Abstract
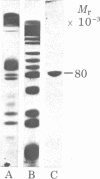
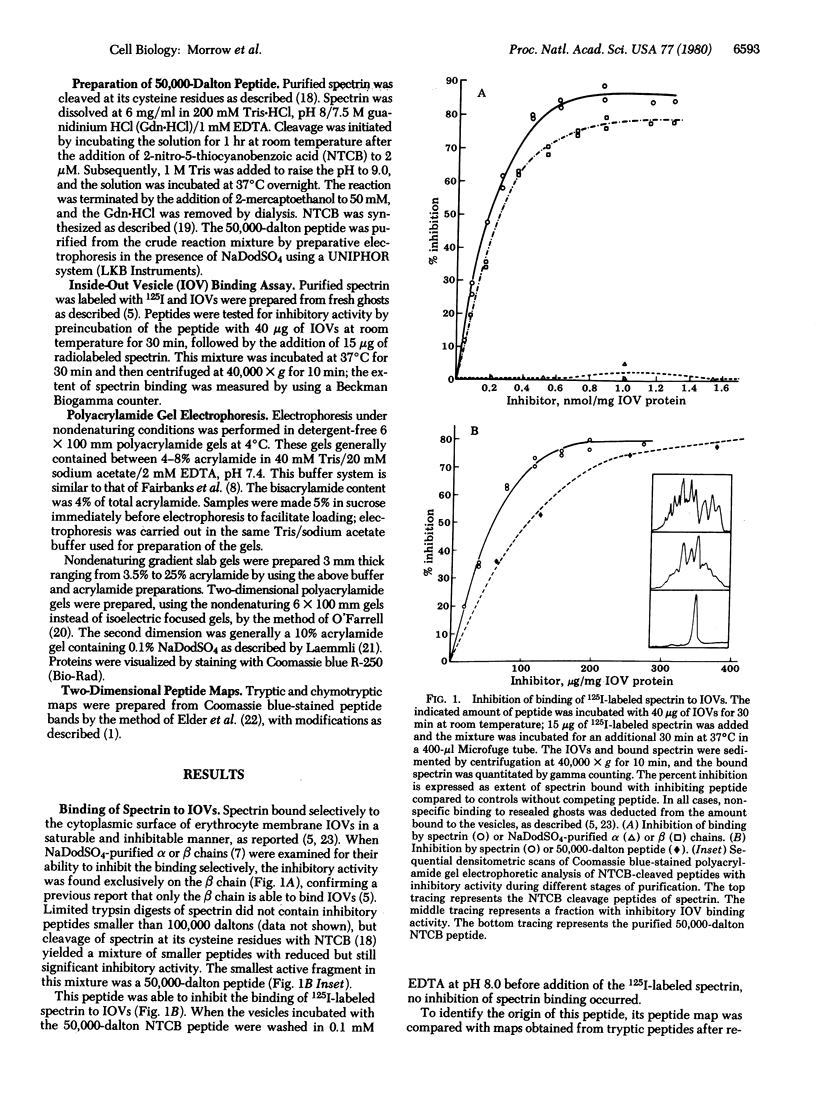
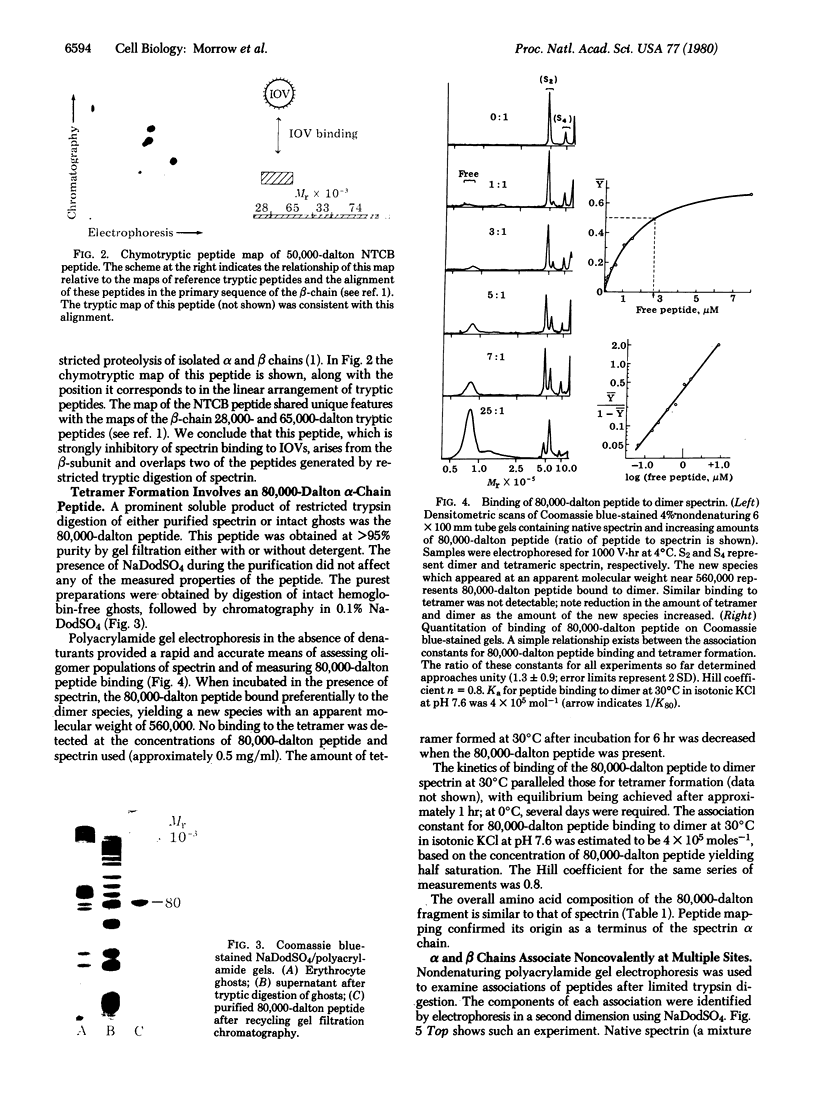
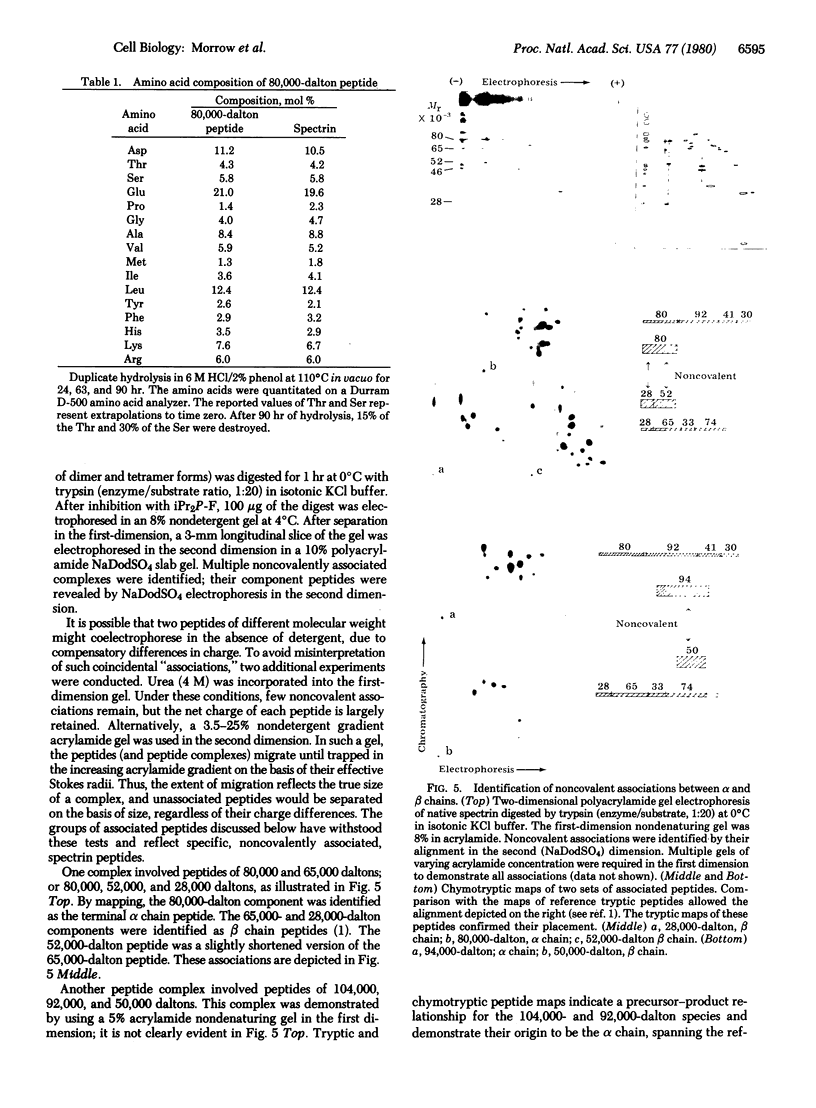
Isolated human erythrocyte spectrin is a dimer of two unique polypeptide chains. The dimer (alpha beta) undergoes reversible salt- and temperature-dependent association to form (alpha beta)2 tetramers. Spectrin also binds with high affinity to a protein receptor on the cytoplasmic surface of erythrocyte membrane vesicles. By cleavage of spectrin at its cysteine residues with 2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid, a 50,000-dalton peptide fragment has been isolated which inhibits the binding of spectrin to erythrocyte membrane vesicles. This peptide arises from a terminal region of the beta chain. An 80,000-dalton peptide generated by restricted trypsin digestion binds preferentially to dimeric spectrin. This peptide arises from a terminal portion of the alpha chain. Multiple peptides involved in noncovalent associations between the chains have also been identified. These associations indicate that the two subunits of spectrin are aligned parallel to one another and that the tetramer formation site and the high-affinity membrane binding site are in close proximity to one another.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M. Structural studies on human spectrin. Comparison of subunits and fragmentation of native spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):939–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Branton D. Selective association of spectrin with the cytoplasmic surface of human erythrocyte plasma membranes. Quantitative determination with purified (32P)spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2753–2763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Identification and partial purification of ankyrin, the high affinity membrane