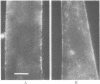
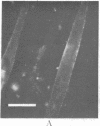
Abstract
A biotinylated derivative of alpha-bungarotoxin and tetramethylrhodamine-labeled avidin were employed to fluorescence label the acetylcholine receptors (AcChoR) on the surface of rat myotubes in primary culture. Because of the multivalency of both the biotinylated bungarotoxin and the avidin, this treatment extensivey crosslinks the AcChoR. AcChoR crosslinking immobilizes more than 90% of the normally laterally mobile AcChoR as verified by the fluorescence photobleaching recovery technique; it also redistributes the AcChoR into visible micropatches. Biotinylated alpha-bungarotoxin/avidin-induced AcChoR crosslinking greatly accelerates the rate of internalization of surface AcChoR; this rapid internalization affects both the normally immobile AcChoR in areas of diffuse distribution and the normally immobile AcChoR in preexisting patches. The peculiar pattern of fluorescent avidin binding to AcChoR patches previously bound with biotinylated bungarotoxin suggests that almost all AcChoR patches are in very close contact (< 70 A) with the glass substrate. AcChoR immobilization leads to a partial immobilization of concanavalin A receptors in the myotube membrane.
Full text
PDF

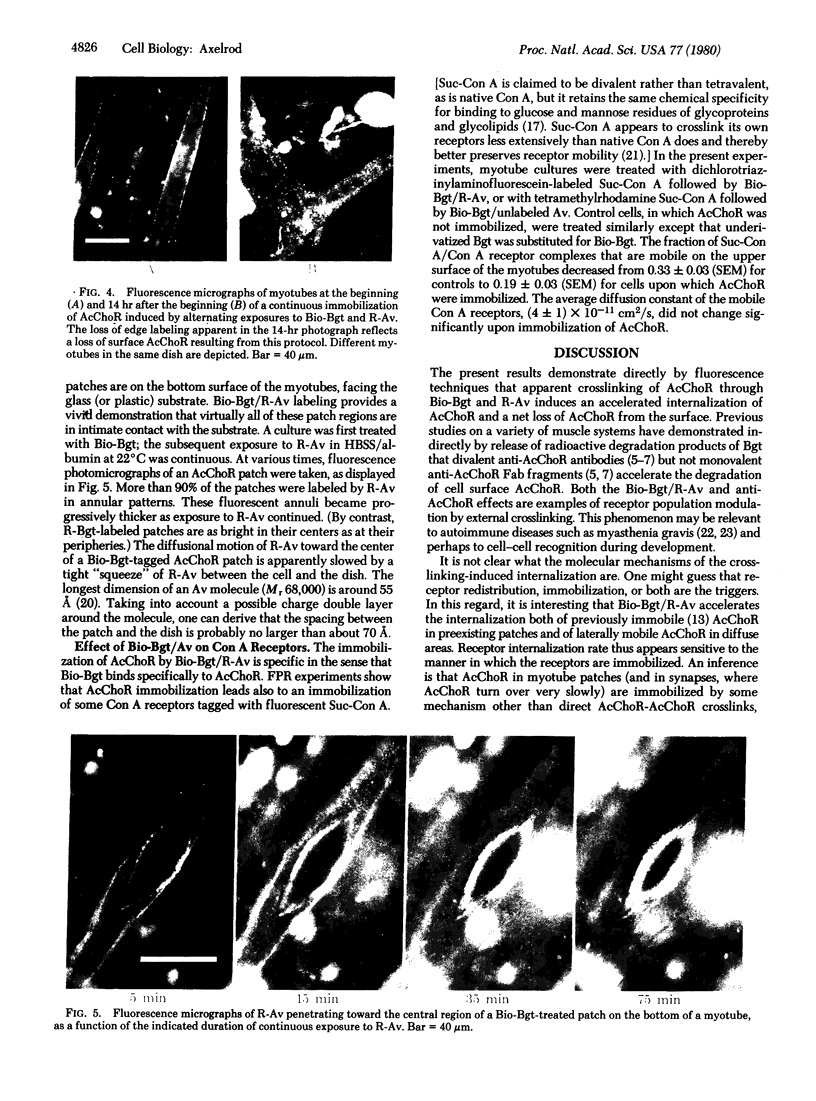

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Hall Z. W. Acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated rat diaphragm muscle. II. Comparison of junctional and extrajunctional receptors. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2100–2106. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Huang M. C. Turnover of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors of the rat diaphragm. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):643–644. doi: 10.1038/253643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptor turnover in membranes of developing muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1975 May;65(2):335–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., Angus C. W., Adams R. N., Michelson J. D., Hoffman G. J. Myasthenic antibodies cross-link acetylcholine receptors to accelerate degradation. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 18;298(20):1116–1122. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805182982004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther G. R., Wang J. L., Yahara I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Concanavalin A derivatives with altered biological activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. L., Jarrett D. B., Flier J. S. Direct demonstration that receptor crosslinking or aggregation is important in insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A. The immunopathology of myasthenia gravis. Hum Pathol. 1978 Sep;9(5):541–551. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Collection of insulin, EGF and alpha2-macroglobulin in the same patches on the surface of cultured fibroblasts and common internalization. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90336-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Heinemann S., Einarson B., Lindstrom J. M. Degradation of acetylcholine receptor in diaphragms of rats with experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6328–6332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Heinemann S., Lindstrom J. M. Acetylcholine receptor degradation in adult rat diaphragms in organ culture and the effect of anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6320–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives J., Hoffman L., Tarrab-Hazdai R., Fuchs S., Amsterdam A. Ligand induced changes in stability and distribution of acetylcholine receptors on surface membranes of muscle cells. Life Sci. 1979 Apr 30;24(18):1713–1718. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin P., Axelrod D. Fluorescent tetramethyl rhodamine derivatives of alpha-bungarotoxin: preparation, separation, and characterization. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jun;80(2):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90682-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schekman R., Singer S. J. Clustering and endocytosis of membrane receptors can be induced in mature erythrocytes of neonatal but not adult humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4075–4079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Koppel D. E., Axelrod D., Jacobson K., Webb W. W., Elson E. L. Lateral transport on cell membranes: mobility of concanavalin A receptors on myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2409–2413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Quantitative determination of the lateral diffusion coefficients of the hormone-receptor complexes of insulin and epidermal growth factor on the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Axelrod D. Reduced lateral mobility of a fluorescent lipid probe in cholesterol-depleted erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 27;597(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E. L., Webb W. W., Blumenthal R., Henkart P. Diffusion and patching of macromolecules on planar lipid bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3476–3483. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]