Abstract
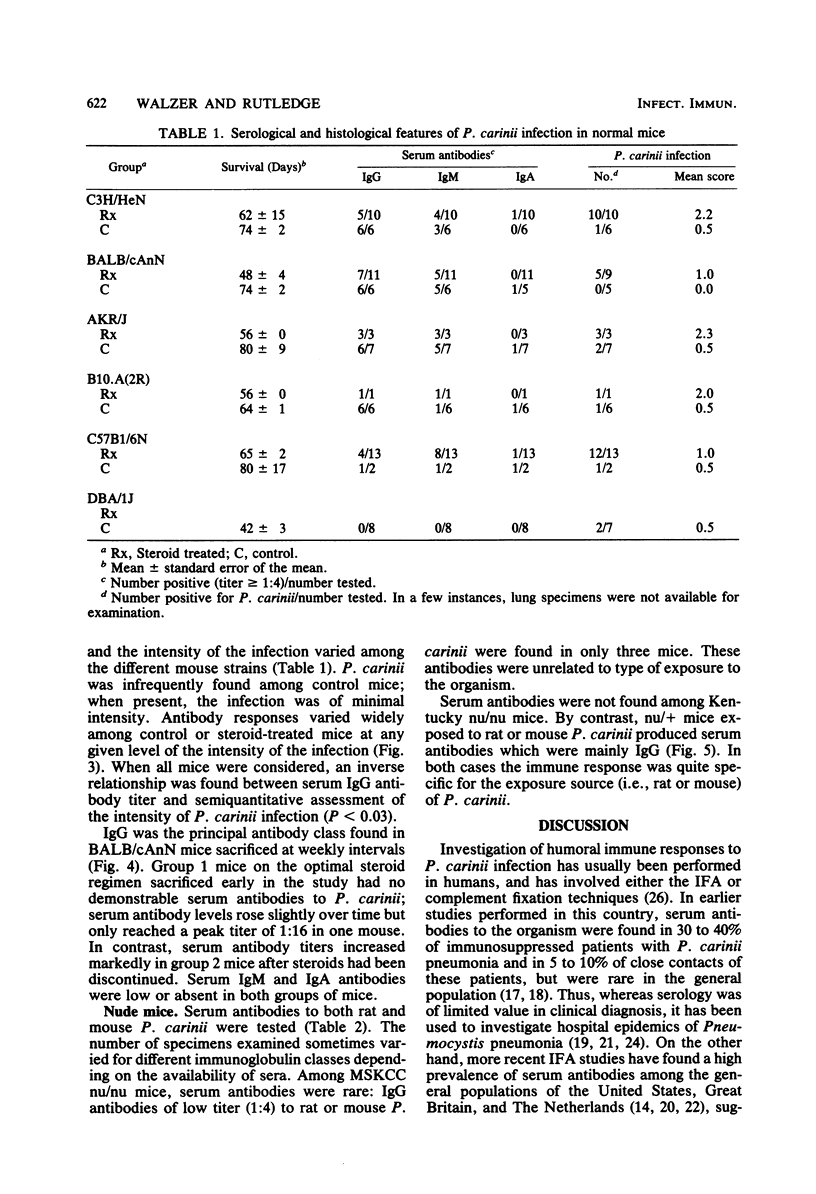
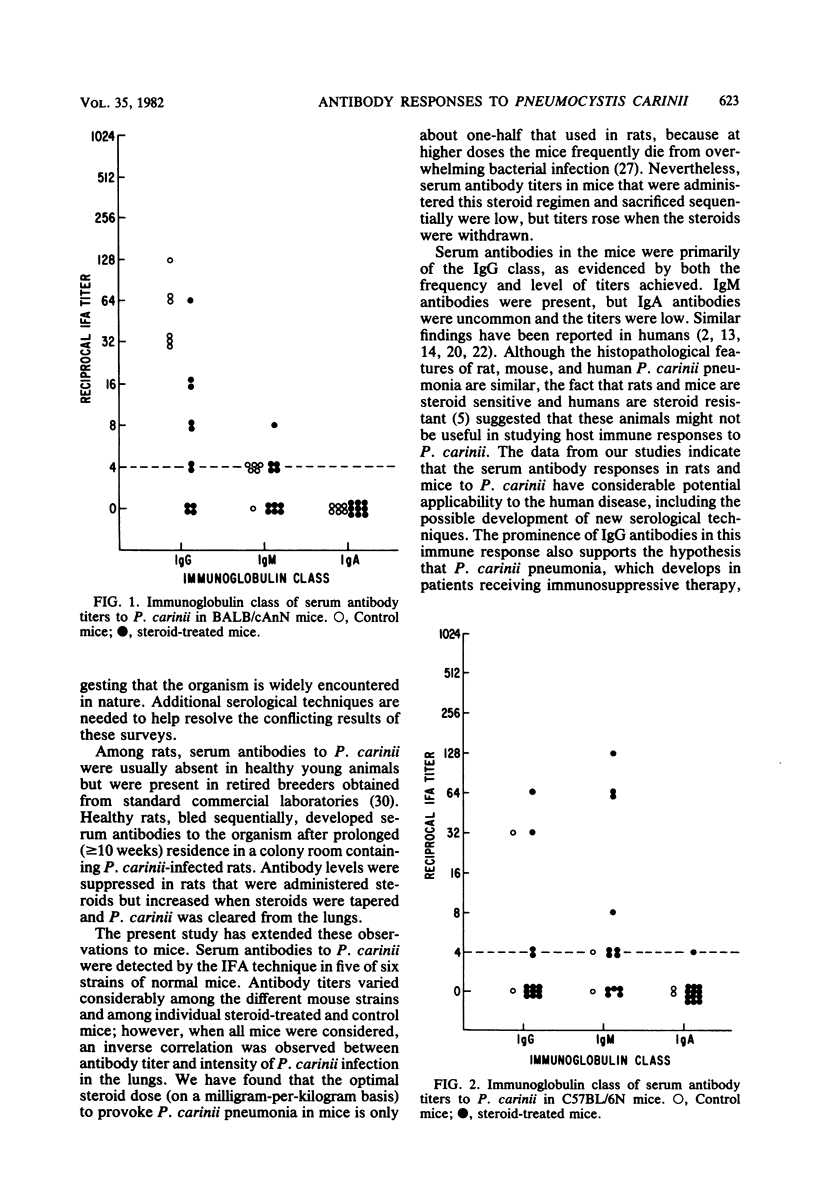
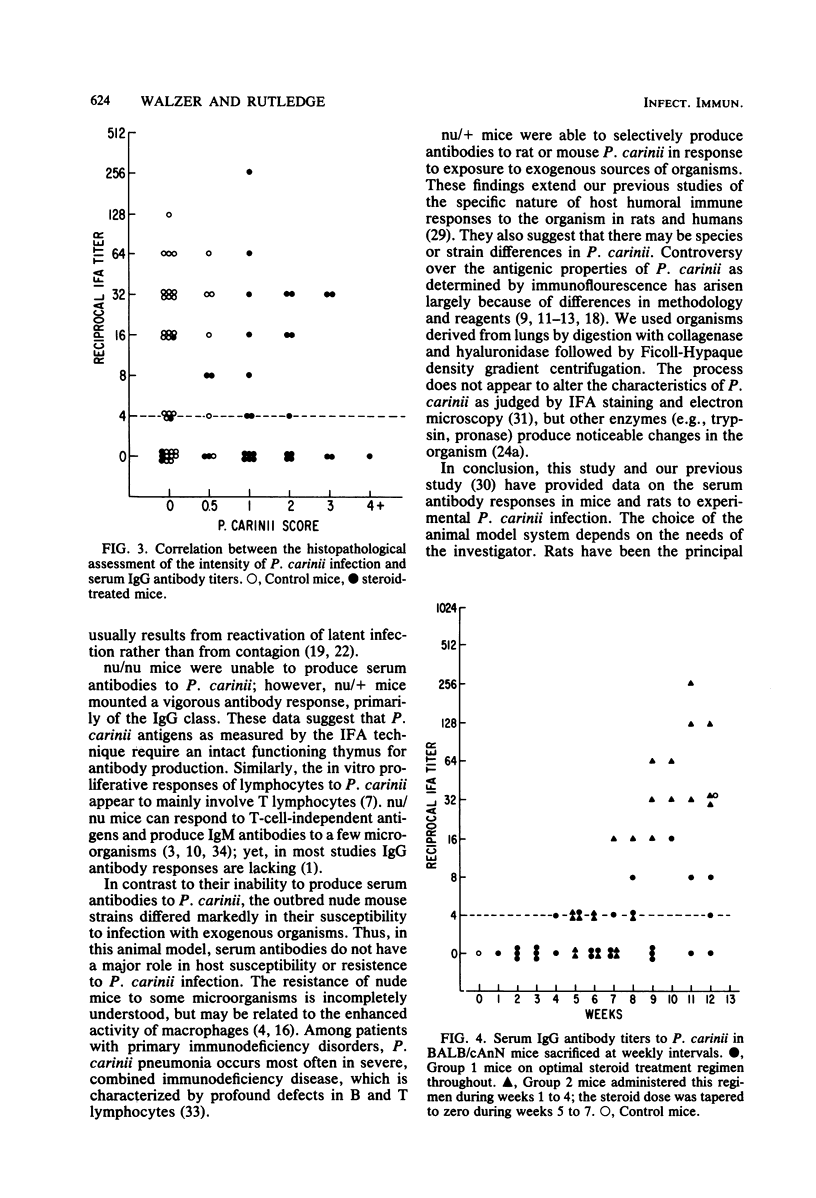
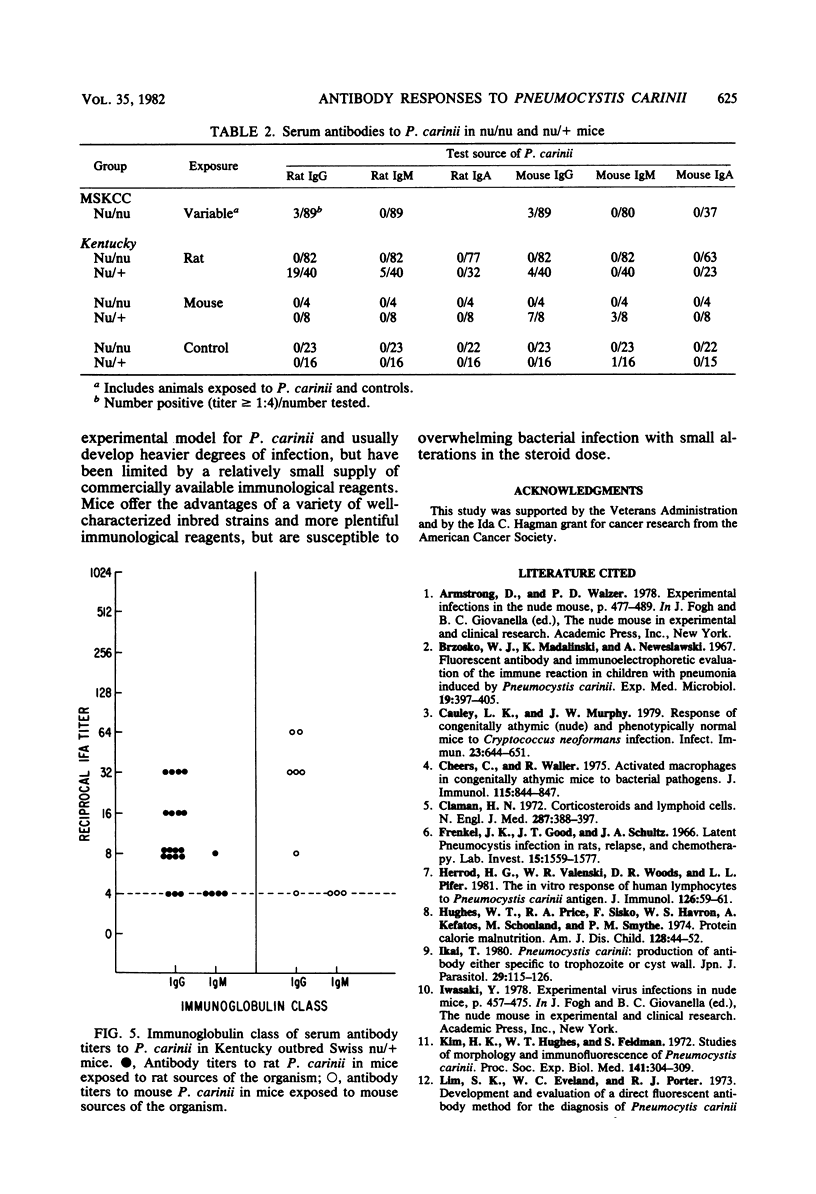
Pneumocystis carinii infection was produced in normal mice by the administration of corticosteroids and in athymic mice by the transmission of exogenous mouse- or rat-derived organisms. Serum antibodies to P. carinii, measured by an indirect fluorescent-antibody technique, were found in five of six strains of normal mice. Although antibody titers varied widely among the control and steroid-treated mice, they were inversely proportional to the intensity of P. carinii infection in the lungs. In sequential studies, antibody titers were low during steroid administration but rose with steroid withdrawal. Antibodies were mainly of the immunoglobulin G (IgG) class; IgM antibodies also occurred, but IgA antibodies were rare. nu/nu mice rarely produced serum antibodies to P. carinii despite the fact that one strain was sensitive and the other was resistant to exogenous infection. nu/+ mice produced specific antibodies to rat and mouse P. carinii which were primarily IgG. Thus, the host produces antibodies to P. carinii which are mainly IgG and T-cell dependent; yet, these antibodies do not appear to be important in susceptibility or resistance to P. carinii infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N. Corticosteroids and lymphoid cells. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 24;287(8):388–397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208242870806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrod H. G., Valenski W. R., Woods D. R., Pifer L. L. The in vitro response of human lymphocytes to Pneumocystis carinii antigen. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Sisko F., Havron W. S., Kafatos A. G., Schonland M., Smythe P. M. Protein-calorie malnutrition. A host determinant for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Jul;128(1):44–52. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110260046008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Hughes W. T., Feldman S. Studies of morphology and immunofluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):304–309. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Eveland W. C., Porter R. J. Development and evaluation of a direct fluorescent antibody method for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii infections in experimental animals. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):666–671. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.666-671.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Eveland W. C., Porter R. J. Direct fluorescent-antibody method for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis from sputa or tracheal aspirates from humans. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):144–149. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.144-149.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder J. E., Walzer P. D., Coonrod J. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of histological and immunological techniques for detection of Pneumocystis carinii in rat bronchial lavage fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):409–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.409-417.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol A. D., Bonventre P. F. Anomalous high native resistance to athymic mice to bacterial pathogens. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):636–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.636-645.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. A preliminary report of an indirect fluorescent antibody test for detecting antibodies to cysts of Pneumocystis carinii in human sera. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;58(2):170–176. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. Some observations on the serology of Pneumocystis carinii infections in the United States. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.317-321.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera D. R., Western K. A., Johnson H. D., Johnson W. W., Schultz M. G., Akers P. V. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in a hospital for children. Epidemiologic aspects. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1074–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruebush T. K., 2nd, Weinstein R. A., Baehner R. L., Wolff D., Bartlett M., Gonzles-Crussi F., Sulzer A. J., Schultz M. G. An outbreak of pneumocystis pneumonia in children with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Feb;132(2):143–148. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120270041009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd V., Jameson B., Knowles G. K. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis: a serological study. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;32(8):773–777. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.8.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P., Schottenfeld D. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a cluster of eleven cases. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):772–777. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahr B. J., Walzer P. D., Yoneda K. Effect of proteolytic enzymes on Pneumocystis carinii in rat lung tissue. J Parasitol. 1981 Apr;67(2):196–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Goto Y., Yamazaki S., Fujiwara K. Chronic fatal pneumocystosis in nude mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1977 Dec;47(6):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D. Pneumocystis carinii infection. South Med J. 1977 Nov;70(11):1330–1337. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197711000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in different strains of cortisonized mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):939–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.939-947.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K., Rutledge M. E., Milder J. E. Growth characteristics and pathogenesis of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):928–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.928-937.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of rat, mouse, and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):449–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Humoral immunity in experimental Pneumocystis carinii infection. I. Serum and bronchial lavage fluid antibody responses in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jun;97(6):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K., Stahr B. J. Pneumocystis carinii: new separation method from lung tissue. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Schnelle V., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P. Nude mouse: a new experimental model for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.301657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Schultz M. G., Western K. A., Robbins J. B. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and primary immune deficiency diseases of infancy and childhood. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):416–422. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


