Abstract
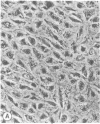
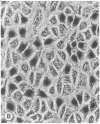
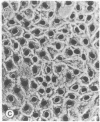
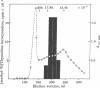
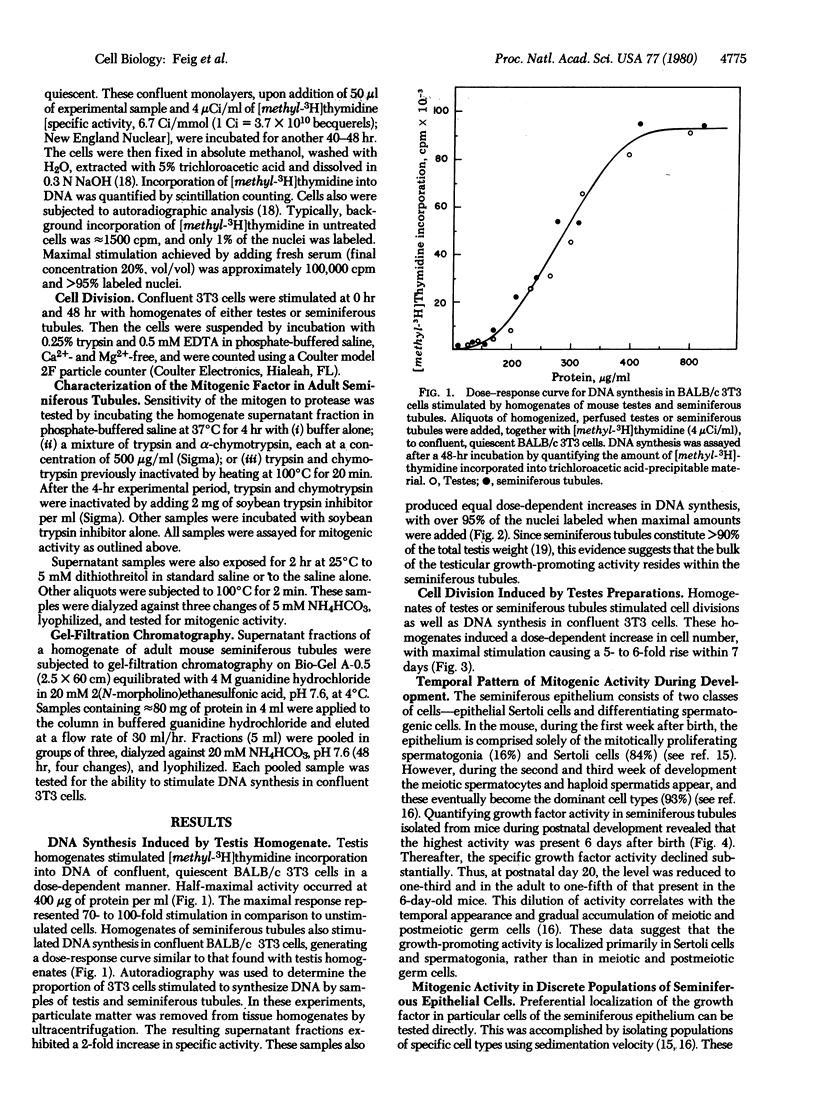
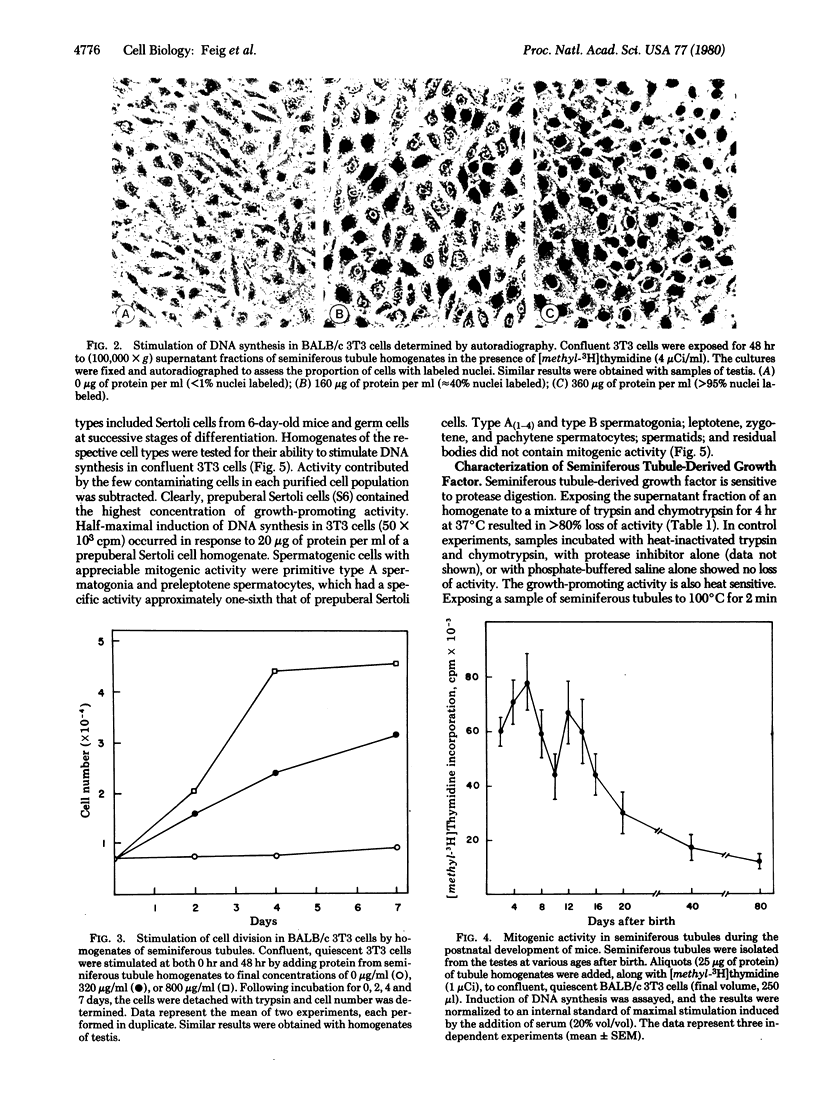
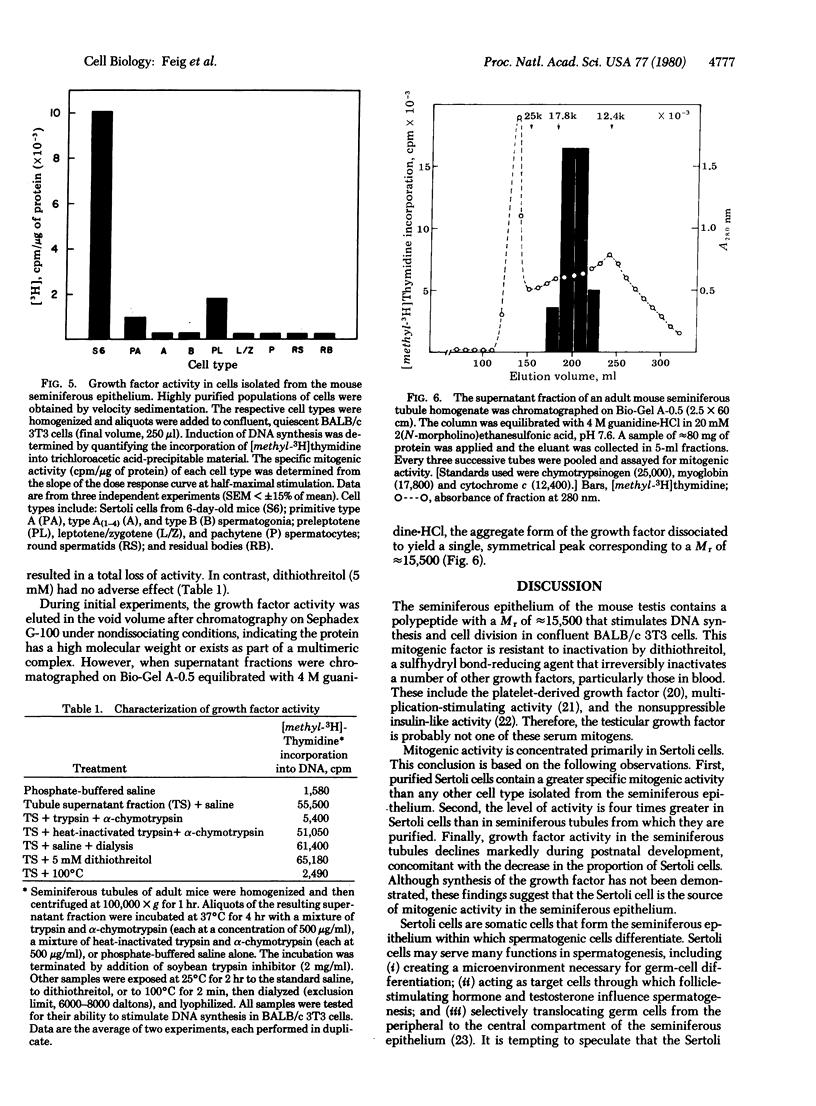
The seminiferous epithelium of the mouse testis contains a potent mitogen that induces DNA synthesis and cell division in cutures of confluent, quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Homogenates of adult mouse seminiferous tubules, when added to 3T3 cells for 48 hr, produce a dose-dependent increase in DNA synthesis with half-maximal activity at 400 micrograms of protein per ml. Maximal stimulation causes a 70- to 100-fold increase in [methyl-3H]thymidine incorporation into DNA, a labeling of > 99% of 3T3 cell nuclei, and a doubling in cell number. The level of mitogenic activity in seminiferous tubules isolated from newborn mice is five times greater than that in tubules of adult mice. Furthermore, prepuberal Sertoli cells contain substantially greater levels of mitogenic activity than any other cell type purified from the seminiferous epithelium. A homogenate of prepuberal Sertoli cells induces half-maximal DNA synthesis at 20 micrograms of protein per ml. The mitogenic factor is sensitive to proteases and to heating at 100 degrees C for 2 min but not to dithiothreitol. Gel-filtration chromatography reveals that the factor is a polypeptide with a Mr of approximately 15,500. These observations provide evidence for the presence of a growth factor in the mammalian testis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson J. W., Brown J. E. Aspects of erythroid differentiation and proliferation. Symp Soc Dev Biol. 1978;(35):161–179. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-612981-6.50015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D., Stiles C. D. Purification of human platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1809–1813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki A., Fawcett D. W. Is there a local feedback from the seminiferous tubules affecting activity of the Leydig cells? Biol Reprod. 