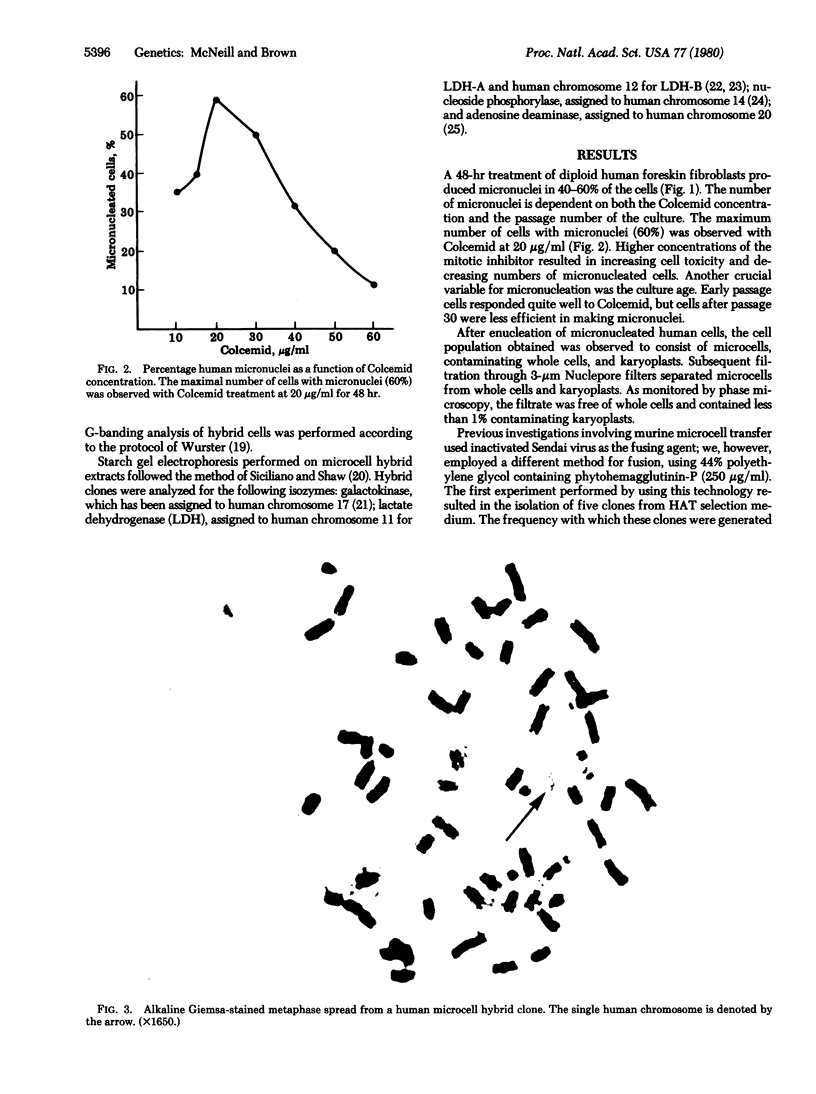
Abstract
Microcell-mediated chromosome transfer is an innovative approach to the production of karyotypically simple hybrids. This method of gene transfer, employing micronuclei formed by prolonged Colcemid treatment, has been utilized for rodent systems. Expansion of this technology to include transfer of normal human genetic material has been hindered because large micronucleate populations from diploid human cells have been unobtainable. This report describes the production of micronuclei in 40-60% of normal human fibroblasts. These micronucleated cells have been enucleated by combining centrifugation and cytochalasin B treatment, and the resultant microcells have been purified and fused to recipient mouse (LMTK-) cells. Microcell hybrid clones containing a single human chromosome have been isolated from three separate fusion experiments. The time course for production of these hybrids, from fusion to karyotypic analysis, was 6 weeks. With a transfer frequency of about 2 x 10(-6), a single intact human chromosome has become a functioning element of the murine genome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajiro K., Zweidler A., Borun T., Croce C. M. Species-specific suppression of histone H1 and H2B production in human/mouse hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5599–5603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C., Chen T. R., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of three human genes to chromosomes (LDH-A to 11, TK to 17, and IDH to 20) and evidence for translocation between human and mouse chromosomes in somatic cell hybrids (thymidine kinase-lactate dehydrogenase A-isocitrate dehydrogenase-C-11, E-17, and F-20 chromosomes). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):510–514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. R., McMorris F. A., Creagan R., Ricciuti F., Tischfield J., Ruddle F. Assignment of the genes for malate oxidoreductase decarboxylating to chromosome 6 and peptidase B and lactate dehydrogenase B to chromosome 12 in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Mar;25(2):200–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Talavera A., Basilico C., Miller O. J. Suppression of production of mouse 28S ribosomal RNA in mouse-human hybrids segregating mouse chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):694–697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ege T., Ringertz N. R., Hamberg H., Sidebottom E. Preparation of microcells. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;15:339–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ege T., Ringertz N. R. Preparation of microcells by enucleation of micronucleate cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Aug;87(2):378–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90494-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier R. E., Ruddle F. H. Microcell-mediated transfer of murine chromosomes into mouse, Chinese hamster, and human somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):319–323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend K. K., Dorman B. P., Kucherlapati R. S., Ruddle F. H. Detection of interspecific translocations in mouse-human hybrids by alkaline Giemsa staining. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90676-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L., MOORHEAD P. S. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Dec;25:585–621. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Mullinger A. M., Skaer R. J. Perturbation of mammalian cell division: human mini segregants derived from mitotic cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 17;189(1097):591–602. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Brown R. L., Arrighi F. E. Induction of premature chromosome condensation in CHO cells fused with polyethylene glycol. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Nov;110(1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas J. J., Szekely E., Kates J. R. The regeneration and division of mouse L-cell karyoplasts. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydersen B. K., Kao F. T., Pettijohn D. Expression of genes coding for non-histone chromosomal proteins in human-Chinese hamster cell hybrids. An electrophoretic analysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3002–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Ozer H. L. Transfer of genetic information by purified metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Schlegel R. A. Phytohemagglutinin enhancement of cell fusion reduces polyethylene glycol cytotoxicity. Exp Cell Res. 1979 May;120(2):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkwiszewski K. G., Tedesco T. A., Croce C. M. Assignment of the human gene for galactokinase to chromosome 17. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):60–62. doi: 10.1038/252060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciuti F., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of nucleoside phosphorylase to D-14 and localization of X-linked loci in man by somatic cell genetics. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 7;241(110):180–182. doi: 10.1038/newbio241180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L. Cell replication and aging: in vitro and in vivo studies. Fed Proc. 1979 Apr;38(5):1857–1861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y. Gene transfer and gene mapping in mammalian cells in culture. In Vitro. 1980 Jan;16(1):55–76. doi: 10.1007/BF02618200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Creagan R. P., Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of a gene for adenosine deaminase to human chromosome 20. Hum Hered. 1974;24(1):1–11. doi: 10.1159/000152631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourian A., Johnson R. T., Burg K., Nicolson S. W., Sperling K. Transfer of human chromosomes via human minisegregant cells into mouse cells and the quantitation of the expression of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase in the hybrids. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:193–209. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veomett G., Prescott D. M., Shay J., Porter K. R. Reconstruction of mammalian cells from nuclear and cytoplasmic components separated by treatment with cytochalasin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1999–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Green H. Human-mouse hybrid cell lines containing partial complements of human chromosomes and functioning human genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1104–1111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster D. H. Mouse chromosomes identified by trypsin-Giemsa (T-G) banding. Cytogenetics. 1972;11(5):379–387. doi: 10.1159/000130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]