Abstract
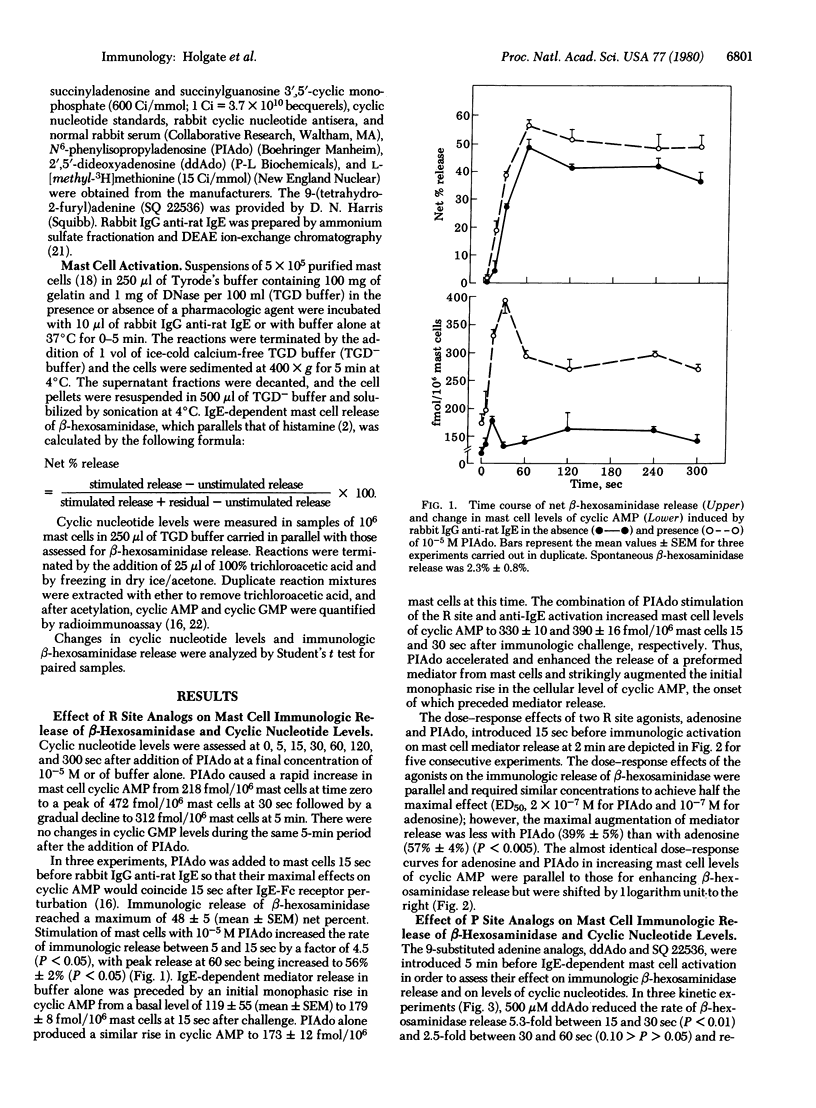
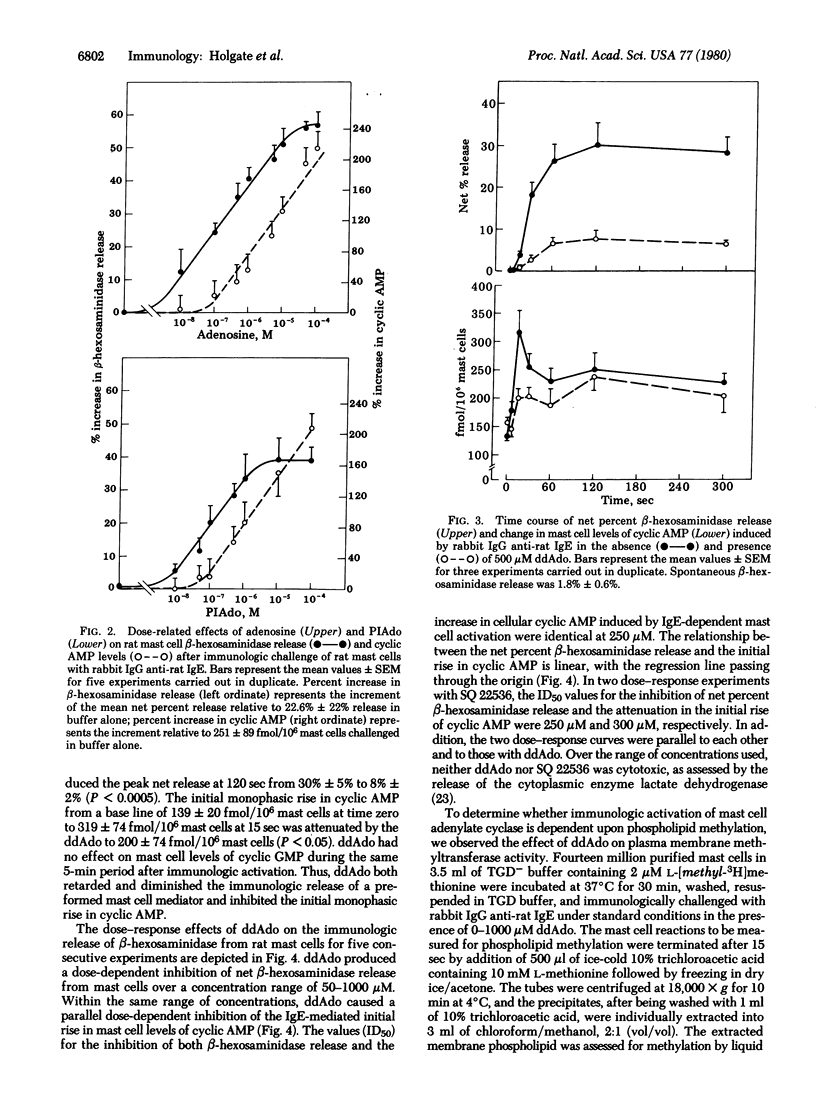
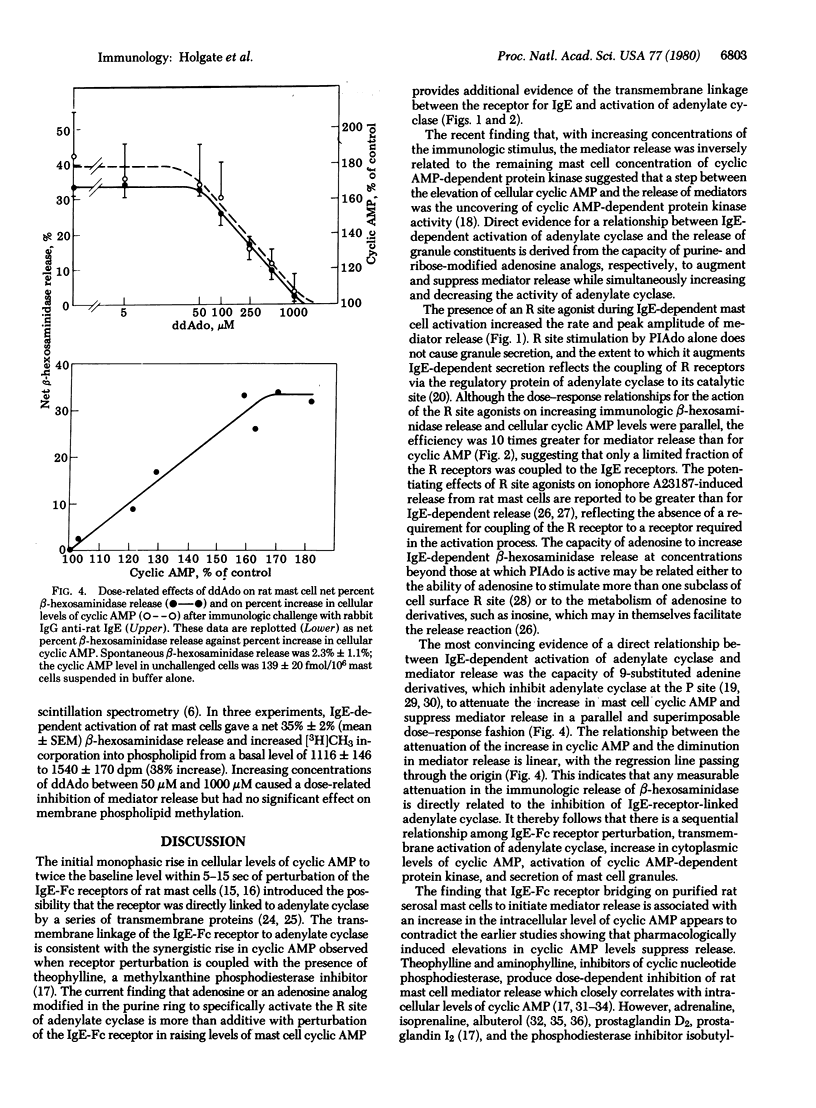
The initial monophasic rise in cyclic AMP beginning 5-15 sec after bridging of rat mast cell IgE-Fc receptors precedes the secretion of granule constituents, thereby implying a causal relationship. Direct evidence for a relationship between IgE-dependent transmembrane activation of adenylate cyclase and granule secretion was provided by the capacity of purine-modified (R site active) and ribose-modified (P site active) adenosine analogs, respectively, to augment and suppress mediator release while simultaneously increasing and decreasing the activity of adenylate cyclase. R site stimulation alone does not cause granule secretion but augments the rate and magnitude of IgE-Fc receptor-induced secretion, reflecting the coupled relationship of such receptors. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase at the P site attenuates the rise in cellular cyclic AMP and suppresses IgE-dependent mediator release in a parallel and superimposable dose-response fashion. Further, the relationship between the attenuation in the rise in cyclic AMP and the diminution in immunologic mediator release is linear with the regression line passing through the origin, indicating a direct relationship between the IgE-dependent activation of adenylate cyclase and preformed mediator release. Although not the only events in coupled mast cell activation--secretion, there is a sequential relationship among perturbation of IgE-Fc receptors, transmembrane activation of adenylate cyclase, elevation of cytoplasmic levels of cyclic AMP, activation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, and secretion of mast cell granules.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMADOR E., DORFMAN L. E., WACKER W. E. SERUM LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY: AN ANALYTICAL ASSESSMENT OF CURRENT ASSAYS. Clin Chem. 1963 Aug;12:391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Austen K. F. Mechanisms of immunologic injury of rat peritoneal mast cells. I. The effect of phosphonate inhibitors on the homocytotropic antibody-mediated histamine release and the first component of rat complement. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):379–395. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Henson P. M. In vitro studies of immunologically induced secretion of mediators from cells and related phenomena. Adv Immunol. 