Abstract
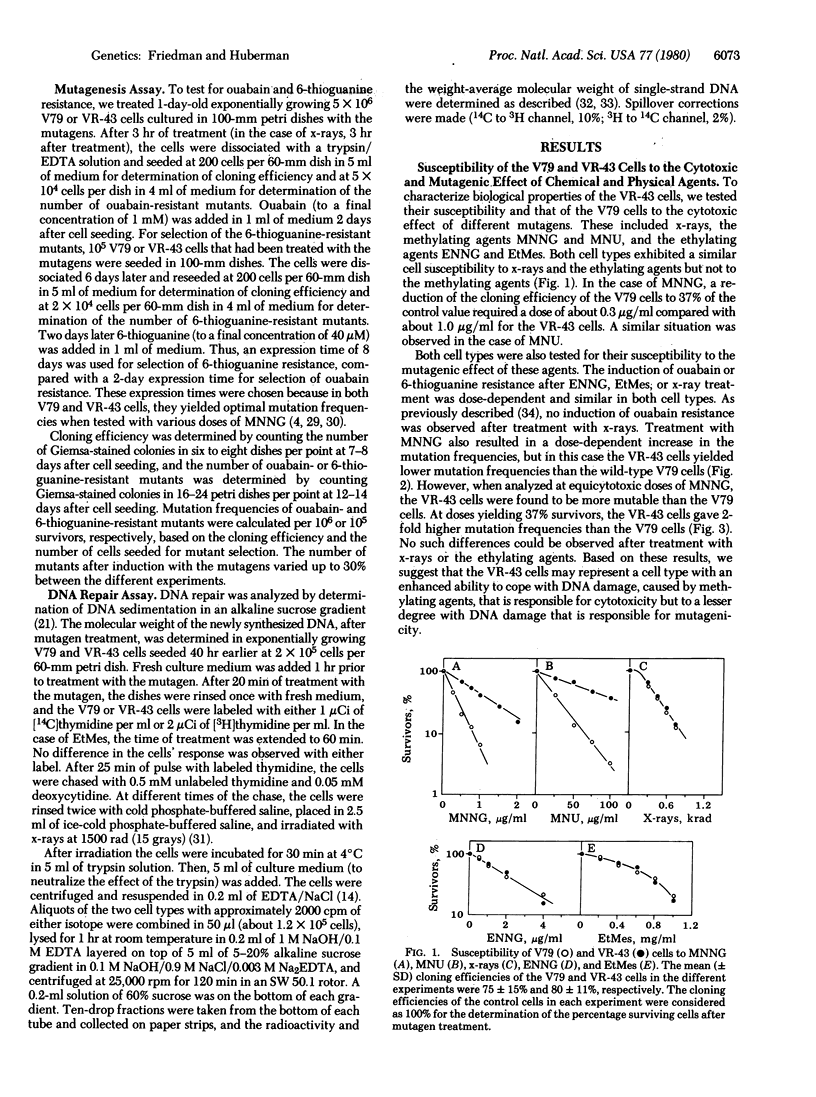
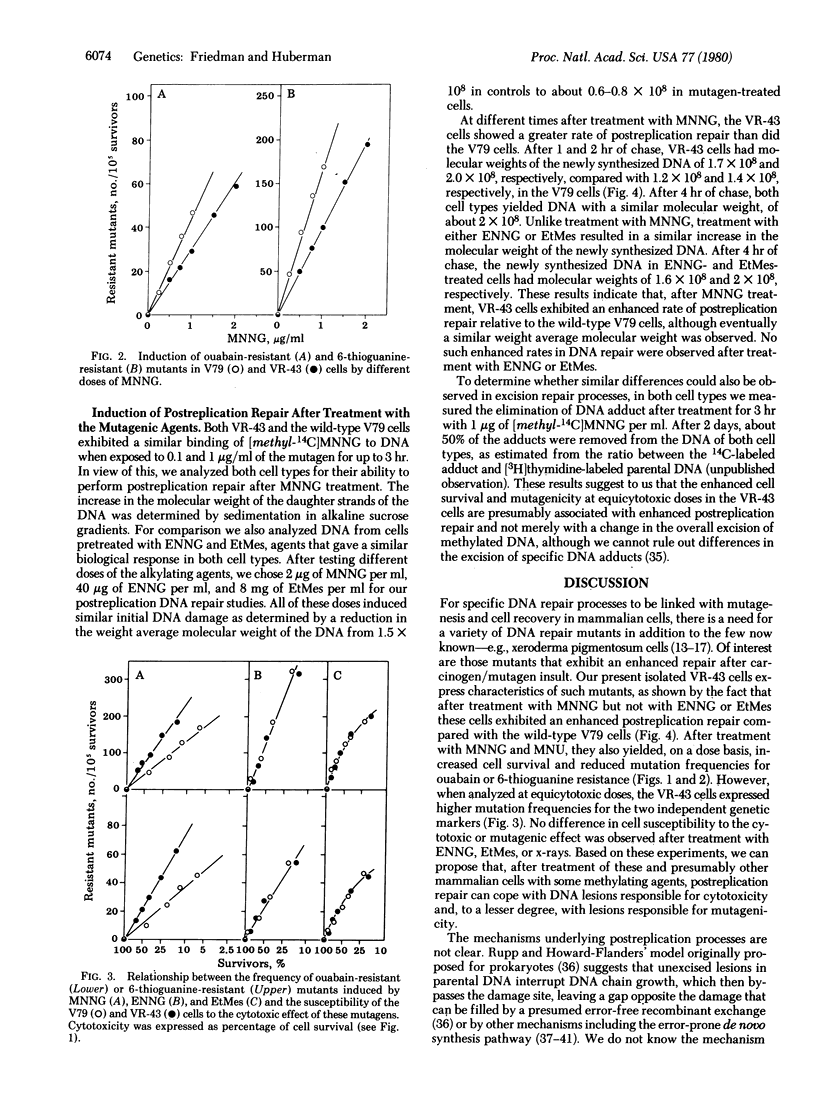
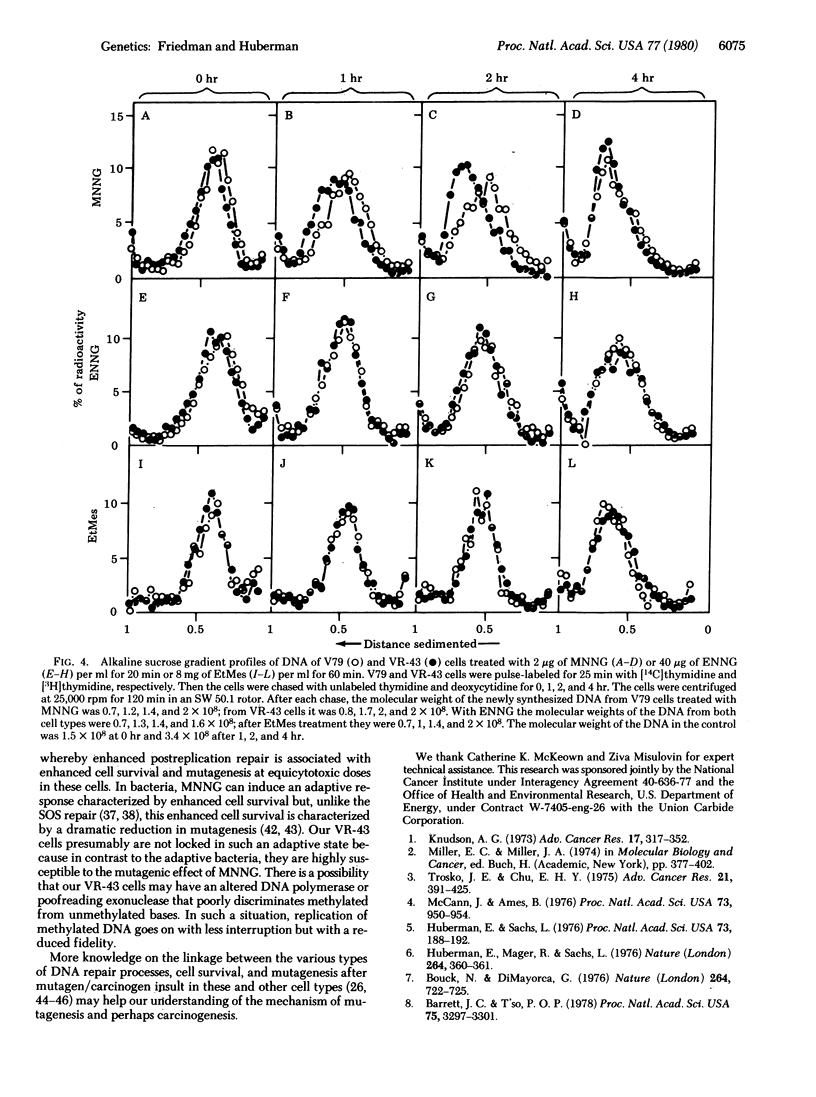
A cell variant (VR-43) resistant to the cytotoxic effect of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine and N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosourea was isolated from Chinese hamster V79 cells for use in studies of the relationship among cell survival, mutagenesis, and DNA repair by alkylating agents. Resistance to ouabain or 6-thioguanine was used as the genetic marker. After treatment with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, the VR-43 cells exhibited mutation frequencies that were lower, on a dose basis, than those of the wild-type V79 cells. However, when analyzed at equicytotoxic doses, the VR-43 cells were more mutable than the V79 cells. No difference in cell survival or mutagenicity could be observed after treatment with other mutagens such as N-ethyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, ethyl methanesulfonate, or x-rays. Postreplication repair was analyzed by determination of the molecular weight of the newly synthesized DNA by alkaline sucrose gradients. After treatment with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, the VR-43 cells exhibited an enhanced postreplication repair relative to the V79 cells. No such enhancement was found after N-ethyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine or ethyl methanesulfonate treatment. Based on these results we propose that, after treatment of these and presumably other mammalian cells with some methylating mutagens, postreplication repair can cope with DNA lesions responsible for cytotoxicity and, to a lesser degree, with lesions responsible for mutagenicity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlett C. F., Turnbull D., Harcourt S. A., Lehmann A. R., Colella C. M. A comparison of the 8-azaguanine and ouabain-resistance systems for the selection of induced mutant Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;33(2-3):261–278. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. M., Van Voorhis W. C., Spencer L. A. HeLa cell variants that differ in sensitivity to monofunctional alkylating agents, with independence of cytotoxic and mutagenic responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5249–5253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. C., Ts'o P. O. Relationship between somatic mutation and neoplastic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3297–3301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck N., di Mayorca G. Somatic mutation as the basis for malignant transformation of BHK cells by chemical carcinogens. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):722–727. doi: 10.1038/264722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Hart R. W. DNA damage and repair in vivo. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1978 Sep-Oct;2(1):79–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier W. L., Setlow R. B. Paper strip method for assaying gradient fractions containing radioactive macromolecules. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Bootsma D. Xeroderma pigmentosum: biochemical and genetic characteristics. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:19–38. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. DNA repair and its coupling to DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 11;516(4):489–516. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Xeroderma pigmentosum: a human disease in which an initial stage of DNA repair is defective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):428–435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio S. M., Setlow R. B. Enhancement of postreplication repair in Chinese hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkind M. M., Kamper C. Two forms of repair of DNA in mammalian cells following irradiation. Biophys J. 1970 Mar;10(3):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86296-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Kato K., Strauss B. A model for replication repair in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Mager R., Sachs L. Mutagenesis and transformation of normal cells by chemical carcinogens. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):360–361. doi: 10.1038/264360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Sachs L. Mutability of different genetic loci in mammalian cells by metabolically activated carcinogenic polycyclic hydrocarbons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P., Defais T. M., Samson L., Schendel P. An adaptive response of E. coli to low levels of alkylating agent: comparison with previously characterised DNA repair pathways. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 29;157(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00268680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. A., Huberman E. A sensitive hepatocyte-mediated assay for the metabolism of nitrosamines to mutagens for mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Feb;40(2):406–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenbach R., Freed H. J., Raveh D., Huberman E. Cell specificity in metabolic activation of aflatoxin B1 and benzo(a)pyrene to mutagens for mammalian cells. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):277–280. doi: 10.1038/276277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher V. M., Dorney D. J., Mendrala A. L., Konze-Thomas B., McCormick J. J. DNA excision-repair processes in human cells can eliminate the cytotoxic and mutagenic consequences of ultraviolet irradiation. Mutat Res. 1979 Sep;62(2):311–323. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher V. M., Ouellette L. M., Curren R. D., McCormick J. J. Frequency of ultraviolet light-induced mutations is higher in xeroderma pigmentosum variant cells than in normal human cells. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):593–595. doi: 10.1038/261593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in the Salmonella/microsome test: assay of 300 chemicals: discussion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano S., Yamagami H., Takaki R. Enhancement of excision-repair efficiency by conditioned medium from density-inhibited cultures in V79 Chinese hamster cells: evidence for excision repair as an error-free repair process. Mutat Res. 1979 Sep;62(2):369–381. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. P., Brimer P. A., Machanoff R., Hirsch G. P., Hsie A. W. A quantitative assay of mutation induction at the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO/HGPRT system): development and definition of the system. Mutat Res. 1977 Oct;45(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(77)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. D., Cleaver J. E. Postreplication repair: questions of its definition and possible alteration in xeroderma pigmentosum cell strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3927–3931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. D., Cleaver J. E. Postreplication repair: questions of its definition and possible alteration in xeroderma pigmentosum cell strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3927–3931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. D., Setlow R. B. Two forms of repair in the DNA of human cells damaged by chemical carcinogens and mutagens. Cancer Res. 1974 Dec;34(12):3318–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. H., Kraemer K. H., Lutzner M. A., Festoff B. W., Coon H. G. Xeroderma pigmentosum. An inherited diseases with sun sensitivity, multiple cutaneous neoplasms, and abnormal DNA repair. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):221–248. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Reno D. L., Howard-Flanders P. Exchanges between DNA strands in ultraviolet-irradiated Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):25–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Cairns J. A new pathway for DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):281–283. doi: 10.1038/267281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Regan J. D., German J., Carrier W. L. Evidence that xeroderma pigmentosum cells do not perform the first step in the repair of ultraviolet damage to their DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1035–1041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B. Repair deficient human disorders and cancer. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):713–717. doi: 10.1038/271713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Shilo B. Z., Goldfarb M. P., Dannenberg A., Weinberg R. A. Passage of phenotypes of chemically transformed cells via transfection of DNA and chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5714–5718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. N-nitroso alkylating agents: formation and persistence of alkyl derivatives in mammalian nucleic acids as contributing factors in carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jun;62(6):1329–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Rubin J. S., Cleaver J. E., Whitmore G. F., Brookman K. A screening method for isolating DNA repair-deficient mutants of CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 May;6(3):391–405. doi: 10.1007/BF01542791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompa A., Langenbach R. Culture of adult rat lung cells: benzo(a)pyrene metabolism and mutagenesis. In Vitro. 1979 Aug;15(8):569–578. doi: 10.1007/BF02623392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trosko J. E., Chu E. H. The role of DNA repair and somatic mutation in carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1975;21:391–425. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeeland A. A., Simons J. W. The effect of calf serum on the toxicity of 8-azaguanine. Mutat Res. 1975 Jan;27(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


