Abstract
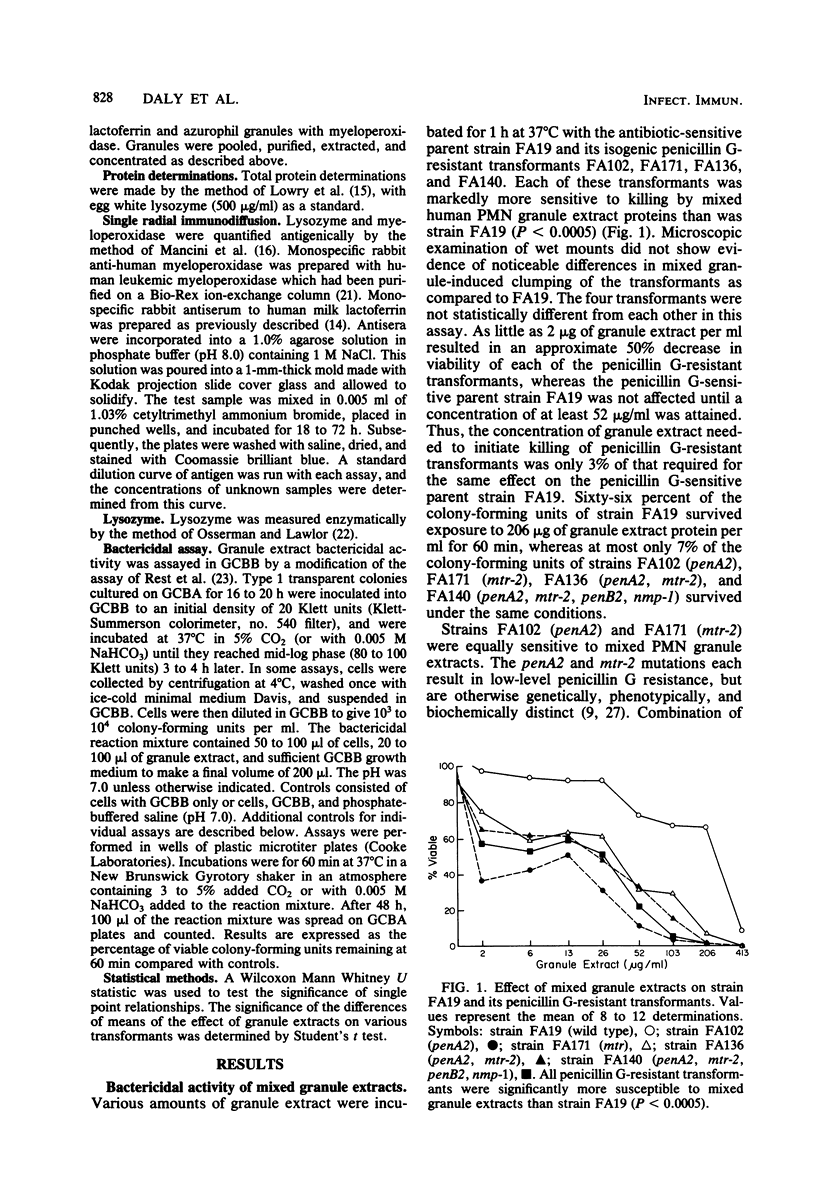
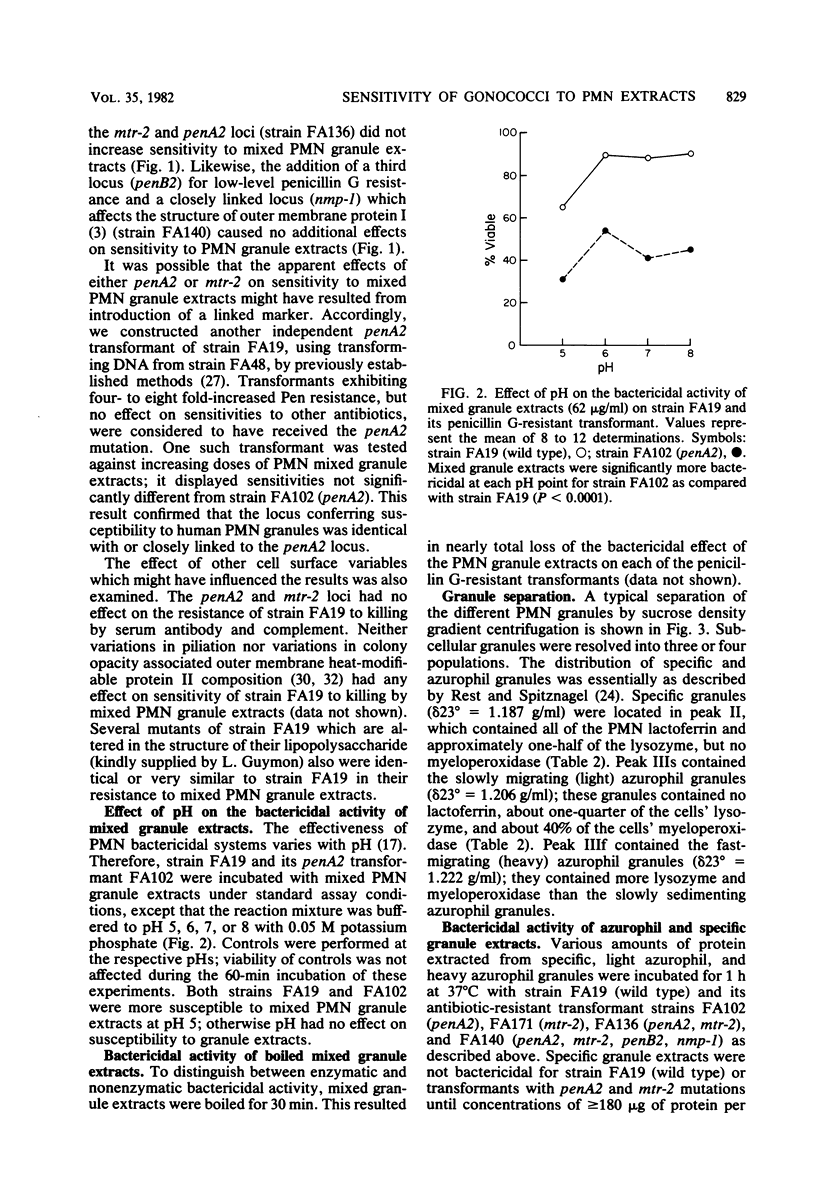
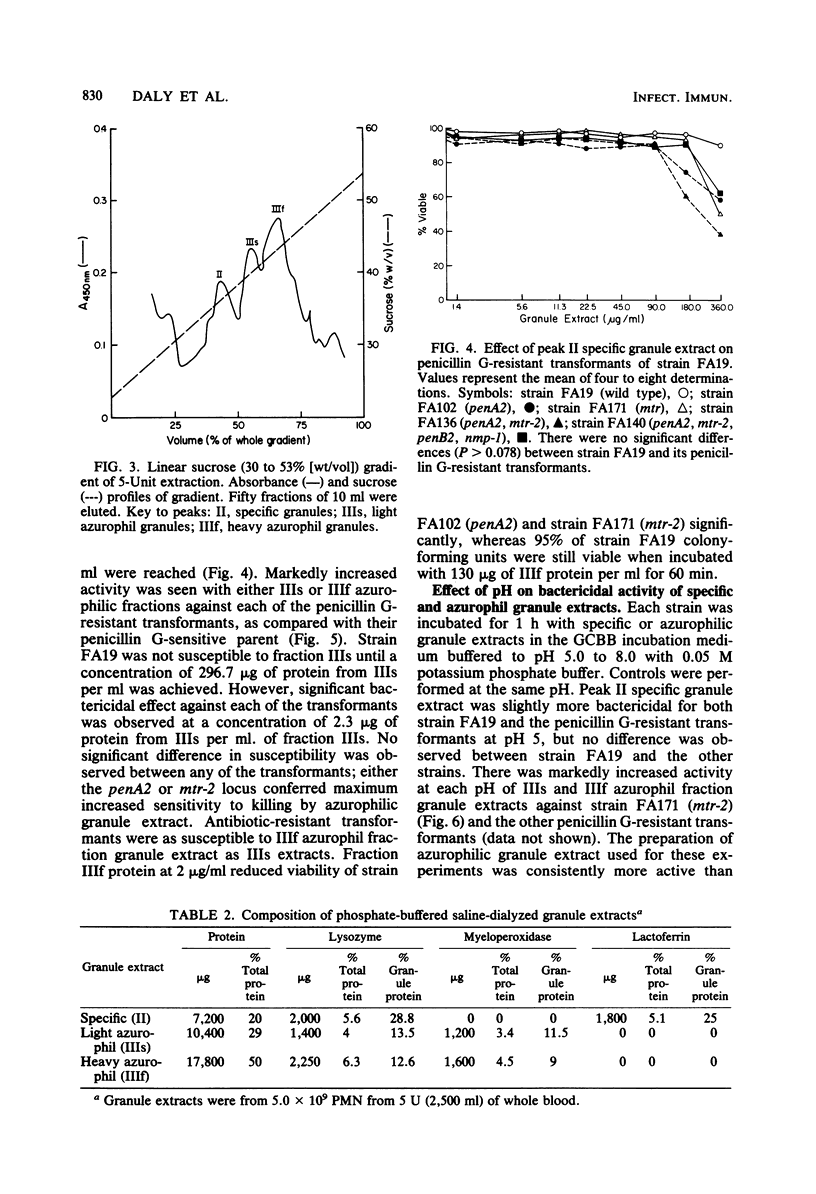
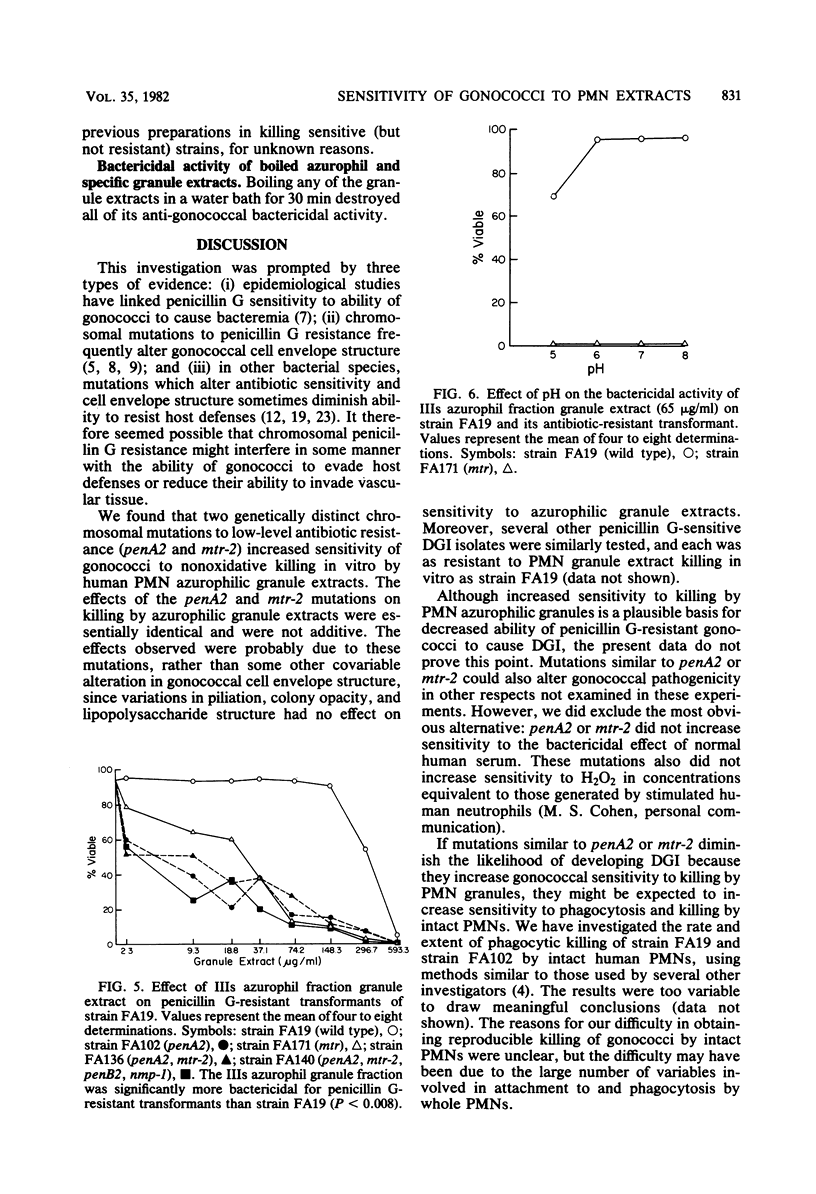
Gonococci which cause disseminated gonococcal infection are nearly always highly penicillin sensitive, in contrast to many isolates causing uncomplicated gonorrhea. We questioned whether any of the known chromosomal mutations to low-level penicillin resistance might adversely affect virulence. The penA2 locus is known to result in low-level resistance to penicillins, whereas mtr-2 results in nonspecific resistance to a variety of antimicrobial agents. We found that the penA2 and mtr-2 mutations each markedly increased sensitivity of strain FA19 to oxygen-independent killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocyte mixed or isolated azurophilic granule extracts. The penA2 and mtr-2 mutations had no effect on sensitivity to serum antibody and complement. Isogenic opaque or transparent variants of several strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae were equally resistant to human polymorphonuclear leukocyte mixed granule extract bactericidal systems. There were also no differences in susceptibility of piliated type 1 and nonpiliated type 4 variants to human polymorphonuclear leukocyte mixed granule extracts. Since the penA2 and mtr-2 loci are known to increase the degree of cross-linking of cell wall peptidoglycan, the structure of peptidoglycan apparently affects sensitivity to killing by one or more polymorphonuclear leukocyte azurophilic granule extract bactericidal systems. These observations might explain why gonococci with mutations similar to penA2 and mtr-2 are almost never isolated from patients with disseminated gonococcal infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchanan T. M., Hildebrandt J. F. Antigen-specific serotyping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: characterization based upon principal outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):985–994. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.985-994.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Klapper D. G., Blackman E. Y., Sparling P. F. Genetic locus (nmp-1) affecting the principal outer membrane protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):847–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.847-851.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., Mandell G. L. Gonococcal interactions with polymorphonuclear neutrophils: importance of the phagosome for bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1161–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. L., James J. F., Hadley W. K., Sweet R. L. Auxotypes and antibiotic susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae from women with acute salpingitis. Comparison with gonococci causing uncomplicated genital tract infections in women. Sex Transm Dis. 1981 Apr-Jun;8(2):43–50. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198104000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Lee T. J., Sparling P. F. Penicillin sensitivity and serum resistance are independent attributes of strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae causing disseminated gonococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):834–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.834-841.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered crystal violet permeability and lytic behavior in antibiotic-resistant and -sensitive mutants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):757–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.757-763.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Walstad D. L., Sparling P. F. Cell envelope alterations in antibiotic-sensitive and-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):391–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.391-401.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I., Mellencamp M. W., Kochan I. Use of transferrin-iron enterobactin complexes as the source of iron by serum-exposed bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.439-445.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffell M. S., Spitznagel J. K. Association of lactoferrin with lysozyme in granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.761-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Intraphagosomal pH of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jun;134(2):447–449. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Larsen L. J. The sensitivity of smooth and rough gram-negative bacteria to the immune bactericidal reaction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):345–348. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B. W., Roantree R. J. Analyses of lipopolysaccharides extracted from penicillin-resistant, serum-sensitive salmonella mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):179–188. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Olofsson T., Odeberg H. Myeloperoxidase-mediated iodination in granulocytes. Scand J Haematol. 1972;9(5):483–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1972.tb00974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Spitznagel J. K. Subcellular distribution of superoxide dismutases in human neutrophils. Influence of myeloperoxidase on the measurement of superoxide dismutase activity. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 15;166(2):145–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1660145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Genetic mapping of linked antibiotic resistance loci in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1284-1292.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Buchanan T. M., Holmes K. K. Gonococci causing disseminated gonococcal infection are resistant to the bactericidal action of normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1163–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E. Inheritance of low-level resistance to penicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):740–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.740-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Dalldorf F. G., Leffell M. S., Folds J. D., Welsh I. R., Cooney M. H., Martin L. E. Character of azurophil and specific granules purified from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1974 Jun;30(6):774–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Edebo L. Phagocytosis of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by rabbit polymorphonuclear cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Everson J. S. Comparative virulence of opacity variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain P9. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):965–970. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.965-970.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstad D. L., Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered outer membrane protein in different colonial types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1623–1627. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1623-1627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


