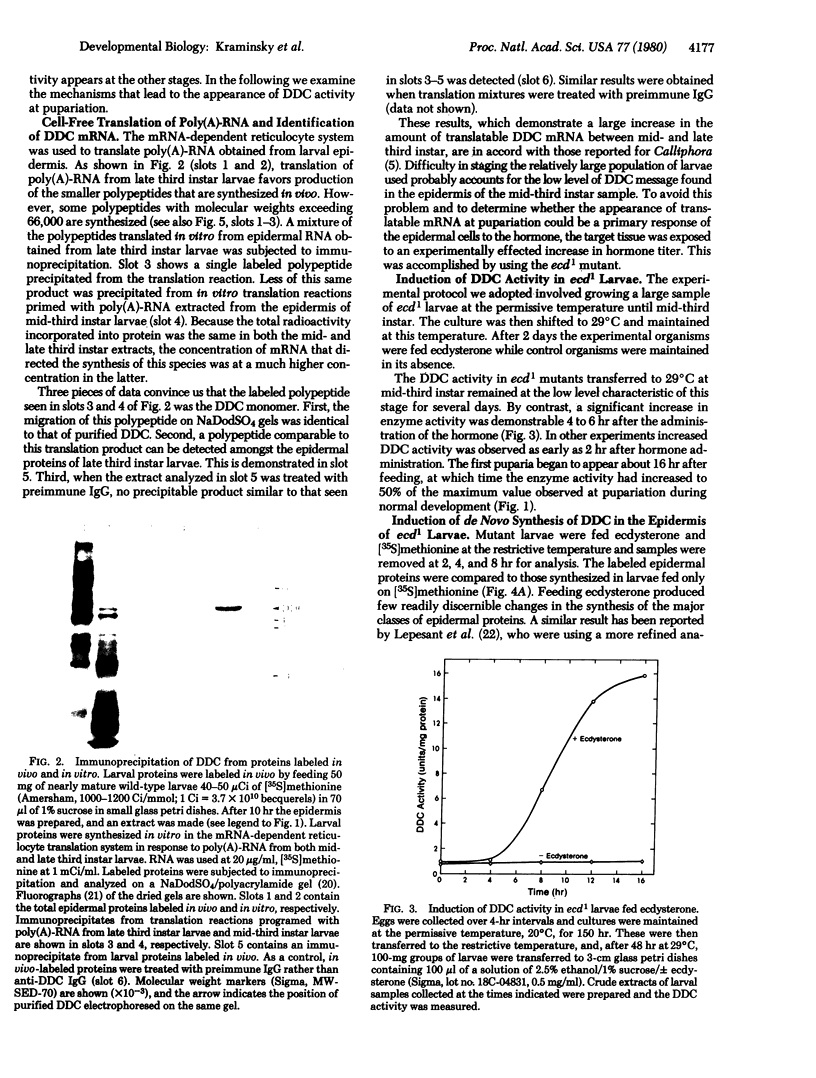
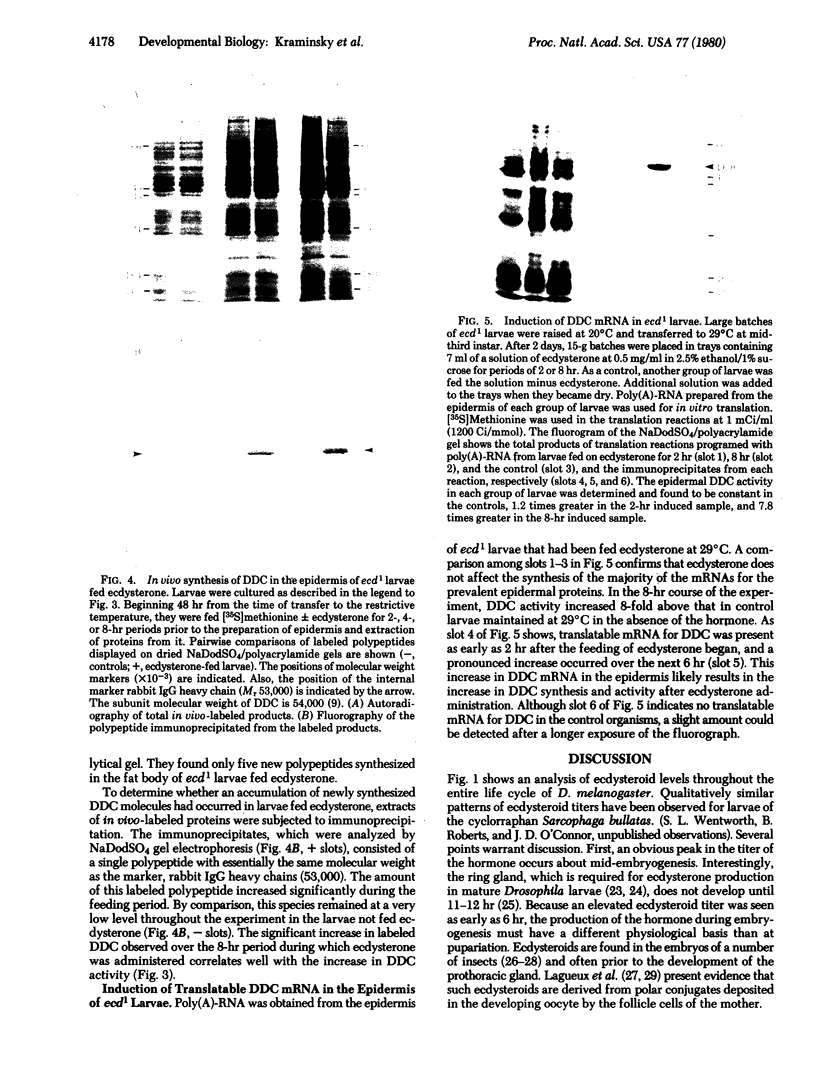
Ecdysteroid titer and dopa decarboxylase (aromatic-L-amino-acid carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.28) activity were determined throughout the life cycle of Drosophila melanogaster. Five peaks in the amount of hormone were observed, which preceeded five dopa decarboxylase peaks by times ranging from 5 to 58 hr. Late in the third instar the hormone and enzyme maxima are nearly coincident. The increase in enzyme activity observed at this time is paralleled by an increase in translatable dopa decarboxylase mRNA. To obtain evidence that ecdysterone induces the appearance of this mRNA we made use of the temperature-sensitive ecd1 mutant. Garen et al. [Garen, A., Kauvar, L. & Lepesant, J.-A. (1977) Proc. Natl, Acad. Sci. USA 74, 5099-5103] have shown that when third instar mutant larvae are kept at 29 degrees C, the ecdysteroid titer remains low. In such larvae we show that the normal increase in dopa decarboxylase activity fails to appear, and no translatable dopa decarboxylase mRNA can be detected. Exogenous feeding of ecdysterone to these larvae results in a rapid synthesis of dopa decarboxylase in the epidermal cells. In addition, a parallel increase in translatable dopa decarboxylase mRNA occurs, which may be a primary response of these target cells to ecdysterone.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres R. Y. Aldehyde oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase from wild-type Drosophila melanogaster and immunologically cross-reacting material from ma-1 mutants. Purification by immunoadsorption and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Rates of induction of specific translatable messenger RNAs for ovalbumin and avidin by steroid hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1870–1874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S. A., Croker S. G., Ikeda K., McCaman R. E. Metabolism of biogenic amines in Drosophila nervous tissue. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1972 Dec 15;43(4):975–981. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(72)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fragoulis E. G., Sekeris C. E. Translation of mRNA for 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylase isolated from epidermis tissue of Calliphora vicina R. -D. in a heterologous system. Dependence of mRNA concentration on the insect steroid hormone ecdysone. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):305–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garen A., Kauvar L., Lepesant J. A. Roles of ecdysone in Drosophila development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5099–5103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgetts R. B., Sage B., O'Connor J. D. Ecdysone titers during postembryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):310–317. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgetts R. B. The response of dopa decarboxylase activity to variations in gene dosage in Drosophila: a possible location of the structural gene. Genetics. 