Abstract
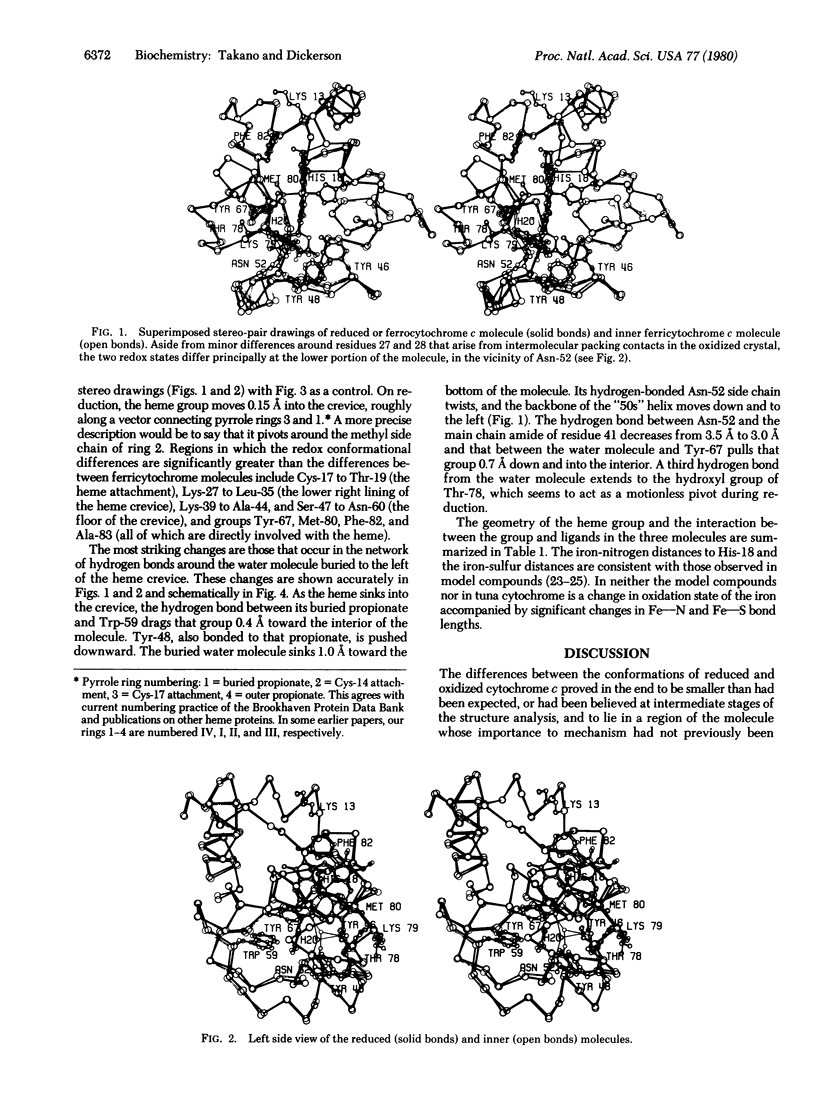
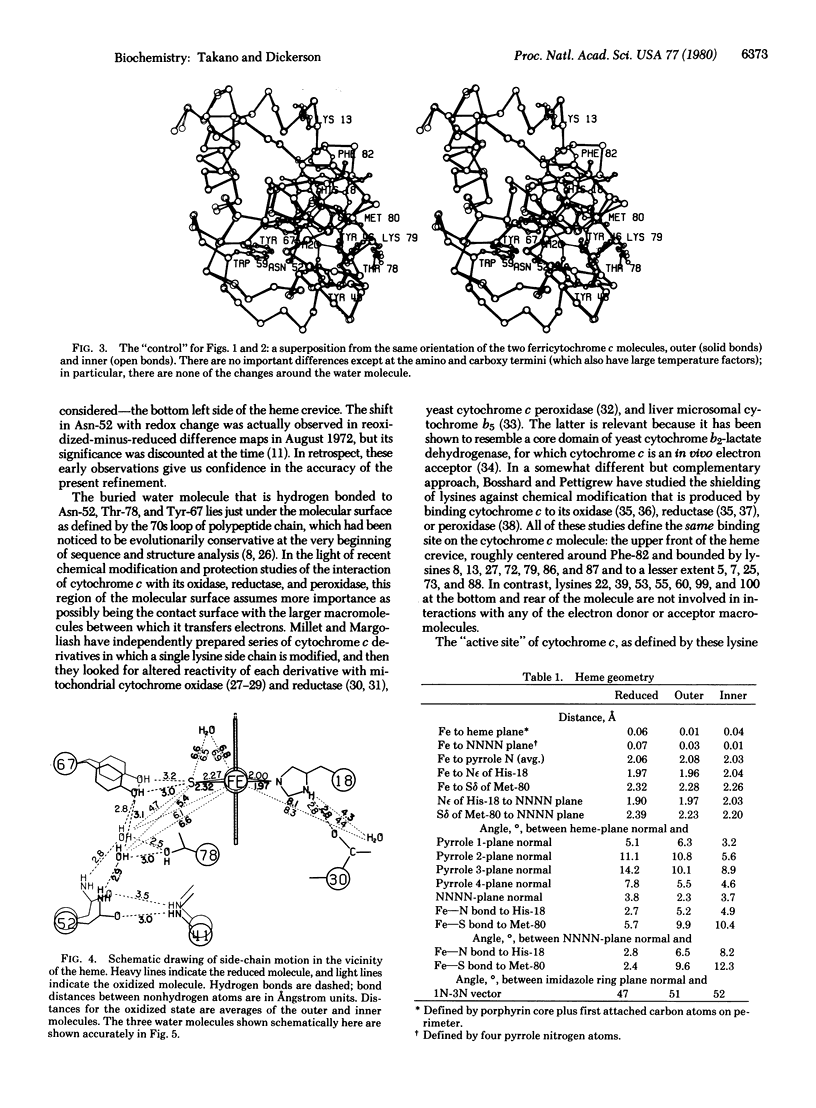
Tuna ferrocytochrome c and ferricytochrome c have been refined independently at high resolution (1.5 A and 1.8 A) to crystallographic residual errors of 17.3% and 20.8%, respectively. Small but significant conformational differences are seen surrounding a buried water molecule that is hydrogen bonded to Asn-52, Tyr-67, and Thr-78. In the oxidized state, this water molecule is 1.0 A closer to the heme and the heme has moved 0.15 A out of its heme crevice; both changes lead to a more polar microenvironment for the heme. Chemical modification studies, patterns of evolutionary conservatism, structural differences in bacterial cytochromes, and x-ray studies all agree that the "active site" for cytochrome c is bounded by lysines 8, 13,27, 72, 79, 86, and 87 (thus containing the evolutionary conservative 72-87 loop) and has the buried water molecule just below its surface and the opening of the heme crevice slightly to one side.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A. J., Smith H. T., Smith M. B., Millett F. S. Effect of specific lysine modification on the reduction of cytochrome c by succinate-cytochrome c reductase. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2479–2483. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashida T., Tanaka N., Yamane T., Tsukihara T., Kakudo M. The crystal structure of bonito (Katsuo) ferrocytochrome c at 2.3 A resolution. J Biochem. 1973 Feb;73(2):463–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashida T., Ueki T., Tsukihara T., Sugihara A., Takano T. The crystal structure of Donito (Katsuo) ferrocytochrome c at 4A resolution. J Biochem. 1971 Dec;70(6):913–924. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosshard H. R., Zürrer M., Schägger H., von Jagow G. Binding of cytochrome c to the cytochrome bc1 complex (complex III) and its subunits cytochrome c1 and b1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):250–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90971-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Countryman R., Hoard J. L. Stereochemistry of low-spin iron porphyrins. I. Bis(imidazole)- , , , -tetraphenylporphinatoiron(3) chloride. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Mar 22;94(6):2066–2072. doi: 10.1021/ja00761a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. Real-space refinement of the structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):371–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Cytochrome c and the evolution of energy metabolism. Sci Am. 1980 Mar;242(3):137–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Evolution and gene transfer in purple photosynthetic bacteria. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):210–212. doi: 10.1038/283210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Kopka M. L., Weinzierl J., Varnum J., Eisenberg D., Margoliash E. Location of the heme in horse heart ferricytochrome c by x-ray diffraction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):3015–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Takano T., Eisenberg D., Kallai O. B., Samson L., Cooper A., Margoliash E. Ferricytochrome c. I. General