Abstract
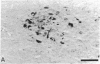
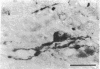
Immunochemical and immunocytochemical techniques have been used to identify and characterize glucagon-related peptides of the rat central nervous system. These peptides show immunoreactivity with antiglucagon sera directed towards the central portion of the hormone, but not with antisera specific for the free COOH terminus of glucagon. Highest concentrations were found in hypothalamus (6.1 +/- 1.6 ng/g wet weight) although lower amounts (approximately 2 ng/g) were found in cortex, thalamus, cerebellum, and brain stem. Gel filtration of brain extracts revealed at least two immunoreactive forms, which have molecular weights of about 12,000 and 8000. Both peptides had radioimmunoassay dilution curves parallel to the curve for glucagon and both had identical counterparts in extracts of rat intestine. Digestion of the brain and intestinal peptides with trypsin plus carboxypeptidase B released the immunoreactive COOH-terminal tryptic fragment of pancreatic glucagon from these larger forms. Immunocytochemical studies using antiglucagon serum and peroxidase-antiperoxidase staining identified glucagon-like material in neuronal cell bodie and processes in the magnocellular portion of the paraventricular nucleus, as well as in scattered cells in the supraoptic nucleus and in fibers in the median eminence. These results suggest that glucagon-containing peptides that have undergone the intestinal type of posttranslational modification are present in neuronal cells of the rat hypothalamus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conlon J. M., Samson W. K., Dobbs R. E., Orci L., Unger R. H. Glucagon-like polypeptides in canine brain. Diabetes. 1979 Jul;28(7):700–702. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.7.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J. Immunochemical evidence of cholecystokinin-like peptides in brain. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):568–570. doi: 10.1038/264568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. P. Immunoreactive somatostatin is present in discrete cells of the endocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1340–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Schmechel D., Roth J., Brownstein M. Identification of insulin in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5737–5741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa I., Jessell T. Post mortem changes and regional distribution of substance P in the rat and mouse nervous system. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 26;117(2):362–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer K. J., Speirs R. D., Childs C. N. Immunochemical evidence for a gastrin-like peptide in insect neuroendocrine system. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1977 Aug;32(4):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(77)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky De Muckadell O., Sundler F., Håkanson R., Rehfeld J. R. Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to central and peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3197–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorén I., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F., Thorell J. Gut-type glucagon immunoreactivity in nerves of the rat brain. Histochemistry. 1979 Jul 11;61(3):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00508455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino E., Lernmark A., Seo H., Steiner D. F., Refetoff S. High concentration of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4265–4267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller J. E., Straus E., Yalow R. S. Cholecystokinin and its COOH-terminal octapeptide in the pig brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3035–3037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S., Takahashi T. Hypothalamic substance P as a candidate for transmitter of primary afferent neurons. Fed Proc. 1975 Sep;34(10):1922–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt C., Tager H. S., Carroll R. J., Steiner D. F. Identification and processing of proglucagon in pancreatic islets. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):260–266. doi: 10.1038/282260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt C., Tager H. S., Carroll R. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of prosomatostatin in pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2410–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Siperstein A., Moody A. J., Sundby F., Jacobsen H., Orci L. Glicentin immunoreactive cells: their relationship to glucagon-producing cells. Endocrinology. 1979 Aug;105(2):499–508. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-2-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F. Immunochemical studies on cholecystokinin. II. Distribution and molecular heterogeneity in the central nervous system and small intestine of man and hog. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4022–4030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Rosenberg R. N. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science. 1976 May 28;192(4242):907–908. doi: 10.1126/science.1273576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikant C. B., McCorkle K., Unger R. H. Properties of immunoreactive glucagon fractions of canine stomach and pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1847–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundby F., Jacobsen H., Moody A. J. Purification and characterization of a protein from porcine gut with glucagon-like immunoreactivity. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Sep;8(5):366–371. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Hohenboken M., Markese J. High titer glucagon antisera. Endocrinology. 1977 Feb;100(2):367–372. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Markese J. Intestinal and pancreatic glucagon-like peptides. Evidence for identity of higher molecular weight forms. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2229–2233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Markese J., Kramer K. J., Speirs R. D., Childs C. N. Glucagon-like and insulin-like hormones of the insect neurosecretory system. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):515–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1560515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Markese J., Spiers R. D., Kramer K. J. Glucagon-like immunoreactivity in insect corpus cardiacum. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):707–708. doi: 10.1038/254707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Patzelt C., Assoian R. K., Chan S. J., Duguid J. R., Steiner D. F. Biosynthesis of islet cell hormones. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:133–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Steiner D. F. Isolation of a glucagon-containing peptide: primary structure of a possible fragment of proglucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2321–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Rigopoulou D., Marco J., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. Characterization of glucagon-like immunoreactivity (GLI). Diabetes. 1970 Sep;19(9):614–623. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.9.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]