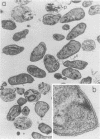
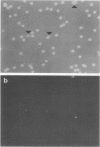
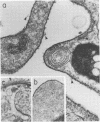
Abstract
In this report, we demonstrate that the variable antigens present on the surface of Plasmodium knowlesi-infected erythrocytes could not be found on the surface of merozoites. A number of technical problems had to be solved to make such a comparative study possible, including the purification of merozoites by affinity columns and gradient centrifugation, the use of hyperimmune rabbit sera instead of monkey sera, and the use of immunocytological methods (indirect immunofluorescence antibody test and electron microscopy with ferritin-labeled antibodies) instead of the schizont-infected cell agglutination test. To ensure that these new techniques were valid for variant-specific serotyping, we compared two well-characterized variant populations with both the standard and the new methods. The removal of variant antigens from the surface of infected erythrocytes by proteolytic enzymes provides further information on the biochemical nature of these antigens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown I. N., Brown K. N., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria: the antibody response to antigenic variation by Plasmodium knowlesi. Immunology. 1968 Jan;14(1):127–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N. Immunity to malaria: antigenic variation in chronic infections of Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2081286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Hills L. A. Antigenic variation and immunity to Plasmodium knowlesi: antibodies which induce antigenic variation and antibodies which destroy parasites. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1974;68(2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(74)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. A., Mitchell G. H., Cohen S. Antibody mediated mechanisms of immunity to malaria induced by vaccination with Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites. Immunology. 1978 Jan;34(1):77–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Butcher G. A., Crandall R. B. Action of malarial antibody in vitro. Nature. 1969 Jul 26;223(5204):368–371. doi: 10.1038/223368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Identification, purification and properties of clone-specific glycoprotein antigens constituting the surface coat of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):393–417. doi: 10.1017/s003118200004717x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J. Self-tolerance maintained by active suppressor mechanisms. Transplant Rev. 1976;31:23–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David P. H., Hommel M., Benichou J. C., Eisen H. A., da Silva L. H. Isolation of malaria merozoites: release of Plasmodium chabaudi merozoites from schizonts bound to immobilized concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5081–5084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. A., Cohen S. Localization and chemical characterization of Plasmodium knowlesi schizont antigens. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):93–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. A., Dennis E. D., Cohen S. Antigenic analysis of sequential erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium knowlesi. Parasitology. 1978 Dec;77(3):333–344. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. D., Mitchell G. H., Butcher G. A., Cohen S. In vitro isolation of Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites using polycarbonate sieves. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):475–481. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000047235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J. Alterations of red blood cell metabolism in simian malaria: evidence for abnormalities of nonparasitized cells. Mil Med. 1969 Sep;134(10):1100–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D. THE AGGLUTINATION OF PLASMODIUM KNOWLESI BY IMMUNE SERUM. J Exp Med. 1938 May 31;67(6):857–870. doi: 10.1084/jem.67.6.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homewood C. A., Neame K. D. A comparison of methods used for the removal of white cells from malaria-infected blood. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1976 Jun;70(2):249–251. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1976.11687119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A., Abati A., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium coatneyi: immunogenicity of "knob-like protrusions" on infected erythrocyte membranes. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T. Antigenicity of the infected-erythrocyte and merozoite surfaces in Falciparum malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1241–1254. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Osborn J. S., Stuart P. R., Williamson J. Internal architecture of the malaria-infected red cell, as revealed by ion-etching and scanning electron microscopy. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1969;63(4):418–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ultrastructure of parasitized erythrocytes in cardiac vessels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Sep;20(5):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick G. J. Amino acid transport and incorporation in red blood cells of normal and Plasmodium knowlesi-infected rhesus monkeys. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Feb;27(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4894(70)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., Bannister L. H., Trigg P. I., Butcher G. A. Freeze fracture studies on the interaction between the malaria parasite and the host erythrocyte in Plasmodium knowlesi infections. Parasitology. 1979 Aug;79(1):125–139. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000052021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Dvorak J. A. Malaria (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites: immunity and the surface coat. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1237–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. H., Butcher G. A., Cohen S. A merozoite vaccine effective against Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):311–313. doi: 10.1038/252311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Wallach D. F., Lightholder J. Two Plasmodium knowlesi-specific antigens on the surface of schizont-infected Rhesus monkey erythrocytes induce antibody production in immune hosts. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):86–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Wallach D. F. Plasmodium knowlesi-induced antigens in membranes of parasitized rhesus monkey erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4949–4953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakespeare P. G., Trigg P. I., Tappenden L. Some properties of membranes in the simian malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1979 Aug;73(4):333–343. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1979.11687267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trigg P. I., Hirst S. I., Shakespeare P. G., Tappenden L. Labelling of membrane glycoprotein in erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium knowlesi. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):205–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. On the surface coat and flagellar adhesion in trypanosomes. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):163–193. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent H. M., Wilson R. J. Reduced lectin binding on erythrocytes of monkeys infected with malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):449–451. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., O'Neill P. Immunofluorescence method suitable for large-scale application to malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;45(4):524–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]