Abstract
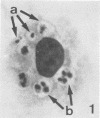
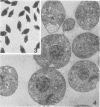
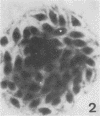
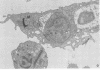
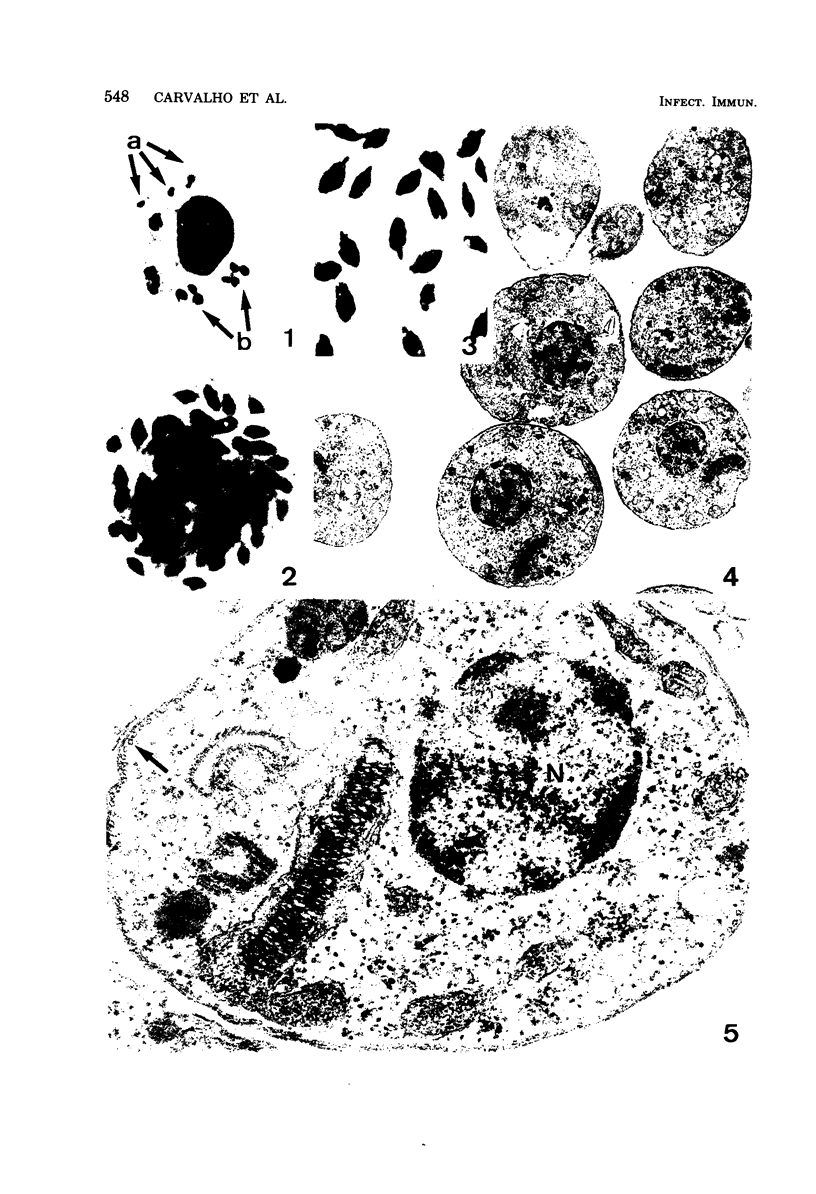
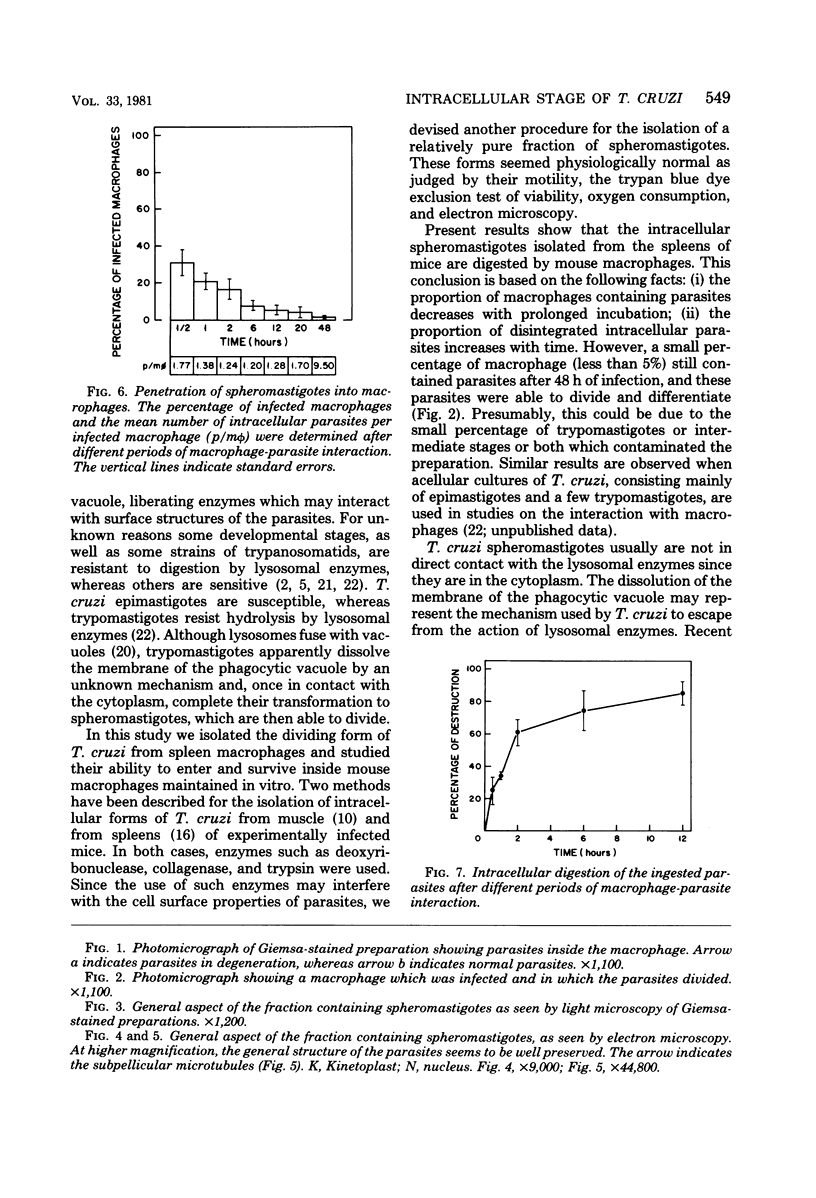
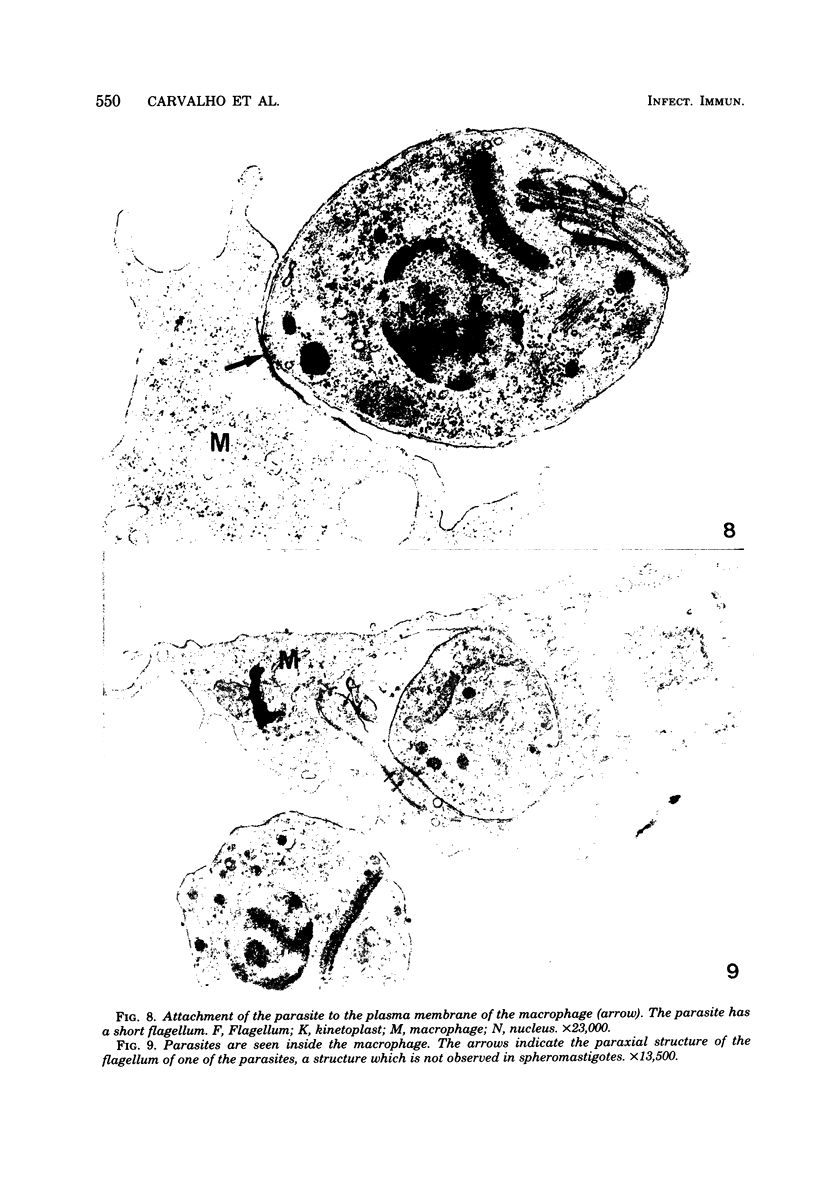
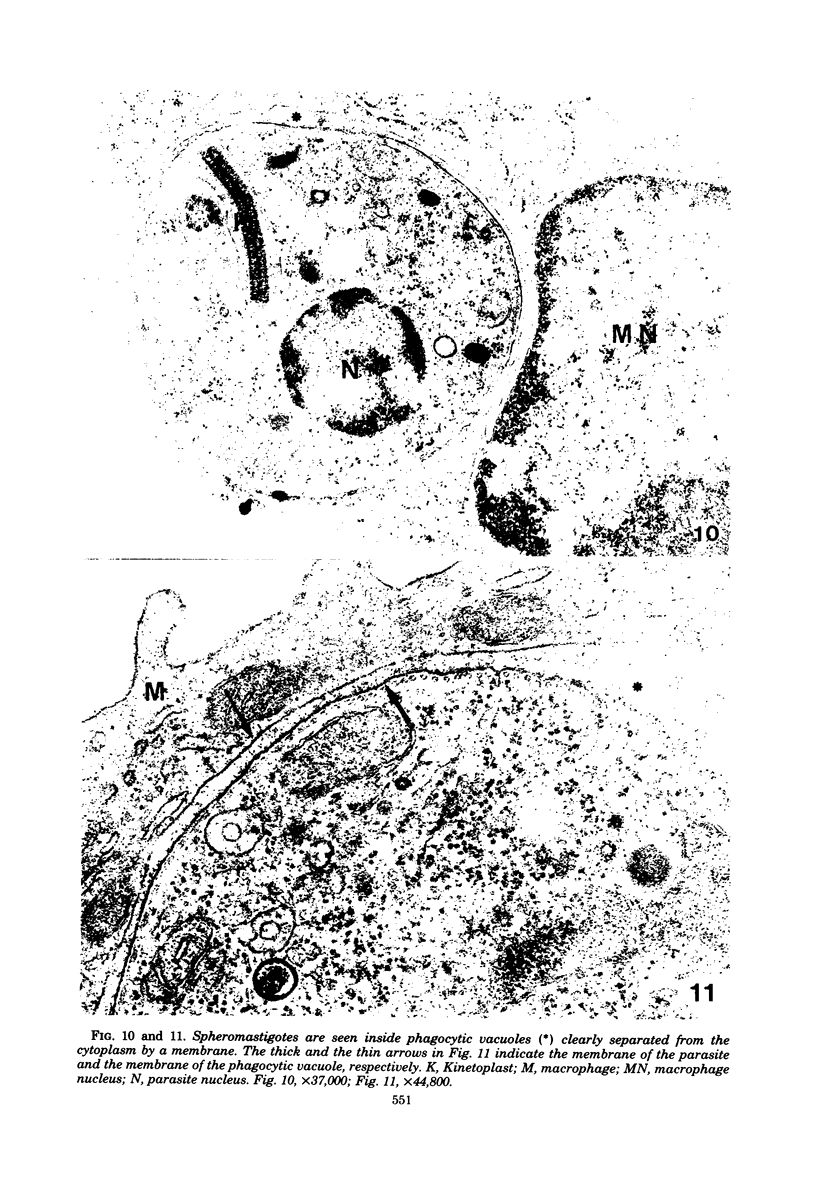
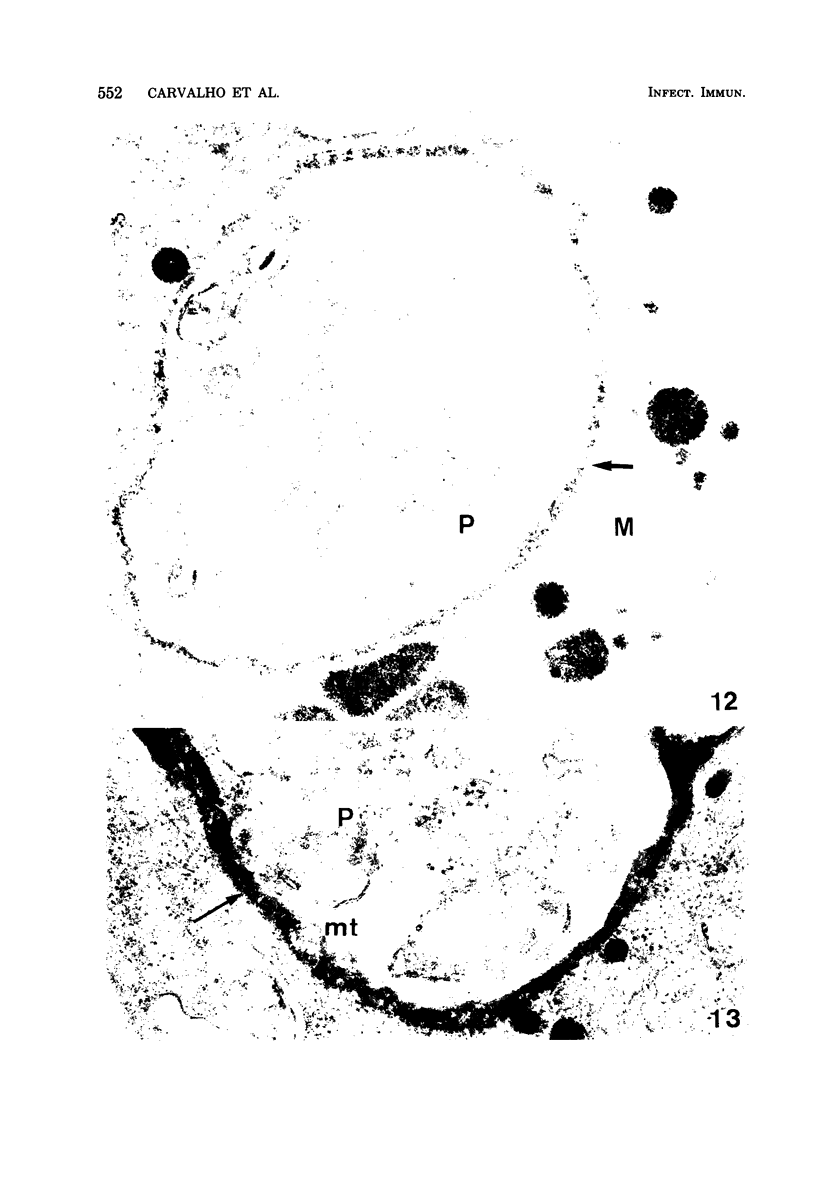
Interaction between Trypanosoma cruzi spheromastigotes (amastigotes) and mouse macrophages was studied. The spheromastigotes, isolated from the spleens of infected mice, were incorporated and digested by the macrophages. By use of horseradish peroxidase labeling of the macrophage lysosomes we showed that fusion of lysosomes with phagocytic vacuoles containing T. cruzi occurred. Parasites showing alterations indicative of digestion were seen inside the phagocytic vacuoles. Our results suggest that intracellular sphermastigotes of T. cruzi, isolated from the spleens of infected mice, and not able to induce a protective infection in mouse macrophages maintained in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcantara A., Brener Z. The in vitro interaction of Trypanosoma cruzi bloodstream forms and mouse peritoneal macrophages. Acta Trop. 1978 Sep;35(3):209–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J., Vickerman K. Fusion of host cell secondary lysosomes with the parasitophorous vacuoles of Leishmania mexicana-infected macrophages. J Protozool. 