1973;17:93–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60732-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butchers P. R., Fullarton J. R., Skidmore I. F., Thompson L. E., Vardey C. J., Wheeldon A. A comparison of the anti-anaphylactic activities of salbutamol and disodium cromoglycate in the rat, the rat mast cell and in human lung tissue. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;67(1):23–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Lewis R. A., Hein A., Austen K. F. Secretion in dissociated human pulmonary mast cells. Evidence for solubilization of granule contents before discharge. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):299–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty N., Echetebu Z. Plasma membrane adenosine triphosphatases in rat peritoneal mast cells and macrophages--the relation of the mast cell enzyme to histamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(11):1561–1569. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90486-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant B. Energy production in rat mast cells and its role for histamine release. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(1-2):155–171. doi: 10.1159/000231391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Malbon C. C. Regulation of adenylate cyclase by adenosine. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Jun 15;25(3):143–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00235364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C., Hallett M. B., Mongar J. L. The relationship between histamine secretion and 45calcium uptake by mast cells. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):193–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Guschin I., Elwin K., Schwab G., Uvnäs B. Cyclic AMP independent inhibition by papaverine of histamine release induced by compound 48/80. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Jul 15;25(14):1583–1588. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. N., Asaad M. M., Phillips M. B., Goldenberg H. J., Antonaccio M. J. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase in human blood platelets by 9-substituted adenine derivatives. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;5(2):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M., Desjardins J. V. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase by adenosine analogues in preparations of broken and intact human platelets. Evidence for the unidirectional control of platelet function by cyclic AMP. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):83–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1760083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. T., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. 