Abstract
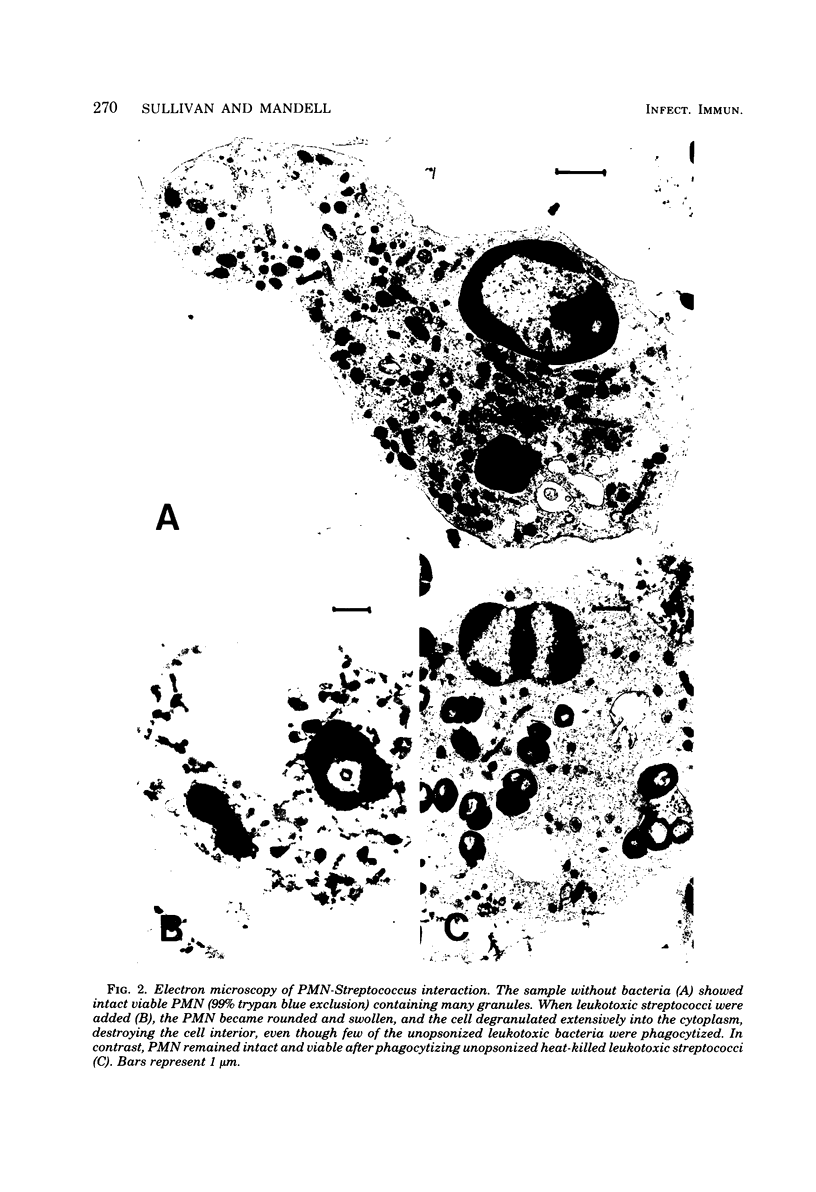
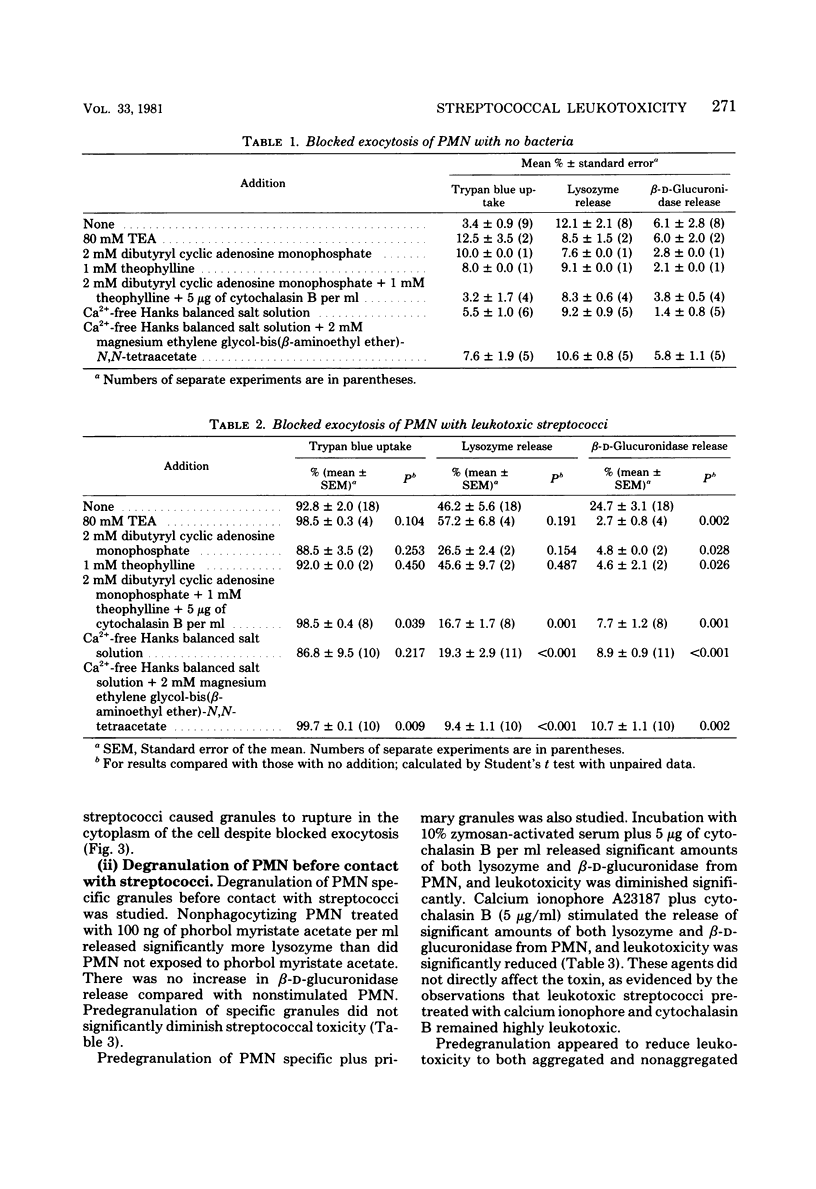
Cinemicrography and electron microscopy suggested that leukotoxic Streptococcus pyogenes killed polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) by inducing intracytoplasmic rupture of the PMN granules. To further study the relationship between granule rupture and the mode of action of the streptococcal leukotoxin, PMN degranulation was experimentally altered. Exocytosis of PMN granule contents was blocked with 80 mM tetraethylammonium chloride, 2 mM dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate, or 2 mM magnesium ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N-tetraacetate in calcium-free medium. This treatment did not prevent the granules from firing into the cytoplasm of the PMN, nor did it significantly diminish leukotoxicity. Degranulating the PMN before exposure to the leukotoxic streptococci did partially block leukotoxicity if both the specific and the primary granules were released with either 5 microM calcium ionophore A23187 or 10% zymosan-activated serum plus 5 micrograms of cytochalasin B per ml. Leukotoxic streptococci stimulated intracytoplasmic rupture of granules, and this granule lysis contributed significantly to the ability of these streptococci to kill PMN.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):661–717. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., Mandell G. L. Gonococcal interactions with polymorphonuclear neutrophils: importance of the phagosome for bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1161–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. M., Schulemann W. THE ACTION OF VITAL STAINS BELONGING TO THE BENZIDINE GROUP. Science. 1914 Mar 27;39(1004):443–454. doi: 10.1126/science.39.1004.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Kato K., Anstiss C. L., Green S. Human serum beta-glucuronidase; its measurement and some of its properties. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Mar;15(3):435–447. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG I., BENTWICH Z., HARRIS T. N. OXYGEN-STABLE HEMOLYSINS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI. 3. THE RELATIONSHIP OF THE CELL-BOUND HOMOLYSIN TO STREPTOLYSIN S. J Exp Med. 1965 Apr 1;121:633–645. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Hoffstein S. T., Weissmann G. Influence of divalent cations upon complement-mediated enzyme release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Hoffstein S. T., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Effects of phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):647–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Horn J. K., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Calcium-induced lysozyme secretion from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):807–812. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., BERNHEIMER A. W., WEISSMANN G. MOTION PICTURE STUDY OF THE TOXIC ACTION OF STREPTOLYSINS ON LEUCOCYTES. J Exp Med. 1963 Aug 1;118:223–228. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane A. B., Stanton R. P., Raymond E. G., Dobson M. E., Knafelc M. E., Farber J. L. Dissociation of intracellular lysosomal rupture from the cell death caused by silica. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):643–651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Bergner-Rabinowitz S., Ginsburg I. Oxygen-stable hemolysins of group A streptococci. VII. The relation of the leukotoxic factor to streptolysin S. J Infect Dis. 1970 Dec;122(6):517–522. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.6.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOLELIS A. N., HARTSELL S. E. The determination of lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1949 Dec;58(6):731–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.6.731-736.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanne F. A., Kane A. B., Young E. E., Farber J. L. Calcium dependence of toxic cell death: a final common pathway. Science. 1979 Nov 9;206(4419):700–702. doi: 10.1126/science.386513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W. Cytotoxic effects of leukocidin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on polymorphonuclear leukocytes from cattle. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.836-843.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W. Purification and characterization of leucocidin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):292–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan G. W., Mandell G. L. Interactions of human neutrophils with leukotoxic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):272–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.272-280.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., McArthur W. P., Baehni P. C., Hammond B. F., Taichman N. S. Extraction and partial characterization of a leukotoxin from a plaque-derived Gram-negative microorganism. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):427–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.427-439.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., KEISER H., BERNHEIMER A. W. STUDIES ON LYSOSOMES. III. THE EFFECTS OF STREPTOLYSINS O AND S ON THE RELEASE OF ACID HYDROLASES FROM A GRANULAR FRACTION OF RABBIT LIVER. J Exp Med. 1963 Aug 1;118:205–222. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. T. The leukotoxic action of streptococci. J Exp Med. 1957 May 1;105(5):463–484. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.5.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodin A. M., Wieneke A. A. Role of leucocidin and triphosphoinositide in the control of potassium permeability. Nature. 1968 Oct 19;220(5164):283–286. doi: 10.1038/220283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodin A. M., Wieneke A. A. The participation of calcium, adenosine triphosphate and adenosine triphosphatase in the extrusion of the granule proteins from the polymorphonuclear leucocyte. Biochem J. 1964 Mar;90(3):498–509. doi: 10.1042/bj0900498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodin A. M., Wieneke A. A. The secretion of protein by the polymorphonuclear leucocyte treated with streptolysin O. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Sep;43(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Cytochalasin B: effect on lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. I. Effect of cyclic nucleotides and colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):27–41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]