1975 Nov;22(4):502–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb05219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener Z. Biology of Trypanosoma cruzi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:347–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Dwyer D. M. Leishmania donovani. Hamster macrophage interactions in vitro: cell entry, intracellular survival, and multiplication of amastigotes. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):515–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P. Leishmania infection of human skin fibroblasts in vitro: absence of phagolysosomal fusion after induced phagocytosis of promastigotes, and their intracellular transformation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1084–1096. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A., Schmunis G. A. Trypanosoma cruzi: interaction with mouse peritoneal macrophages. Exp Parasitol. 1972 Oct;32(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(72)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge W. E., Cover B., Gaborak M. Isolation of blood and intracellular forms of Trypansoma cruzi from rats and other rodents and preliminary studies of their metabolism. Parasitology. 1978 Apr;76(2):159–176. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000047740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff R. Killing in vitro of Trypanosoma cruzi by macrophages from mice immunized with T. cruzi or BCG, and absence of cross-immunity on challege in vivo. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):299–311. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M. C., Cohn Z. A. Phagosome-lysosome fusion. Characterization of intracellular membrane fusion in mouse macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):754–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipnis T. L., Calich V. L., da Silva W. D. Active entry of bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma cruzi into macrophages. Parasitology. 1979 Feb;78(1):89–98. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000048617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress Y., Tanowitz H., Bloom B., Wittner M. Trypanosoma cruzi: infection of normal and activated mouse macrophages. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Apr;41(2):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon W., Villalta F., Queiroz T., Szarfman A. Antibody-induced capping of the intracellular stage of Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1218–1220. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1218-1220.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo R. C., Brener Z. Tissue tropism of different Trypanosoma cruzi strains. J Parasitol. 1978 Jun;64(3):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder R., Kloetzel J., Deane M. P. Observation on the interaction of peritoneal macrophages with Trypanosoma cruzi. II. Intracellular fate of bloodstream forms. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1977 Sep-Oct;19(5):313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder R., Kloetzel J. The development of Trypanosoma cruzi in macrophages in vitro. Interaction with lysosomes and host cell fate. Parasitology. 1980 Feb;80(1):139–145. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000000597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: mechanism of entry and intracellular fate in mammalian cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1402–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan S. C. Trypanosoma cruzi: in vitro interactions between cultured amastigotes and human skin-muscle cells. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Aug;45(2):274–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan S. C. Trypanosoma cruzi: intracellular stages grown in a cell-free medium at 37 C. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Aug;45(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., de Souza W. A morphological study of the interaction between Trypanosoma cruzi and rat eosinophils, neutrophils and macrophages in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1979 Jun;37:275–286. doi: 10.1242/jcs.37.1.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Remington J. S. Effect of human monocytes and macrophages on Trypanosoma cruzi. Immunology. 1977 Jan;32(1):19–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meirelles M. N., de Araujo Jorge T. C., de Souza W. Interaction of epimastigote and trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi with chicken macrophages in vitro. Parasitology. 1980 Oct;81(2):373–381. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000056109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza W., Souto-Padrón T. The paraxial structure of the flagellum of trypanosomatidae. J Parasitol. 1980 Apr;66(2):229–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]