Abstract
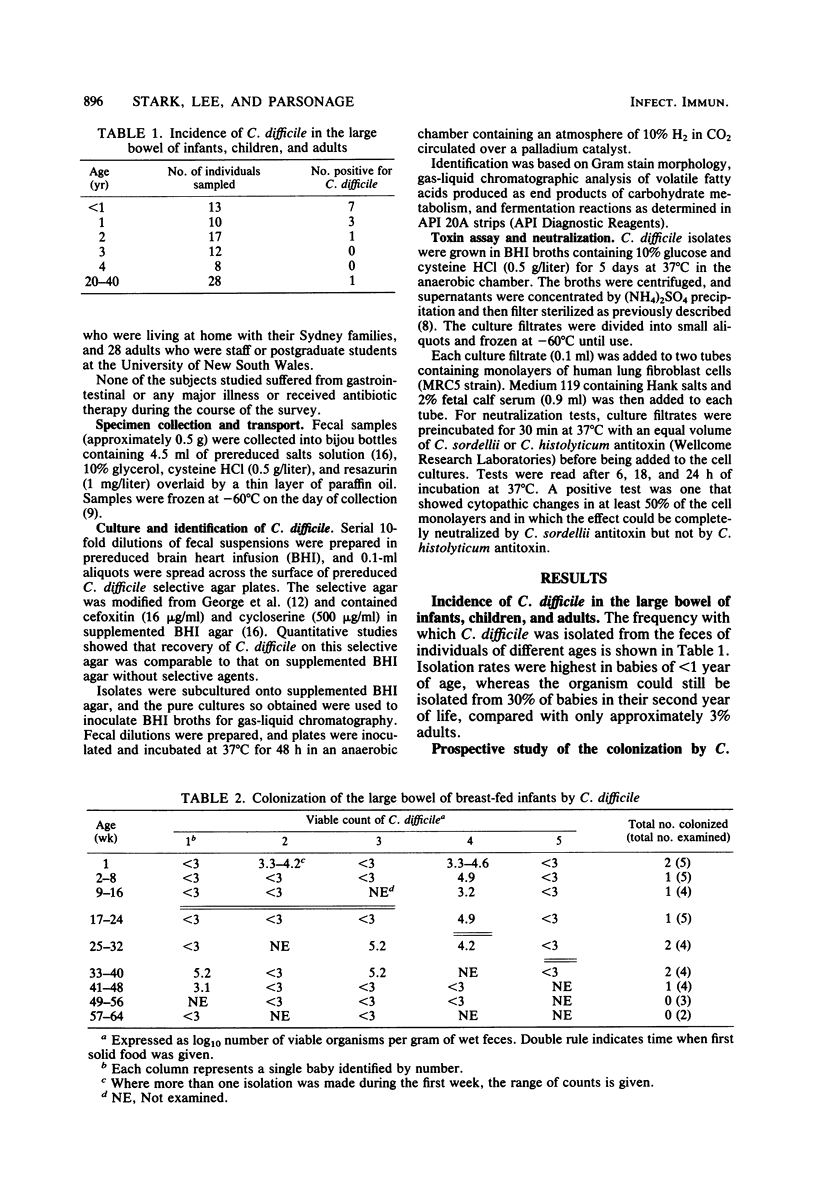
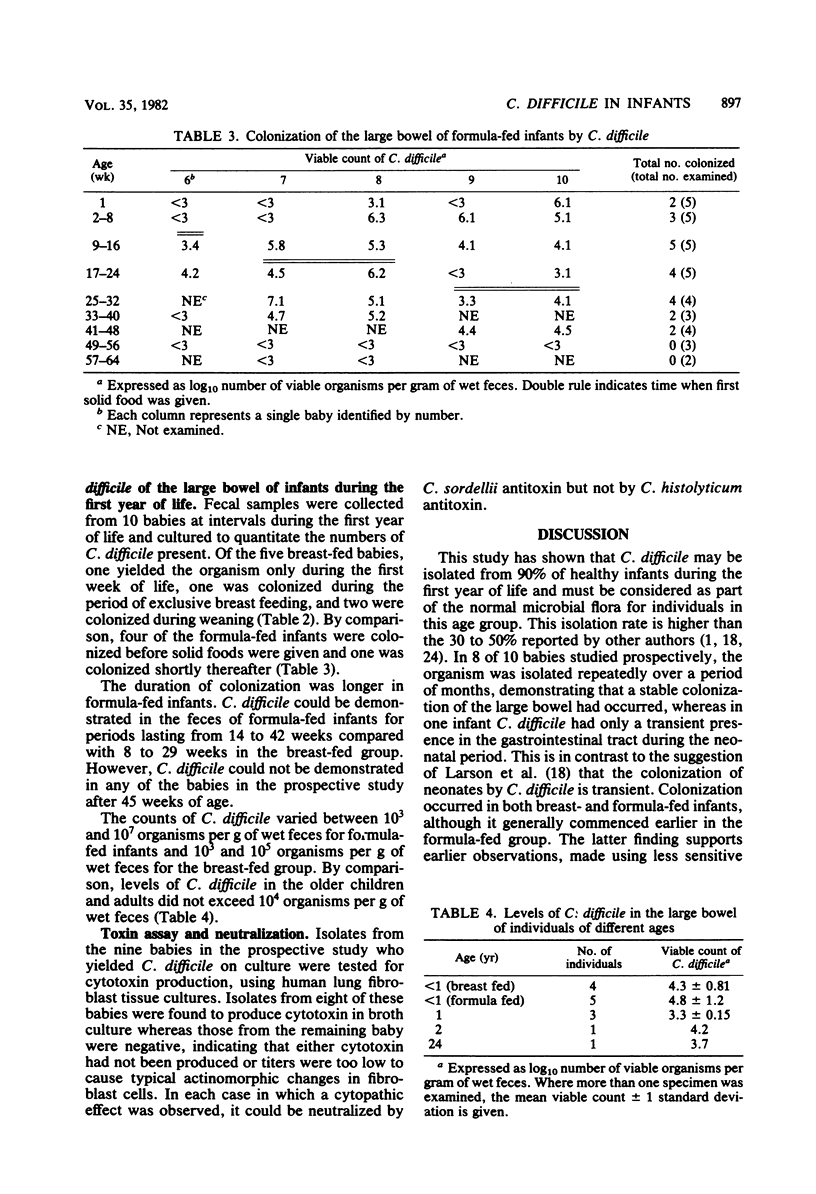
Colonization of the large bowel of healthy infants by Clostridium difficile was studied. Feces were collected from five breast-fed aand five formula-fed infants throughout the first year of life, and levels of C. difficile were quantitated. Three breast-fed and five formula-fed infants were colonized for periods of between 8 and 42 weeks, and another infant harbored the organism only during week 1. Colonization of breast-fed infants commenced before or during weaning, with levels reaching 10(3) to 10(5) organisms per g of wet feces. Colonization of formula-fed infants commenced before solid foods were given, with levels of 10(3) to 10(7) organisms per g of wet feces. Isolates from eight of the babies were shown to produce cytotoxin in vitro. Single fecal specimens from 60 more children aged up to 4 years were also examined, and it was found that the carriage rate of C. difficile fell sharply after 1 year of age, although in the second year it was still higher than in adults. These findings are discussed in relation to the microbial ecology of the large bowel and the paradox that levels of C. difficile in the large bowel of healthy infants are similar to those causing pseudomembranous colitis in patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):530–539. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis (antibiotic-related colitis). Adv Intern Med. 1977;22:455–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Moon N., Chang T. W., Taylor N., Onderdonk A. B. Role of Clostridium difficile in antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Taylor N. S., Chang T., Dzink J. Clinical and laboratory observations in Clostridium difficile colitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Nov;33(11 Suppl):2521–2526. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.11.2521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I. Isolation of toxin producing Clostridium difficile from two children with oxacillin- and dicloxacillin-associated diarrhea. Pediatrics. 1980 Jun;65(6):1154–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashore W. J., Peter G., Lauermann M., Stonestreet B. S., Oh W. Clostridia colonization and clostridial toxin in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):308–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. B. Neutralization of Clostridium difficile toxin by Clostridium sordellii antitoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):418–422. