Abstract
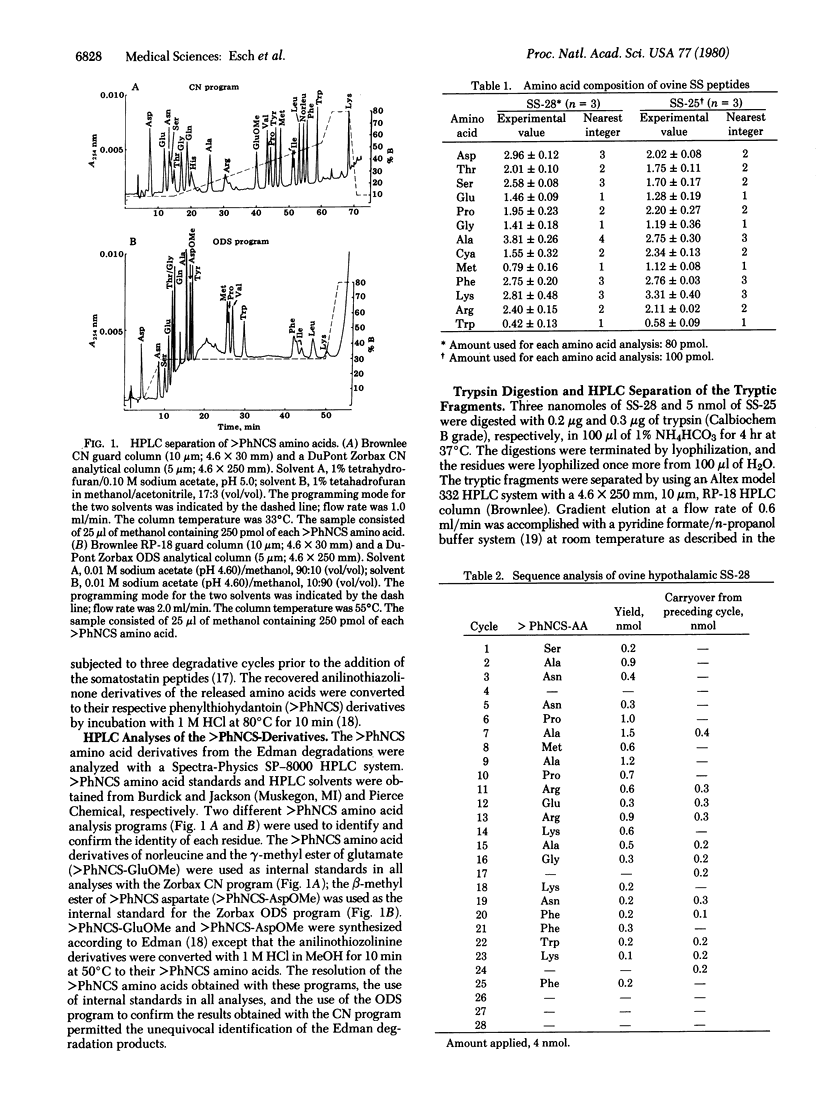
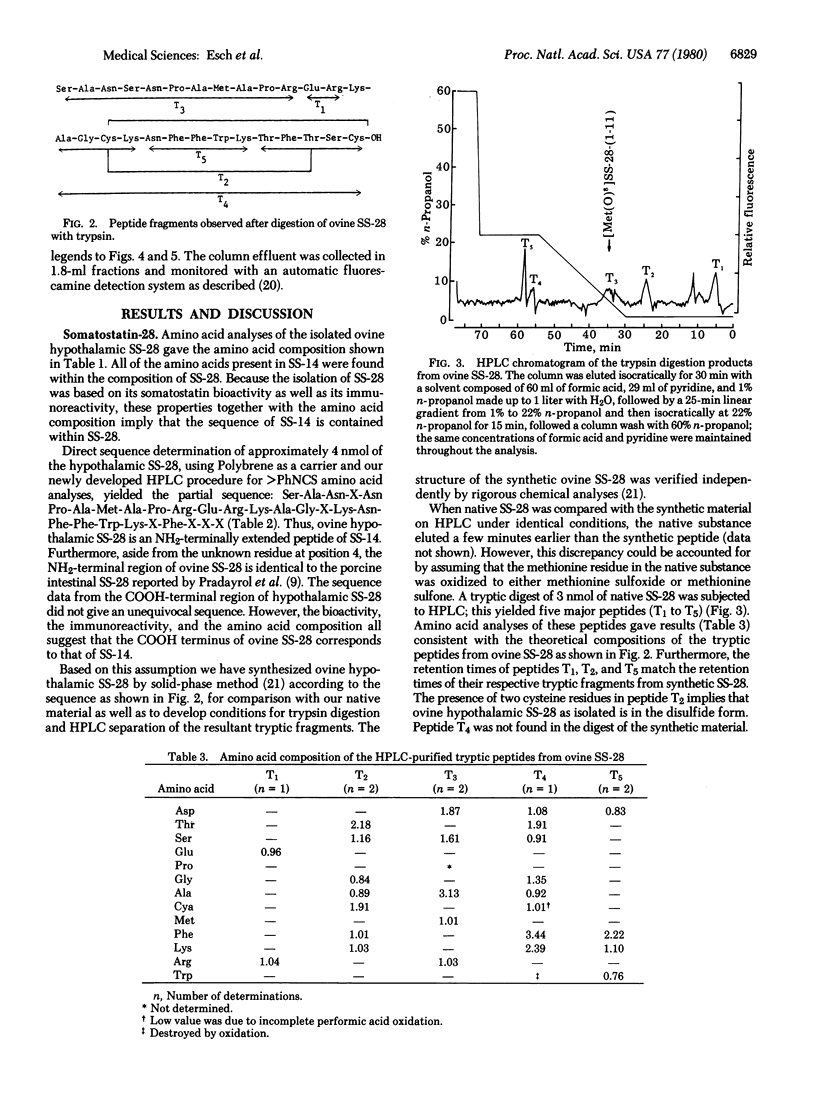
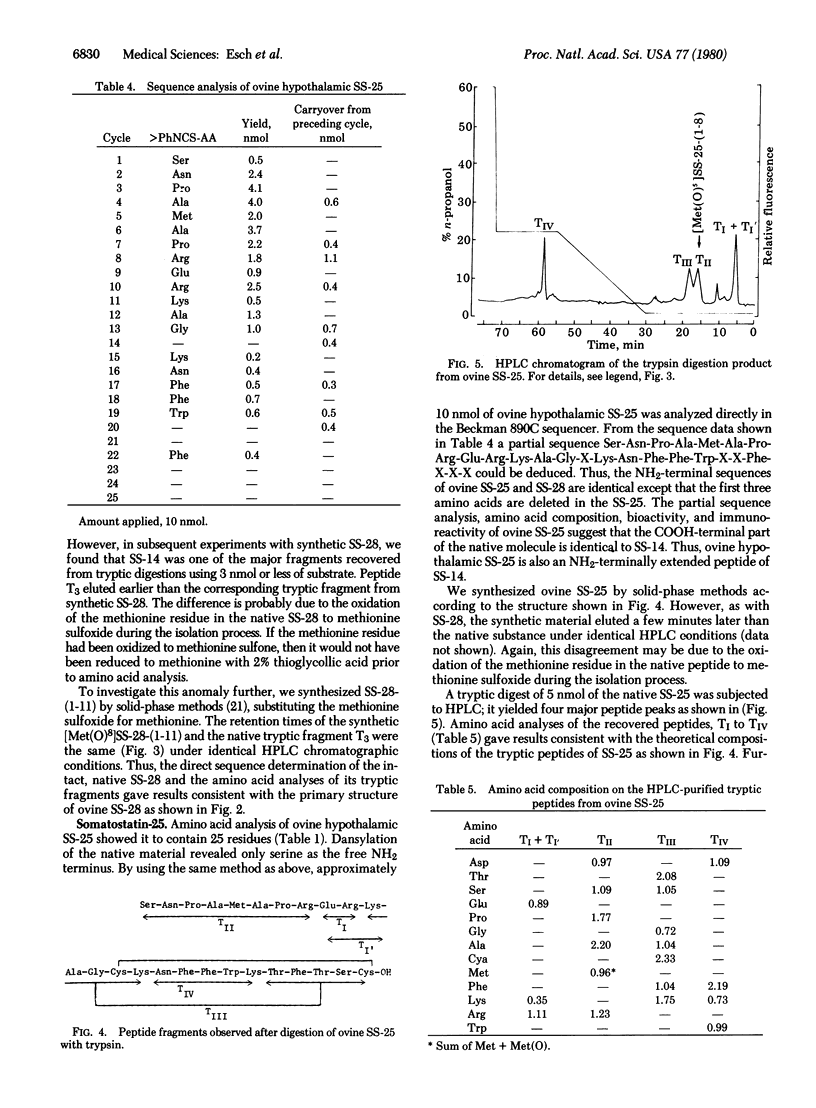
The primary structure of the NH2-terminally extended somatostatins isolated from ovine hypothalamic extracts, one containing 28 residues and the other 25, has been determined. The structure of somatostatin-28 is Ser-Ala-Asn-Ser-Asn-Pro-Ala-Met-Ala-Pro-Arg-Glu-Arg-Lys-Ala-Gly-Cys-Lys-Asn-Phe-Phe-Trp-Lys-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Cys-OH; the shorter one, somatostatin-25, has the same sequence as somatostatin-28 except that the first three NH2-terminal residues are deleted. The two peptides as isolated were found to be oxidized at the methionine residue to the methionine sulfoxide. Their structures were established by subjecting the native peptides to direct sequence analysis in a Beckman 890C sequencer and identifying the released phenylthiohydantoin derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography. Their structures were confirmed by trypsin digestion and isolation of all the tryptic peptides, followed by amino acid analysis of the tryptic fragments. Moreover, some of the tryptic peptides were matched with their respective synthetic replicates on high-performance liquid chromatography.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brazeau P., Ling N., Esch F., Bohlen P., Benoît R., Guillemin R. Haute activité biologigue des répliques synthétiques de somatostatine-28 et somatostatine-25 hypothalamiques. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1980 Jun 9;290(21):1369–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Rivier J., Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Mellet M. Automated fluorometric amino acid analysis: the determination of proline and hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Stone J., Udenfriend S. Automatic Monitoring of primary amines in preparative column effluents with fluorescamine. Anal Biochem. 1975 Aug;67(2):438–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M., Zyznar E., Vale W., Unger R. H. Multiple forms of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in canine pancreas. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 15;94(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80968-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. R., HARTLEY B. S. THE STRUCTURE OF A CHYMOTRYPTIC PEPTIDE FROM PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:379–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillioz P., Giraud P., Conte-Devolx B., Jaquet P., Codaccioni J. L., Oliver C. Immunoreactive somatostatin in rat hypophysial portal blood. Endocrinology. 1979 May;104(5):1407–1410. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-5-1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Direct microsequence analysis of polypeptides using an improved sequenator, a nonprotein carrier (polybrene), and high pressure liquid chromatography. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2124–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Esch F., Davis D., Mercado M., Regno M., Bohlen P., Brazeau P., Guillemin R. Solid phase synthesis of somatostatin-28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):945–951. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91564-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Sasaki R. M. High recovery of tryptophan from acid hydrolysates of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noe B. D., Spiess J., Rivier J. E., Vale W. Isolation and characterization of somatostatin from anglerfish pancreatic islet. Endocrinology. 1979 Dec;105(6):1410–1415. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-6-1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Reichlin S. Somatostatin in hypothalamus, extrahypothalamic brain, and peripheral tissues of the rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):523–530. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradayrol L., Chayvialle J., Mutt V. Pig duodenal somatostatin: extraction and purification. Metabolism. 1978 Sep;27(9 Suppl 1):1197–1200. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradayrol L., Jörnvall H., Mutt V., Ribet A. N-terminally extended somatostatin: the primary structure of somatostatin-28. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Stein S., Gerber L. D., Udenfriend S. Isolation and characterization of the opioid peptides from rat pituitary: beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3052–3055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Dupont A., Arimura A., Redding T. W., Nishi N., Linthicum G. L., Schlesinger D. H. Isolation and structure of somatostatin from porcine hypothalami. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):509–514. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess J., Rivier J. E., Rodkey J. A., Bennett C. D., Vale W. Isolation and characterization of somatostatin from pigeon pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