1978 Aug;19(1):144–158. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod19.1.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILLIE A. H. Observatons on the growth and histochemistry of the Leydig tissue in the postnatal prepubertal mouse testis. J Anat. 1961 Jul;95:357–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Millette C. F., Bhatnagar Y. M., O'Brien D. A. Dissociation of the mouse testis and characterization of isolated spermatogenic cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):480–494. doi: 10.1177/25.7.893996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Eddy E. M. Fine structural observations on the origin and associations of primordial germ cells of the mouse. Dev Biol. 1975 Nov;47(1):136–155. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clermont Y., Mauger A. Effect of a spermatogonial chalone on the growing rat testis. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1976 Jan;9(1):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1976.tb01256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham G. R., Huckins C. Failure to identify a spermatogonial chalone in adult irradiated testes. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1979 Jan;12(1):81–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1979.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCHI L. L., MANDL A. M. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF GERM CELLS IN FOETAL AND NEONATAL MALE RATS. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1964 Jun;12:289–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J. S. Stimulation of division of sparse and confluent 3T3 cell populations by a fibroblast growth factor, dexamethasone, and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4584–4588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckins C. Cell cycle properties of differentiating spermatogonia in adult Sprague-Dawley rats. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1971 Mar;4(2):139–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1971.tb01524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckins C., Oakberg E. F. Morphological and quantitative analysis of spermatogonia in mouse testes using whole mounted seminiferous tubules, I. The normal testes. Anat Rec. 1978 Dec;192(4):519–528. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091920406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iturriza F. C., Irusta O. Hyperplasia of the interstitial cells of the testis in experimental cryptorchidism. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1969;19(3):236–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M. Human milk stimulates DNA synthesis and cellular proliferation in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5057–5061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Langer R., Levenson R., Smith S., Lillehei C. The stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in chondrocytes and 3T3 cells by a growth factor isolated from cartilage. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 1;105(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F. Cell division kinetics and DNA synthesis in the immature sertoli cells of the rat testis. J Reprod Fertil. 1972 Mar;28(3):389–395. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0280389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. J., Svoboda D. J. Alterations in rat testes due to an antispermatogenic agent. Light and electron microscopic study. Arch Pathol. 1967 Oct;84(4):376–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romrell L. J., Bellvé A. R., Fawcett D. W. Separation of mouse spermatogenic cells by sedimentation velocity. A morphological characterization. Dev Biol. 1976 Mar;49(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Vogel A. The platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberger A., Steinberger E. Replication pattern of Sertoli cells in maturing rat testis in vivo and in organ culture. Biol Reprod. 1971 Feb;4(1):84–87. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/4.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]