3',5'-Cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of the rat serosal mast cell and its immunologic activation. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2093–2099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. T., Lewis R. A., Maguire J. F., Roberts L. J., 2nd, Oates J. A., Austen K. F. Effects of prostaglandin D2 on rat serosal mast cells: discordance between immunologic mediator release and cyclic AMP levels. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1367–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Hirata F., Ishizaka K., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipid methylation, Ca2+ influx, and histamine release by bridging of IgE receptors on rat mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1903–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Moran N. C., Mayer S. E. Cyclic AMP content and histamine release in rat mast cells. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):511–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliner M., Austen K. F. Cyclic AMP, ATP, and reversed anaphylactic histamine release from rat mast cells. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):664–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff D. Membrane fusion during mast cell secretion. J Cell Biol. 1973 Apr;57(1):252–259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D., Raff M. C., Gomperts B., Fewtrell C., Gilula N. B. Molecular events during membrane fusion. A study of exocytosis in rat peritoneal mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):242–259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Holgate S. T., Roberts L. J., 2nd, Maguire J. F., Oates J. A., Austen K. F. Effects of indomethacin on cyclic nucleotide levels and histamine release from rat serosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1663–1668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Wolff J. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt D. L., Parker C. W., Sullivan T. J. Potentiation of mast cell mediator release by adenosine. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):871–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn S., Geisler A., Skov P. S., Klysner R. Differentiation between cyclic AMP level and allergic histamine release in mast cells [proceedings]. Agents Actions. 1979 Apr;9(1):64–65. doi: 10.1007/BF02024115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn S., Geisler A., Stahl Skov P., Klysner R. Cyclic AMP and allergic histamine release. Influence of methylxanthines on rat mast cells. Acta Allergol. 