Abstract
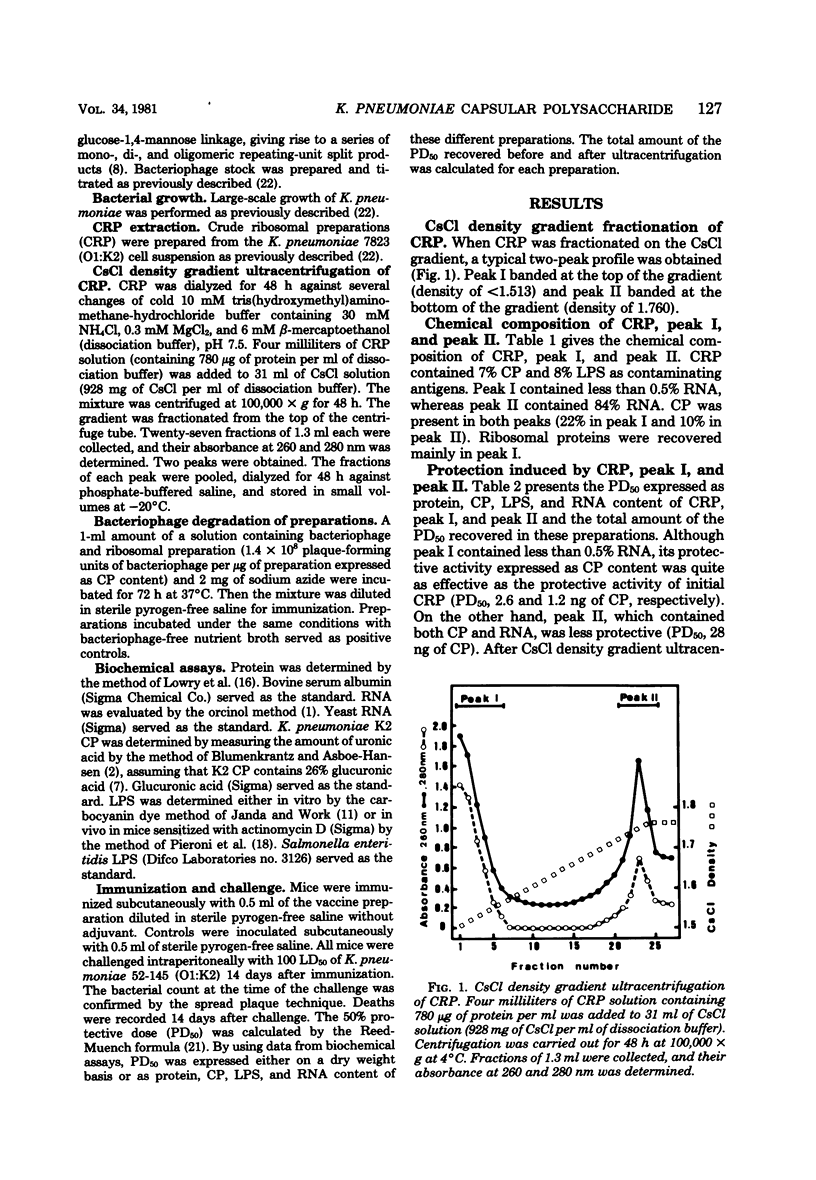
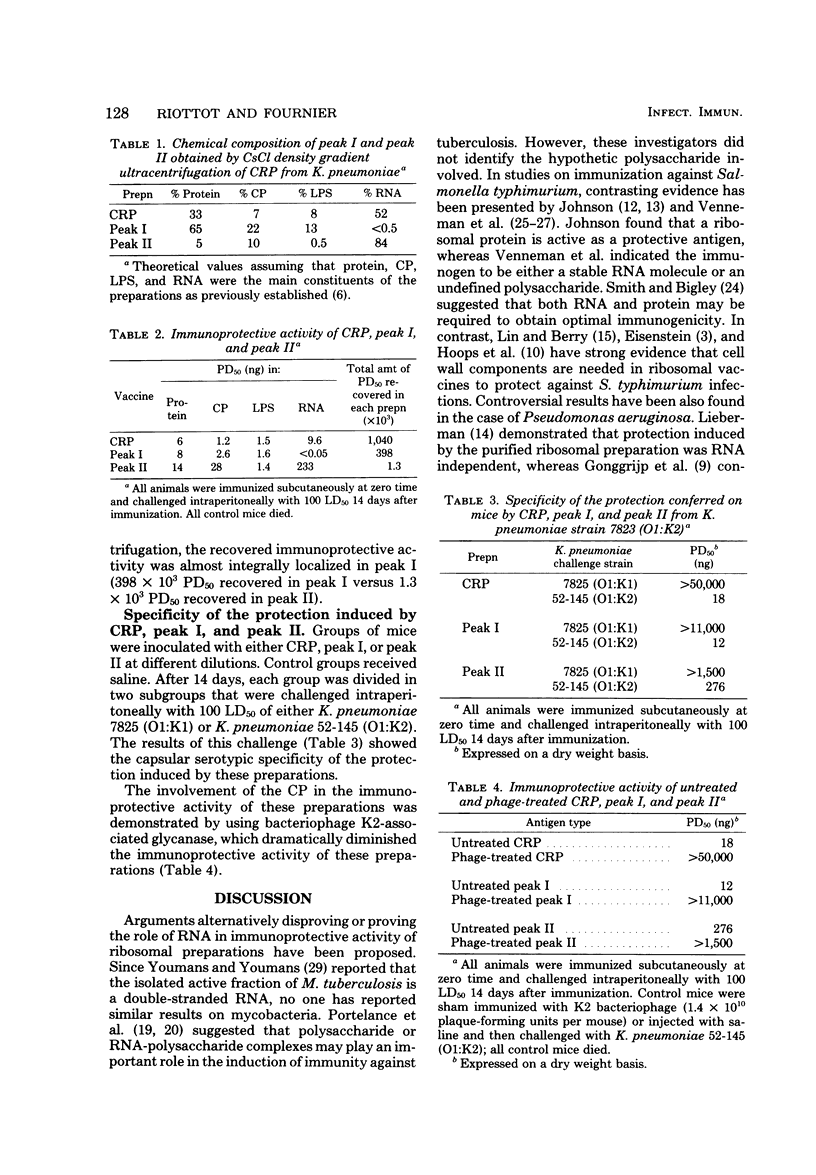
Two peaks were obtained by cesium chloride density gradient ultracentrifugation of Klebsiella pneumoniae ribosomal preparations. Peak I contained capsular polysaccharide, lipopolysaccharide, protein, and less than 0.5% ribonucleic acid. Peak II consisted mainly of ribonucleic acid, with low amounts of protein and capsular polysaccharide. Expressed as capsular polysaccharide content, the 50% protective dose of peak I and of nonfractionated ribosomal preparations was nearly constant (2.6 and 1.2 ng, respectively). Since peak I contained less than 0.5% ribonucleic acid, these results provide evidence that ribosomal ribonucleic acid is not required for protection of mice by K. pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide which contaminates ribosomal preparations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K. Evidence for O antigens as the antigenic determinants in "ribosomal" vaccines prepared from Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):364–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.364-377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontanges R., Robert D., Content Y., Nis G. Study of the immunogenicity of ribosomes and ribosomal RNA extracted from K. pneumoniae and S. pneumoniae. Arzneimittelforschung. 1980;30(1A):142–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier J. M., Jolivet-Reynaud C., Riottot M. M., Jouin H. Murine immunoprotective activity of Klebsiella pneumoniae cell surface preparations: comparative study with ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):420–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.420-426.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahan L. C., Sandford P. A., Conrad H. E. The structure of the serotype 2 capsular polysaccharide of Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2755–2767. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer H., Stirm S., Himmelspach K. Immunochemical properties of oligosaccharide-protein conjugates with Klebsiella-K2 specificity. I. Specificity and crossreactivity of anti-conjugate versus anti-bacterial antibodies. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979 Jan 24;165(4):271–288. doi: 10.1007/BF02152925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonggrijp R., Mullers W. J., Lemmens P. J., van Boven C. P. Ribonuclease-sensitive ribosomal vaccine of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.204-210.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoops P., Prather N. E., Berry J., Ravel J. M. Evidence for an extrinsic immunogen in effective ribosomal vaccines from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1184–1192. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1184-1192.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J., Work E. A colorimetric estimation of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. I. Immunogenicity of ribosomal fractions isolated from Salmonella typhimurium and Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):947–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.947-952.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. II. Specificity of the immune response to ribosomal ribonucleic acid and protein isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):395–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.395-400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M. Pseudomonas ribosomal vaccines: preparation, properties, and immunogenicity. