Abstract
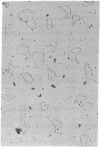
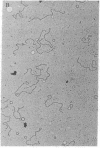
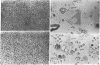
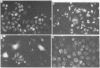
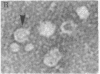
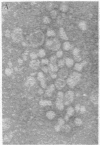
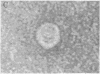
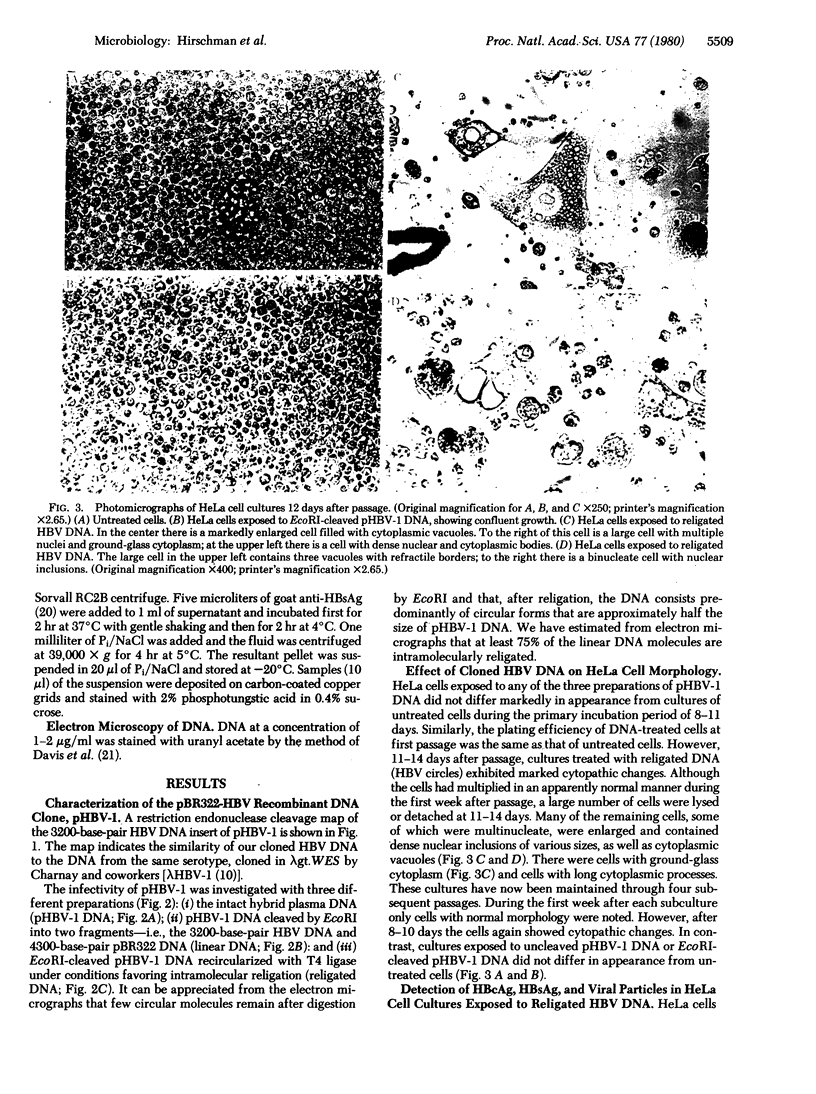
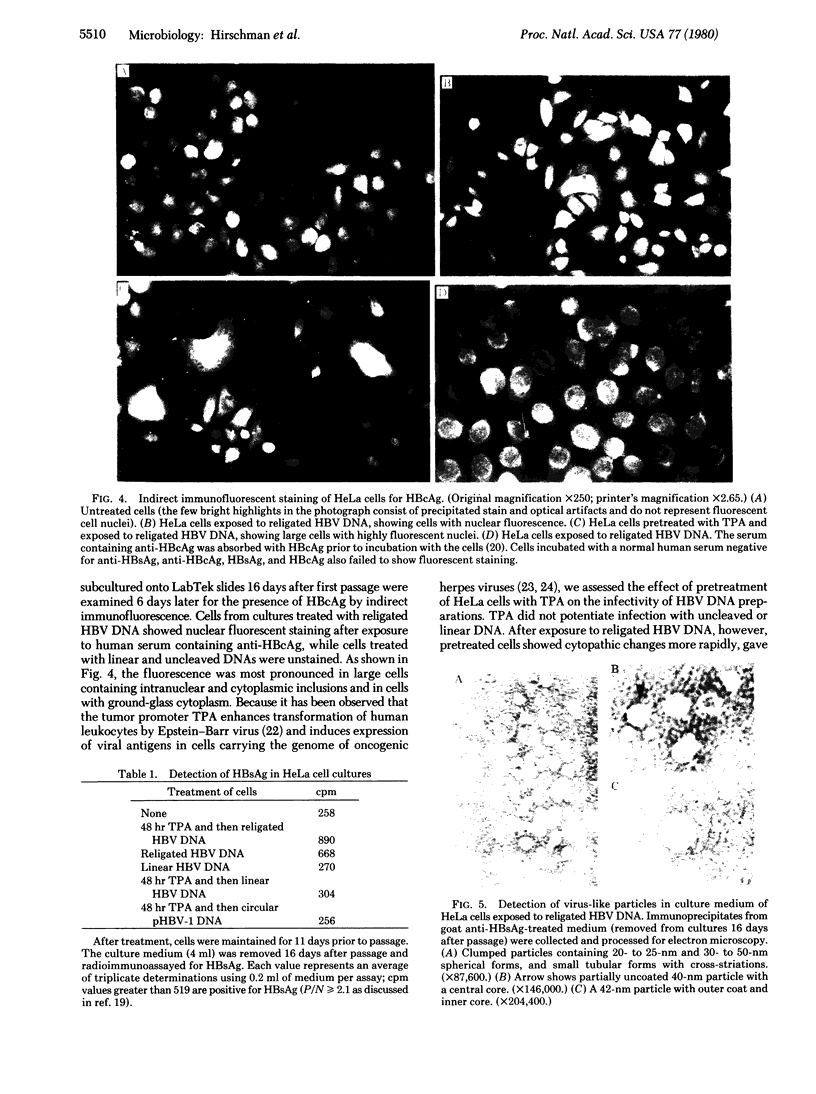
DNA was isolated from the ayw subtype of hepatitis B virus (HBV) that had been incubated in vitro with all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates in order to complete the circular viral genome by means of the endogenous DNA polymerase. The purified viral DNA was cleaved with EcoRI restriction endonuclease, inserted into the EcoRI site of plasmid pBR322, and cloned in Escherichia coli chi 1776. DNA from a clone, pHBV-1, that contained a 3200-base-pair insert of HBV DNA was cleaved with EcoRI and incubated with phage T4 ligase under conditions favoring intramolecular ligation. HeLa cell cultures exposed to this DNA showed marked cytopathic changes, accompanied by production of hepatitis B core and surface antigens, 11-14 days after subculture. Electron microscopic examination of anti-hepatitis B surface antigen immunoprecipitates from culture media of these cells revealed both 42-nm particles with central cores and 20-nm round particles. Although neither intact circular nor EcoRI-cleaved linear pHBV-1 DNAs evoked these effects in HeLa cells, both cytopathic changes and intranuclear hepatitis B core antigen were detected in HeLa cells infected with Dane particles.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier G. L., Williams A. Serotypes of hepatitis B antigen (HBs Ag): the problem of "new" determinants, as exemplified by "t". Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):165–171. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell C. J., Mackay P., Greenaway P. J., Hofschneider P. H., Murray K. Expression in Escherichia coli of hepatitis B virus DNA sequences cloned in plasmid pBR322. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):43–47. doi: 10.1038/279043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
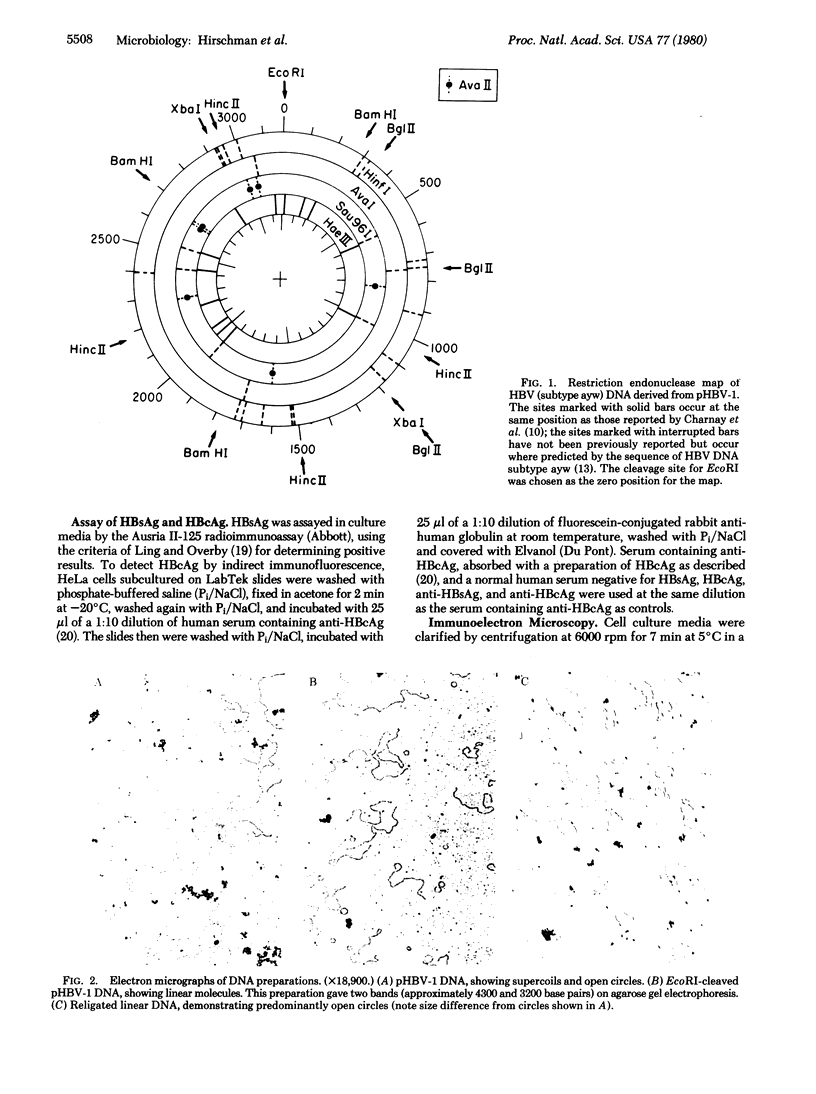
- Charnay P., Pourcel C., Louise A., Fritsch A., Tiollais P. Cloning in Escherichia coli and physical structure of hepatitis B virion DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2222–2226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z., Garfinkel E. Ionic requirements of the DNA polymerase associated with serum hepatitis B antigen. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):897–910. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z., Gerber M., Garfinkel E. Purification of naked intranuclear particles from human liver infected by hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3345–3349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z. The hepatitis B virus and its DNA polymerase: the prototype three-D virus. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Jul 15;26(1):47–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00226820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling C. M., Overby L. R. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus antigen as revealed by direct radioimmune assay with 125 I-antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N. Association of hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg) determinants with the core of Dane particles. J Gen Virol. 1979 Mar;42(3):645–649. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-3-645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. The genome of hepatitis B virus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:357–377. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Siddiqui A., Robinson W. S., Cohen S. N. Cloning and endonuclease mapping of the hepatitis B viral genome. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):346–348. doi: 10.1038/279346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., O'Connell A., Millman I. Genome of hepatitis B virus: restriction enzyme cleavage and structure of DNA extracted from Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Akahane Y., Gotanda T., Mishiro T., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Demonstration of hepatitis B e antigen in the core of Dane particles. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Gray P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Goodman H. M., Rutter W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major protein of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):815–819. doi: 10.1038/280815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Bister K., zur Hausen H. Retinoic acid inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus induction. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):553–554. doi: 10.1038/278553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Tumour promoter TPA enhances transformation of human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):244–245. doi: 10.1038/280244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Bornkamm G. W., Schmidt R., Hecker E. Tumor initiators and promoters in the induction of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):782–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]