attachment site for human erythrocyte spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2533–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. Spectrin-actin interaction. Phosphorylated and dephosphorylated spectrin tetramer cross-link F-actin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8620–8627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M., Branton D. The role of spectrin in erythrocyte membrane-stimulated actin polymerisation. Nature. 1979 May 10;279(5709):163–165. doi: 10.1038/279163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Lemay A. Specific fragmentation of human erythrocyte spectrin by chemical cleavage at cysteine residues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 25;577(2):360–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner K., Bisswanger H. Multifunctional proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:143–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman D., Hsu D. J., Marchesi V. T. Evidence that spectrin binds to macromolecular complexes on the inner surface of the red cell membrane. J Cell Sci. 1980 Apr;42:1–22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.42.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Kidd G. H., Branton D. Identification by peptide analysis of the spectrin-binding protein in human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2526–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E. Spectrin-actin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal red blood cells. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jan;16(1):21–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Steers E., Jr Selective solubilization of a protein component of the red cell membrane. Science. 1968 Jan 12;159(3811):203–204. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3811.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen A., Elgsaeter A. Human spectrin. II. An electro-optic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 26;536(1):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston G., Dunbar J., White M. The temperature-dependent dissociation of spectrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Sharp M., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Erythrocyte spectrin. Purification in deoxycholate and preliminary characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1897–1904. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Morrow J. S., Knowles W. J., Marchesi V. T. Identification of proteolytically resistant domains of human erythrocyte spectrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Fairbanks G., Wallach D. F. Disposition of the major proteins in the isolated erythrocyte membrane. Proteolytic dissection. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2617–2624. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Hargreaves W. R., Branton D. Purification of two spectrin-binding proteins: biochemical and electron microscopic evidence for site-specific reassociation between spectrin and bands 2.1 and 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungewickell E., Bennett P. M., Calvert R., Ohanian V., Gratzer W. B. In vitro formation of a complex between cytoskeletal proteins of the human erythrocyte. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):811–814. doi: 10.1038/280811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungewickell E., Gratzer W. Self-association of human spectrin. A thermodynamic and kinetic study. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziparo E., Lemay A., Marchesi V. T. The distribution of spectrin along the membranes of normal and echinocytic human erythrocytes. J Cell Sci. 1978 Dec;34:91–101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.34.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]