Abstract
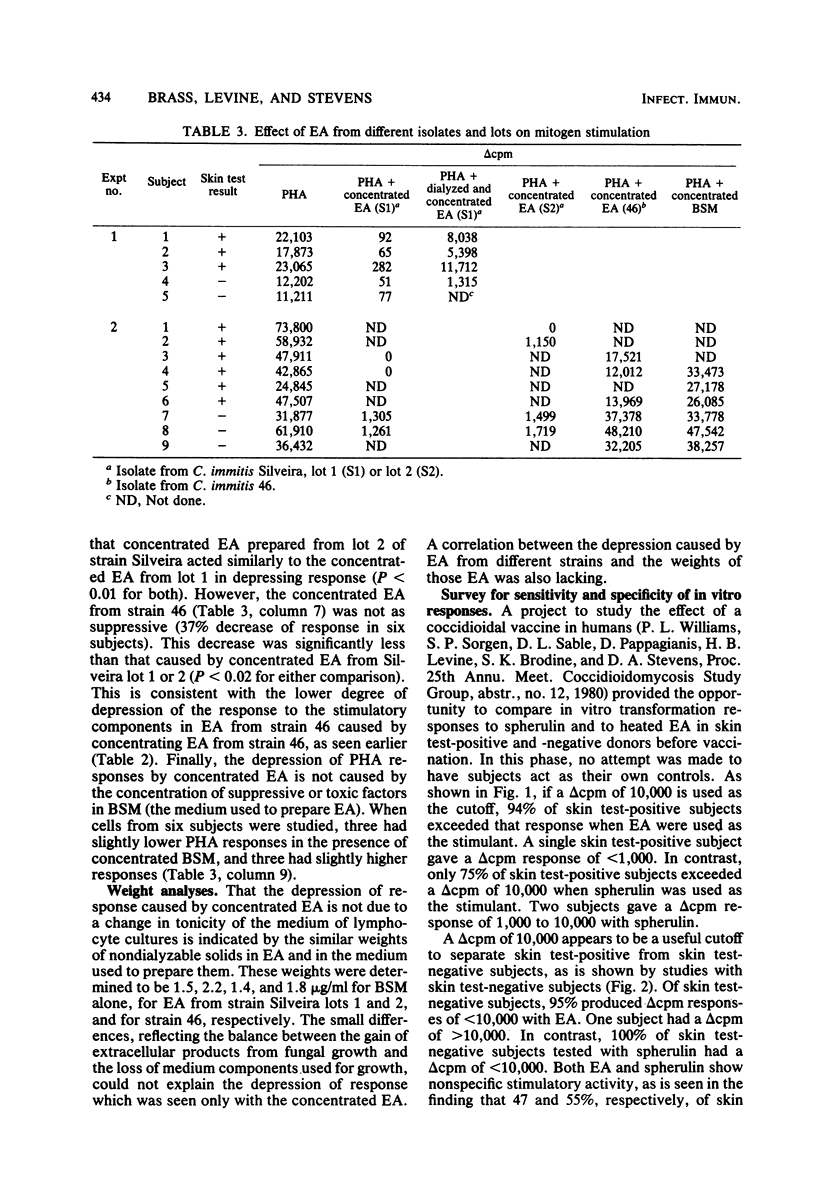
The culture filtrate of Coccidioides immitis induced to replicate in its parasitic phase in vitro, termed endosporulation antigens (EA), was assayed for ability to stimulate human lymphocyte blastogenesis in vitro. Stimulation of lymphocytes from skin test-positive healthy subjects by EA was comparable to stimulation by spherulin at optimal dilutions, but EA are 500 times more potent when compared on the basis of weight. Both preparations slightly stimulated lymphocytes from skin test-negative subjects. Heating or dialysis of EA enhanced the effect on skin test-positive subjects, but concentration depressed it. Concentrated EA also depressed nonspecific stimulation caused by phytohemagglutinin. Dialysis of concentrated EA reduced the ability to depress responses. EA from an avirulent strain of C. immitis were as stimulatory as EA from a virulent strain, but concentrating the former did not produce as much depression as concentrating the latter did. A survey of subjects with an optimal dose of EA in lymphocyte transformation showed that EA could separate skin test-positive from -negative subjects as well as spherulin could. The survey also showed that a delta cpm (the difference of incorporated counts of tritiated thymidine per minute in the presence or absence of the reagent) of 10,000 is useful for this separation. These results also indicate the presence of suppressive substances in EA which are only partially dialyzable and which were significantly more prominent in a preparation from the virulent strain.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CONVERSE J. L. Growth of spherules of Coccidioides immitis in a chemically defined liquid medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Dec;90(3):709–711. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Brummer E., Lecara G. In vitro lymphocyte responses of coccidioidin skin test-positive and -negative persons to coccidioidin, spherulin, and a coccidioides cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):751–755. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.751-755.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. Cross-reactivity between antigens of Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum and Blastomyces dermatitidis in lymphocyte transformation assays. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):932–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.932-938.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deresinski S. C., Levine H. B., Stevens D. A. Soluble antigens of mycelia and spherules in the in vitro detection of immunity to Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):700–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.700-704.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Alford R. H. Variability of sequential studies of lymphocyte blastogenesis in normal adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):28–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Spratt N. S., Vukovich K. R., Sun S. H., Rice E. H. Antigenic analysis of coccidioidin and spherulin determined by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):541–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.541-551.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunity to coccidioi-domycosis induced in mice by purified spherule, arthrospore, and mycelial vaccines. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr;22:436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1960.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine H. B., Cobb J. M., Scalarone G. M. Spherule coccidioidin in delayed dermal sensitivity reactions of experimental animals. Sabouraudia. 1969 Feb;7(1):20–32. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen J., Ablashi D. V., Isenberg R. A., Neel E. U., Miller R. G., Stevens D. A. Cellular immunity in infectious mononucleosis. II. Specific reactivity to Epstein-Barr Virus antigens and correlation with clinical and hematologic parameters. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1239–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., SMITH C. E., KOBAYASHI G. S., SAITO M. T. Studies of antigens from young mycelia of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1961 Jan-Feb;108:35–44. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. H. TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES OF THE HUMAN LYMPHOCYTE. Science. 1964 Dec 25;146(3652):1648–1654. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3652.1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweiman B., Pappagianis D., Maibach H., Hildreth E. A. Coccidioidin delayed hypersensitivity: skin test and in vitro lymphocyte reactivities. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1284–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