1975 Jan;79(1):45–54. doi: 10.1093/genetics/79.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplanis J. N., Dutky S. R., Robbins W. E., Thompson M. J., Lindquist E. L., Horn D. H., Galbraith M. N. Makisterone A:a 28-carbon hexahydroxy molting hormone from the embryo of the milkweed bug. Science. 1975 Nov 14;190(4215):681–682. doi: 10.1126/science.1237931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlson P. New concepts on the mode of action of hormones. Perspect Biol Med. 1963 Winter;6(2):203–214. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1963.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., King J. Genetic control of bacteriophage T4 baseplate morphogenesis. I. Sequential assembly of the major precursor, in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):645–672. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killewich L. A., Feigelson P. Developmental control of messenger RNA for hepatic tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagueux M., Hirn M., Hoffmann J. A. Ecdysone during ovarian development in Locusta migratoria. J Insect Physiol. 1977;23(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(77)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepesant J. A., Kejzlarova-Lepesant J., Garen A. Ecdysone-inducible functions of larval fat bodies in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5570–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash D., Bell J. Larval age and the pattern of DNA synthesis in polytene chromosomes. Can J Genet Cytol. 1968 Mar;10(1):82–90. doi: 10.1139/g68-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Moore P. B., Mulvihill E. R. A significant lag in the induction of ovalbumin messenger RNA by steroid hormones: a receptor translocation hypothesis. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):557–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAAYA E., SEKERIS C. E. ECDYSONE DURING INSECT DEVELOPMENT. 3. ACTIVITIES OF SOME ENZYMES OF TYROSINE METABOLISM IN COMPARISON WITH ECDYSONE TITER DURING THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BLOWFLY, CALLIPHORA ERYTHROCEPHIA MEIG. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1965 Feb;5:35–39. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(65)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward W. R., Ivey J. L., Herbert E. Protein synthesis with rabbit reticulocyte preparations. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:724–731. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. R., Bewley G. C., Sherald A. F. The genetics of dopa decarboxylase in Drosophila melanogaster. II. Isolation and characterization of dopa-decarboxylase-deficient mutants and their relationship to the alpha-methyl-dopa-hypersensitive mutants. Genetics. 1976 Oct;84(2):287–310. doi: 10.1093/genetics/84.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M. Steroid receptors: elements for modulation of eukaryotic transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:721–746. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]