features of the horse and bonito proteins at 2.8 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1511–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Miller S., Brautigan D. L., Margoliash E. Definition of cytochrome c binding domains by chemical modification. III. Kinetics of reaction of carboxydinitrophenyl cytochromes c with cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiard B., Groudinsky O., Lederer F. Homology between bakers' yeast cytochrome b2 and liver microsomal cytochrome b5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2539–2543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R. R., Taniuchi H. Conformational dynamics in cytochrome c. A fragment exchange study. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5373–5380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R. R., Taniuchi H. Formation of a biologically active, ordered complex from two overlapping fragments of cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1367–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juillerat M., Parr G. R., Taniuchi H. A biologically active, three-fragment complex of horse heart cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):845–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. H., Brautigan D. L., Osheroff N., Margoliash E. Definitaion of cytochrome c binding domains by chemical modification. Reaction of carboxydinitrophenyl- and trinitrophenyl-cytochromes c with baker's yeast cytochrome c peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6502–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E. PRIMARY STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION OF CYTOCHROME C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:672–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel N., Mandel G., Trus B. L., Rosenberg J., Carlson G., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. III. Coordinate optimization and comparison of structures. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4619–4636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margoliash E., Schejter A. Cytochrome c. Adv Protein Chem. 1966;21:113–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Hata Y., Yamaguchi T., Tanaka N., Kakudo M. Structure of bonito heart ferricytochrome c and some remarks on molecular interaction in its crystalline state. J Biochem. 1979 Mar;85(3):729–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan E. B., Stellwagen E. Reactivity of individual tyrosyl residues of horse heart ferricytochrome c toward iodination. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 21;9(15):3047–3053. doi: 10.1021/bi00817a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn C. A. Further observations on Myohaematin and the Histohaematins. J Physiol. 1887 Jun;8(2):51–116.1. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1887.sp000243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S., Smith M. B., Smith H. T., Millett F. Effect of modification of individual cytochrome c lysines on the reaction with cytochrome b5. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4975–4978. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr G. R., Hantgan R. R., Taniuchi H. Formation of two alternative complementing structures from cytochrome c heme fragment (residue 1 to 38) and the apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5381–5388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew G. Mapping an electron transfer site on cytochrome c. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):14–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R., Bosshard H. R. Cytochrome bc1 and cytochrome oxidase can bind to the same surface domain of the cytochrome c molecule. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80759-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R., Bosshard H. R. The cytochrome c oxidase binding site on cytochrome c. Differential chemical modification of lysine residues in free and oxidase-bound cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6045–6053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter A., Aviram I., Sokolovsky M. Nitrocytochrome c. II. Spectroscopic properties and chemical reactivity. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5118–5122. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. T., Staudenmayer N., Millett F. Use of specific lysine modifications to locate the reaction site of cytochrome c with cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4971–4974. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M., Aviram I., Schejter A. Nitrocytochrome c. I. Structure and enzymic properties. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5113–5118. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Ferguson-Miller S., Osheroff N., Margoliash E. Definition of cytochrome c binding domains by chemical modification: kinetics of reaction with beef mitochondrial reductase and functional organization of the respiratory chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenmayer N., Ng S., Smith M. B., Millett F. Effect of specific trifluoroacetylation of individual cytochrome c lysines on the reaction with cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):600–604. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R., Trus B. L., Mandel N., Mandel G., Kallai O. B., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. I. Ferricytochrome structure analysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):759–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Kallai O. B., Swanson R., Dickerson R. E. The structure of ferrocytochrome c at 2.45 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5234–5255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Trus B. L., Mandel N., Mandel G., Kallai O. B., Swanson R., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. II. Ferrocytochrome structure analysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):776–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Yamane T., Tsukihara T., Ashida T., Kakudo M. The crystal structure of bonito (katsuo) ferrocytochrome c at 2.3 A resolution. II. Structure and function. J Biochem. 1975 Jan 1;77(1?):147–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T., RAY G. S. STUDIES ON CYTOCHROME OXIDASE. VI. KINETICS OF THE AEROBIC OXIDATION OF FERROCYTOCHROME C BY CYTOCHROME OXIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3392–3398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


