Abstract
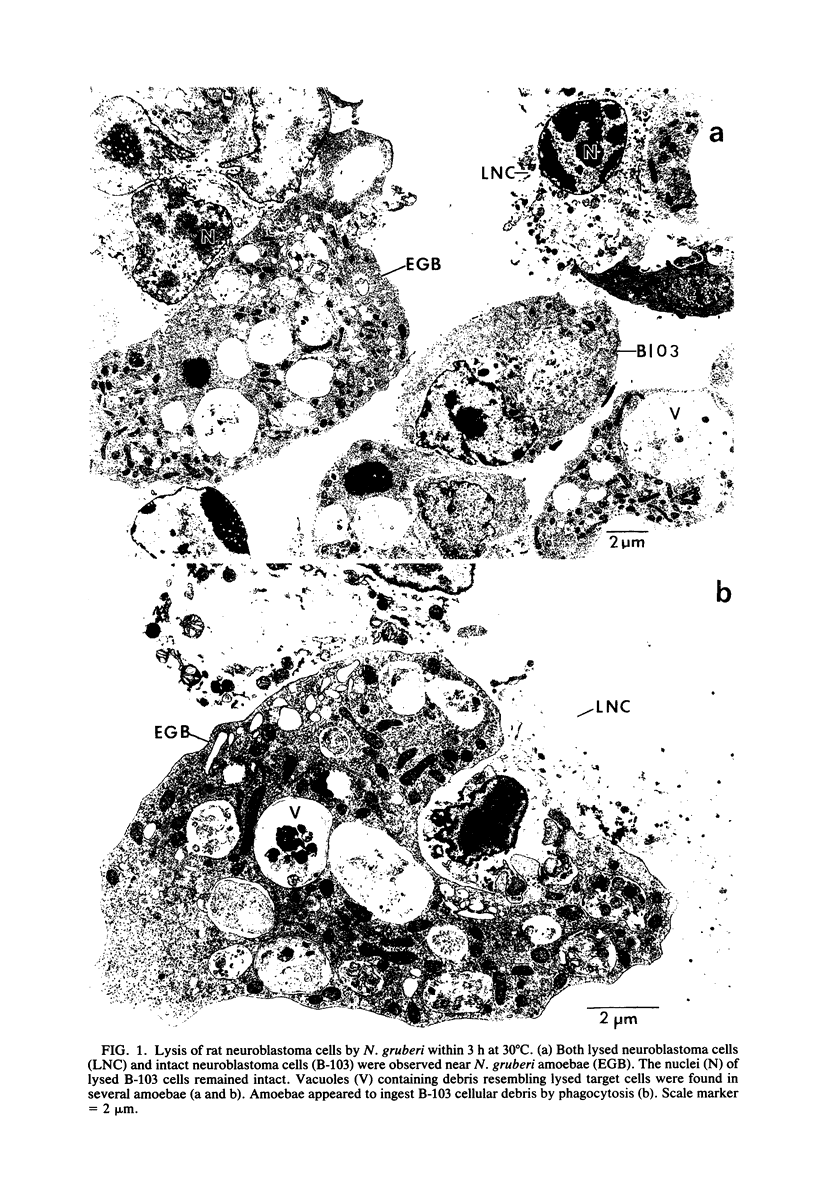
Amoebae of Naegleria gruberi were cytopathic for cultures of rat neuroblastoma (B-103) cells. N. gruberi grew and destroyed B-103 cells at 30 degrees C. As few as one amoeba inoculated per million B-103 cells resulted in cytopathogenicity after extensive growth of N. gruberi.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band R. N., Balamuth W. Hemin replaces serum as a growth requirement for Naegleria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):64–65. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.64-65.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. Observations by immunofluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy on the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in mouse embryo-cell cultures. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):363–371. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J. Use of cell cultures as an indicator of pathogenicity of free-living amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jan;31(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle H. L., Bradley S. G., Harris L. S. Susceptibility of Naegleria fowleri to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):674–679. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Callaway C. S. Light and electron microsopic observations on the pathogenesis of Naegleria fowleri in mouse brain and tissue culture. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]