Abstract
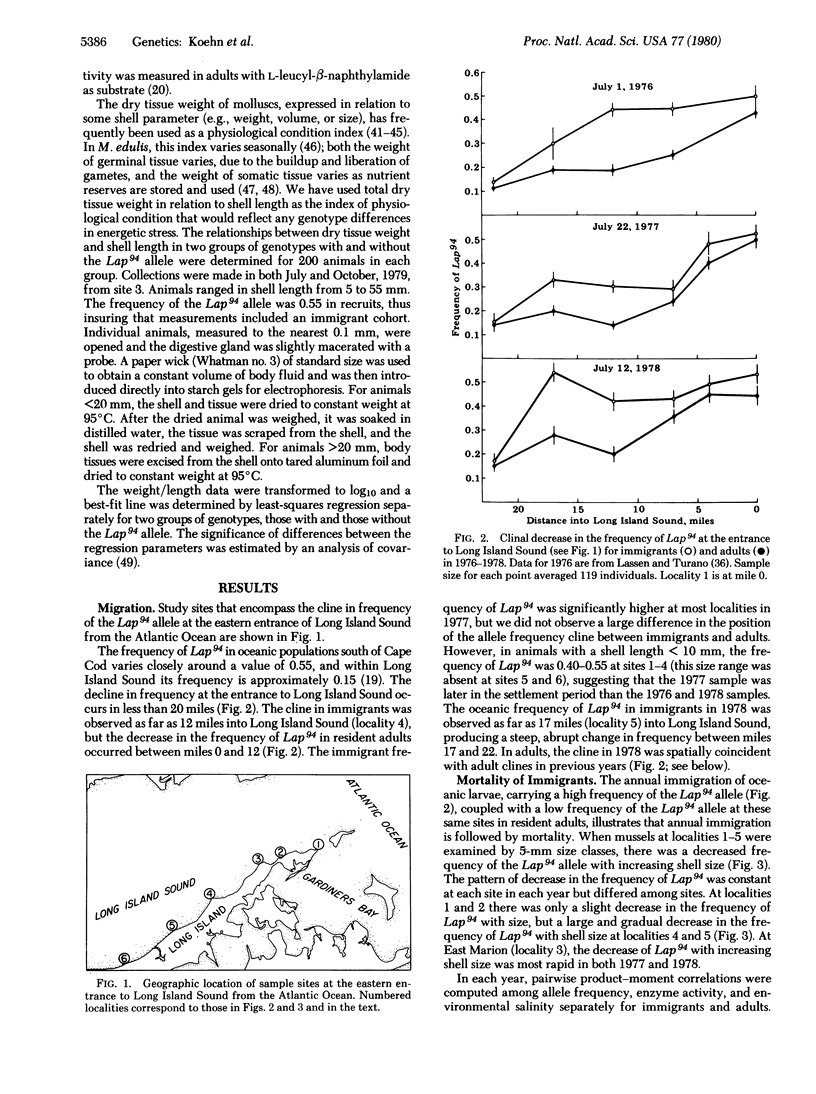
The product of the Lap locus in the marine bivalve Mytilus edulis is a neutral, membrane-associated aminopeptidase that is primarily localized on intestinal microvilli and in digestive cell lysosomes. Natural populations are genetically differentiated at the Lap locus between areas of differing salinity. A steep (0.55-0.15) allele frequency cline connects differentiated populations between the Atlantic Ocean and Long Island Sound. We demonstrate an annual gene flow/mortality cycle in cline populations whereby gene frequencies after mortality are correlated with salinity and enzyme activity. The cline is spatially and temporally unstable in immigrants, but stable in residents after mortality. Mortality is nonrandom with regard to the Lap locus; genotype-dependent properties of the aminopeptidase enzyme apparently led to a differential rate of the utilizaiton of nutrient reserves because selected genotypes exhibited an increased rate of tissue weight loss. Aminopeptidase genotypes are differentially adapted to different temperatures and salinities, which provides a mechanism for the relationship among biochemical, physiological, and population phenotypes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cornish-Bowden A. The effect of natural selection on enzymic catalysis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 15;101(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day T. H., Hillier P. C., Clarke B. Properties of genetically polymorphic isozymes of alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet. 1974 Feb;11(2):141–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00485770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day T. H., Hillier P. C., Clarke B. The relative quantities and catalytic activities of enzymes produced by alleles at the alcohol dehydrogenase locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet. 1974 Feb;11(2):155–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00485771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fern E. B., Hider R. C., London D. R. The sites of hydrolysis of dipeptides containing leucine and glycine by rat jejunum in vitro. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):855–861. doi: 10.1042/bj1140855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazel J. R., Prosser C. L. Molecular mechanisms of temperature compensation in poikilotherms. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):620–677. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. M., Schaffer H. E., Gillaspy J. E., Rockwood E. S. Isozyme genotype-environment relationships in natural populations of the harvester ant, Pogonomyrmex barbatus, from Texas. Biochem Genet. 1969 Oct;3(5):429–450. doi: 10.1007/BF00485604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. M., Schaffer H. E. Isozyme variability in species of the genus Drosophila. VII. Genotype-environment relationships in populations of D. melanogaster from the Eastern United States. Biochem Genet. 1973 Oct;10(2):149–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00485762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Birtwhistle W., Kim Y. W. Peptide hydrolases in the bruch border and soluble fractions of small intestinal mucosa of rat and man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1419–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI106938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S. Intestinal mucosal hydrolysis of proteins and peptides. Ciba Found Symp. 1977;(50):151–176. doi: 10.1002/9780470720318.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Nicholson J. A., Curtis K. J. Intestinal peptide hydrolases: peptide and amino acid absorption. Med Clin North Am. 1974 Nov;58(6):1397–1412. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehn R. K. Esterase heterogeneity: dynamics of a polymorphism. Science. 1969 Feb 28;163(3870):943–944. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3870.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. C. Population subdivision with respect to multiple alleles. Ann Hum Genet. 1969 Jul;33(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1969.tb01625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroux S., Louvard D., Baratti J. The aminopeptidase from hog intestinal brush border. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 15;321(1):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. M. Introduction. Membrane transport of peptides. Ciba Found Symp. 1977;(50):5–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKechnie S. W., Ehrlich P. R., White R. R. Population genetics of euphydryas butterflies. I Genetic variation and the neutrality hypothesis. Genetics. 1975 Nov;81(3):571–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. N., Lowe D. M., Fieth P. E. Responses of lysosomes in the digestive cells of the common mussel, Mytilus edulis, to sex steroids and cortisol. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Mar 31;188(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00220510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen G. Lysosomes, peroxisomes and bivalves. Sci Prog. 1972 Autumn;60(239):299–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Place A. R., Powers D. A. Genetic variation and relative catalytic efficiencies: lactate dehydrogenase B allozymes of Fundulus heteroclitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2354–2358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers D. A., Greaney G. S., Place A. R. Physiological correlation between lactate dehydrogenase genotype and haemoglobin function in killifish. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):240–241. doi: 10.1038/277240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockwood-Sluss E. S., Johnston J. S., Heed W. B. Allozyme genotype-environment relationships. I. Variation in natural populations of Drosophila pachea. Genetics. 1973 Jan;73(1):135–146. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaszewski E. K., Schaffer H. E., Johnson F. M. Isozyme genotype-environment associations in natural populations of the harvester ant, Pogonomyrmex badius. Genetics. 1973 Oct;75(2):405–421. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. P., Koehn R. K., Arnheim N. Biochemical characterization of "LAP," a polymorphic aminopeptidase from the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis. Biochem Genet. 1979 Apr;17(3-4):305–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00498971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


