Abstract
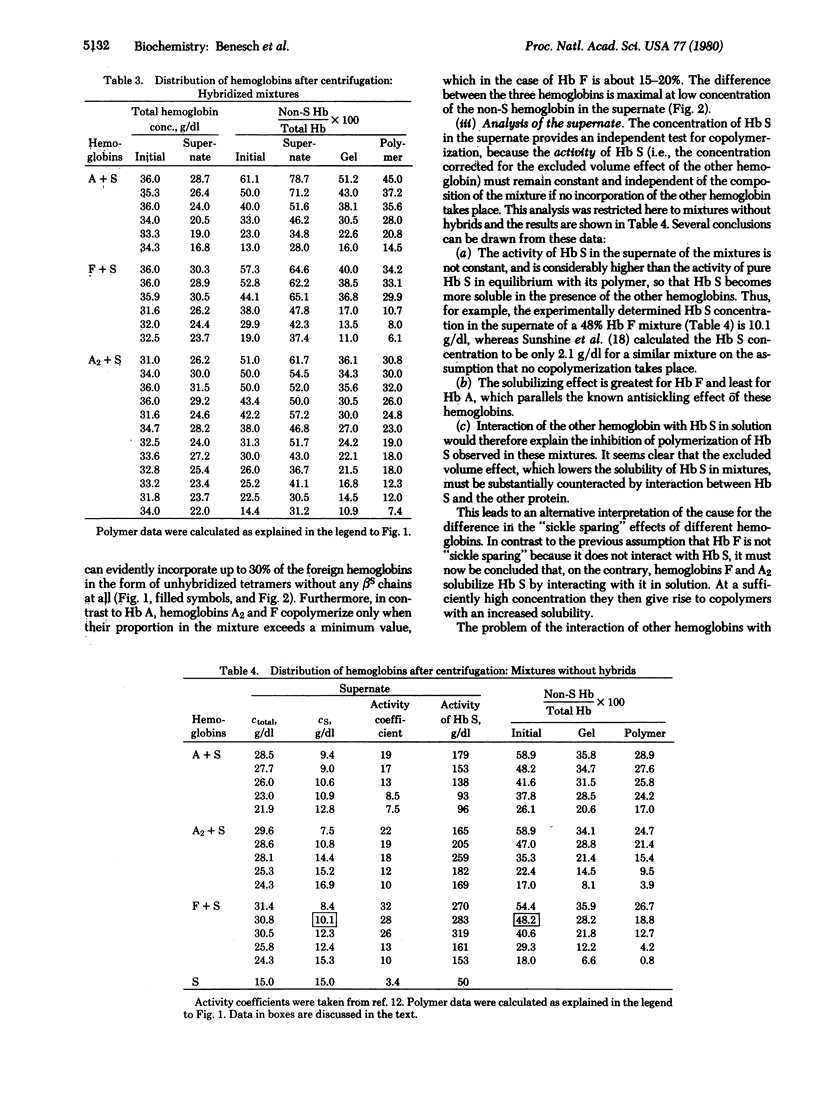
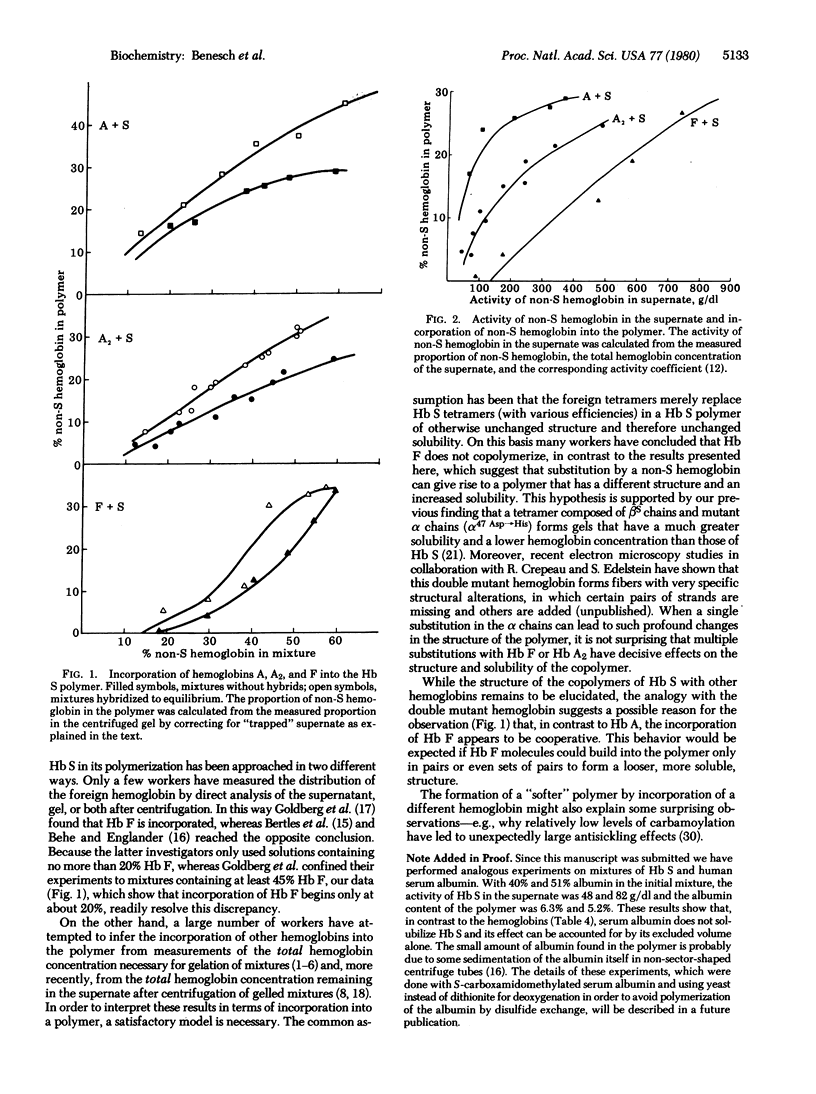
The polymerization of mixtures of Hb S with hemoglobins A, A2, and F has been investigated by analysis of the proportions of S and non-S hemoglobin both in the supernate and in the pellet after centrifugation. In all cases the non-S hemoglobin was incorporated into the polymer even in the absence of hybrids in the order A > A2 > F. The solubility of Hb S is substantially increased by the other hemoglobins, especially by Hb F, which would account for its antisickling effect. It appears that the excluded volume effect of the other hemoglobin on Hb S is largely counterbalanced by the solubilizing effect arising from the interaction between the two hemoglobins in solution. The ability of hybrid hemoglobins to gel was demonstrated directly with tetramers in which alpha beta s dimers were covalently linked to alpha beta A, alpha delta A2, and alpha gamma F dimers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C. Properties of sickle-cell haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):212–219. doi: 10.1042/bj0650212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham E. C., Reese A., Stallings M., Huisman T. H. Separation of human hemoglobins by DEAE-cellulose chromatography using glycine-KCN-NaC1 developers. Hemoglobin. 1976;1(1):27–44. doi: 10.3109/03630267609031020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M. J., Englander S. W. Mixed gelation theory. Kinetics, equilibrium and gel incorporation in sickle hemoglobin mixtures. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 5;133(1):137–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M. J., Englander S. W. Sickle hemoglobin gelation. Reaction order and critical nucleus size. Biophys J. 1978 Jul;23(1):129–145. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85438-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R. E., Benesch R., Edalji R., Kwong S. Intermolecular effects in the polymerization of hemoglobin S. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1307–1312. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R. E., Benesch R., Renthal R. D., Maeda N. Affinity labeling of the polyphosphate binding site of hemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3576–3582. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R. E., Ikeda S., Benesch R. Reaction of haptoglobin with hemoglobin covalently cross-linked between the alpha beta dimers. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):465–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R. E., Kwong S., Edalji R., Benesch R. alpha Chain mutations with opposite effects on the gelation of hemoglobin S. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8169–8172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R., Benesch R. E., Yung S., Edalji R. Hemoglobin covalently bridged across the polyphoshate binding site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):1123–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90685-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertles J. F., Rabinowitz R., Döbler J. Hemoglobin interaction: modification of solid phase composition in the sickling phenomenon. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):375–377. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Nagel R. L. Ligand-induced conformational dependence of hemoglobin in sickling interactios. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheetham R. C., Huehns E. R., Rosemeyer M. A. Participation of haemoglobins A, F, A2 and C in polymerisation of haemoglobin S. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):45–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. A., Husson M. A., Bunn H. F. Participation of hemoglobins A and F in polymerization of sickle hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3414–3421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofrichter J., Ross P. D., Eaton W. A. Supersaturation in sickle cell hemoglobin solutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod R. M., Hill R. J. Demonstration of the hybrid hemoglobin 2 A A S . J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):100–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May A., Huehns E. R. The mechanism and prevention of sickling. Br Med Bull. 1976 Sep;32(3):223–233. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton A. P. Non-ideality and the thermodynamics of sickle-cell hemoglobin gelation. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):89–103. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel R. L., Bookchin R. M., Johnson J., Labie D., Wajcman H., Isaac-Sodeye W. A., Honig G. R., Schilirò G., Crookston J. H., Matsutomo K. Structural bases of the inhibitory effects of hemoglobin F and hemoglobin A2 on the polymerization of hemoglobin S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):670–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Briehl R. W., Minton A. P. Temperature dependence of nonideality in concentrated solutions of hemoglobin. Biopolymers. 1978 Sep;17(9):2285–2288. doi: 10.1002/bip.1978.360170920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Minton A. P. Analysis of non-ideal behavior in concentrated hemoglobin solutions. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):437–452. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER K., SINGER L. Studies on abnormal hemoglobins. VIII. The gelling phenomenon of sickle cell hemoglobin: its biologic and diagnostic significance. Blood. 1953 Nov;8(11):1008–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN W. H., KUNKEL H. G., COLE R. D., SPACKMAN D. H., MOORE S. Observation on the amino acid composition of human hemoglobins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):640–642. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine H. R., Hofrichter J., Eaton W. A. Gelation of sickle cell hemoglobin in mixtures with normal adult and fetal hemoglobins. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 9;133(4):435–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEALE F. W. Cleavage of the haem-protein link by acid methylethylketone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Oct;35:543–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. R., Cottam G. L., Shibata K. Inhibitory effect of deoxyhemoglobin A2 on the rate of deoxyhemoglobin S polymerization. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 5;129(2):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