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.418-422.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther J. S. Transport and storage of faeces for bacteriological examination. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety R., Kim K. H., Batts D. H., Browne R. A., Cudmore M. A., Silva J., Jr, Toshniwal R., Wilson K. H. Studies on the epidemiology of antibiotic-associated Clostridium difficile colitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Nov;33(11 Suppl):2527–2532. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.11.2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Rolfe R. D., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Diarrhea and colitis associated with antimicrobial therapy in man and animals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):251–257. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafiz S., McEntegart M. G., Morton R. S., Waitkins S. A. Clostridium defficiel in the urogenital tract of males and females. Lancet. 1975 Feb 22;1(7904):420–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91489-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey M. C., Vince A. J. Clostridia in neonatal faeces. Lancet. 1979 Jul 14;2(8133):100–100. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Honour P., Borriello S. P. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph M. F., Morris K. E. Clindamycin-associated colitis in children. A prospective study and a negative report. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1977 Aug;16(8):722–725. doi: 10.1177/000992287701600809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietra P. J., Slaterus K. W., Zanen H. C., Meuwissen S. G. Clostridial toxin in faeces of healthy infants. Lancet. 1978 Aug 5;2(8084):319–319. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91723-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Nahmias A. J., Wickliffe C., Brann A. W., Jr, Dowell V. R., Jr, Whaley D. N. Bacterial toxin and neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1980 Jan;96(1):114–115. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R. P., Bartlett J. G. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children. Pediatrics. 1981 Mar;67(3):381–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