1977 Jun;32(3):183–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1977.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Resolution of some components of adenylate cyclase necessary for catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):6966–6969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Howlett A. C., Ferguson K. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity with resolved components of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6401–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhlich P. Membrane-associated actin filaments in the cortical cytoplasm of the rat mast cell. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Jul;93(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90453-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Austen K. F., Wasserman S. I. Immunologic release of beta-hexosaminidase and beta-glucuronidase from purified rat serosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1445–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W., Theoharides T. C., Alper S. L., Douglas W. W., Greengard P. Calcium-dependent protein phosphorylation during secretion by exocytosis in the mast cell. Nature. 1978 Sep 28;275(5678):329–331. doi: 10.1038/275329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaga T. J., Klein-Szanto A. J., Fischer S. M., Weeks C. E., Nelson K., Major S. Studies on mechanism of action of anti-tumor-promoting agents: their specificity in two-stage promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2251–2254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan T. J., Parker K. L., Eisen S. A., Parker C. W. Modulation of cyclic AMP in purified rat mast cells. II. Studies on the relationship between intracellular cyclic AMP concentrations and histamine release. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1480–1485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan T. J., Parker K. L., Kulczycki A., Jr, Parker C. W. Modulation of cyclic AMP in purified rat mast cells. III. Studies on the effects of concanavalin A and anti-IgE on cyclic AMP concentrations during histamine release. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):713–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welton A. F., Simko B. A. Regulatory role of adenosine in antigen-induced histamine release from the lung tissue of actively sensitized guinea pigs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Apr 15;29(8):1085–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


