Abstract
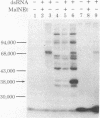
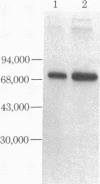
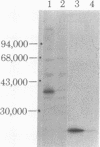
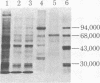
The double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-activated protein kinase (DAI) that phosphorylates the alpha subunit of the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibits chain initiation has been isolated from rabbit reticulocyte lysates. The nonactivated enzyme or the enzyme partially activated by incubation with low levels of dsRNA (pro-DAI) could be purified only to a slight extent. However, the enzyme that was fully activated by incubation with both dsRNA and ATP was purified to near homogeneity. Active DAI is a phosphoprotein with an apparent subunit mass of 68,000 daltons. It can phosphorylate histone as well as the alpha subunit of eIF-2. Our results suggest that, after interaction with dsRNA, the enzyme phosphorylates itself and is thereby activated to phosphorylate alpha eIF-2 and histone.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benne R., Edman J., Traut R. R., Hershey J. W. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):108–112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Ralston R. O., Grace M., Roy R., Ghosh-Dastidar P., Das H. K., Yaghmai B., Palmieri S., Gupta N. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes: mechanism of protein synthesis inhibition by heme-regulated inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5076–5079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., Leroux A., London I. M. Site-specific phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2 by the heme-regulated and double-stranded RNA-activated eIF-2 alpha kinases from rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., London I. M. In situ phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 in reticulocyte lysates inhibited by heme deficiency, double-stranded RNA, oxidized glutathione, or the heme-regulated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2118–2122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. Analysis of phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):517–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Mendelewski J. Additional evidence that the hemin-controlled translational repressor from rabbit reticulocytes is a protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Rabinovitz M. Control of globin synthesis by hemin: factors influencing formation of an inhibitor of globin chain initiation in reticulocyte lysates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E. pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: an inhibitor of protein synthesis synthesized with an enzyme fraction from interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Zilberstein A., Schmidt A., Shulman L., Revel M. The interferon-induced protein kinase PK-i from mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9846–9853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Cimadevilla J. M., Hardesty B. Specificity of the protein kinase activity associated with the hemin-controlled repressor of rabbit reticulocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J. R., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA and phosphorylation of initiation factor, eIF-2. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4219–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Characterization of double-stranded-RNA-activated kinase that phosphorylates alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):832–836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis: activation by double-stranded RNA of a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1121–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., Ranu R. S., Ernst V., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates: phosphorylation of methionyl-tRNAf binding factor by protein kinase activity of translational inhibitor isolated from hemedeficient lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3112–3116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Levin D. H., London I. M. Purification and characterization of a latent precursor of a double-stranded RNA dependent protein kinase from reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1190–1198. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: additional initiation factor required for formation of ternary complex (eIF-2.GTP.Met-tRNAf) and demonstration of inhibitory effect of heme-regulated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1079–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Taira H., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Characteristics of a double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase system partially purified from interferon treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. C., 3rd, Merril C. R., Shifrin S. A highly sensitive silver stain for detecting proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90732-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Traugh J. A., Sharp S. B., Lundak T. S., Safer B., Merrick W. C. Effect of hemin on site-specific phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):789–793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and characterization of heme-reversible translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3654–3658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haro C., Ochoa S. Further studies on the mode of action of the heme-controlled translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1741–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haro C., Ochoa S. Further studies on the mode of action of the heme-controlled translational inhibitor: stimulating protein acts at level of binary complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2163–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haro C., Ochoa S. Mode of action of the hemin-controlled inhibitor of protein synthesis: studies with factors from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2713–2716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]