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):76–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.76-86.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. H., Berry L. J. The use of strain LT2-Ml in identifying the protective antigens in a Salmonella typhimurium-derived ribosomal vaccine. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Feb;23(2):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F. B., Dussourd D'Hinterland L., Bousquet J., Pinel A. M., Normier G. Immuno-stimulation by a ribosomal vaccine associated with a bacterial cell wall adjuvant in humans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.760-769.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni R. E., Broderick E. J., Bundeally A., Levine L. A simple method for the quantitation of submicrogram amounts of bacterial endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):790–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portelance V., Boulanger R. P., Brasseur R. Induction of antituberculous immunity by polysaccharidic contaminants of crude ribosomal vaccines isolated from Mycobacterium bovis, strain BCG. Rev Can Biol. 1977 Sep;36(3):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portelance V., Brasseur R., Boulanger R. P. Factors affecting the immunizing activity of ribosomal fractions isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis strain BCG. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Oct;21(10):1492–1499. doi: 10.1139/m75-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riottot M., Fournier J. M., Pillot J. Capsular serotypic specificity of the protection conferred on mice by Klebsiella pneumoniae ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):476–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.476-482.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Bigley N. J. Ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of virulent Salmonella typhimurium as protective immunogens. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):377–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.377-383.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R. Purification of immunogenically active ribonucleic acid preparations of Salmonella typhimurium: molecular-sieve and anion-exchange chromatography. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):269–282. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.269-282.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. NATURE OF THE LABILE IMMUNOGENIC SUBSTANCE IN THE PARTICULATE FRACTION ISOLATED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1030–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1030-1037.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Immunogenic mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic Acid preparations: chemical and physical characteristics. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):659–668. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.659-668.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Youmans A. S. The effect of mycobacterial RNA on the primary antibody response of mice to bovine globulin. J Immunol. 1972 Aug;109(2):217–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


