Abstract
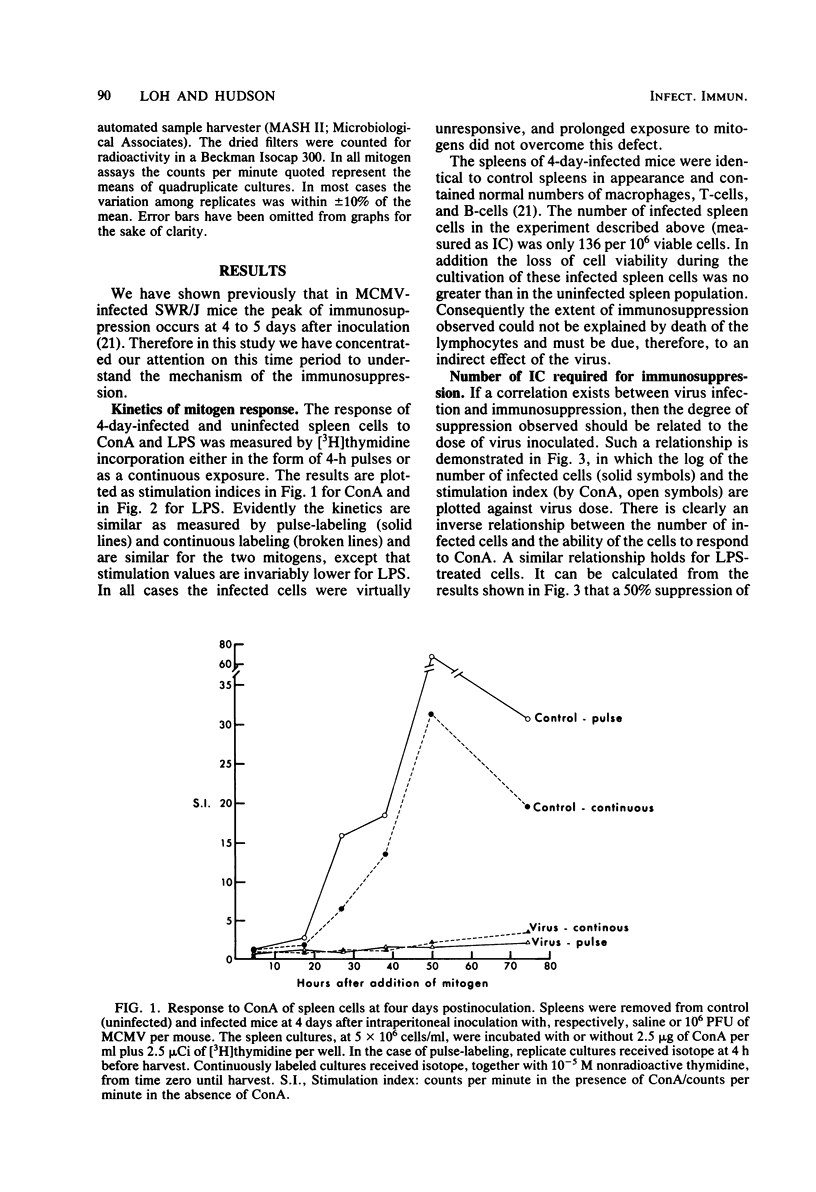
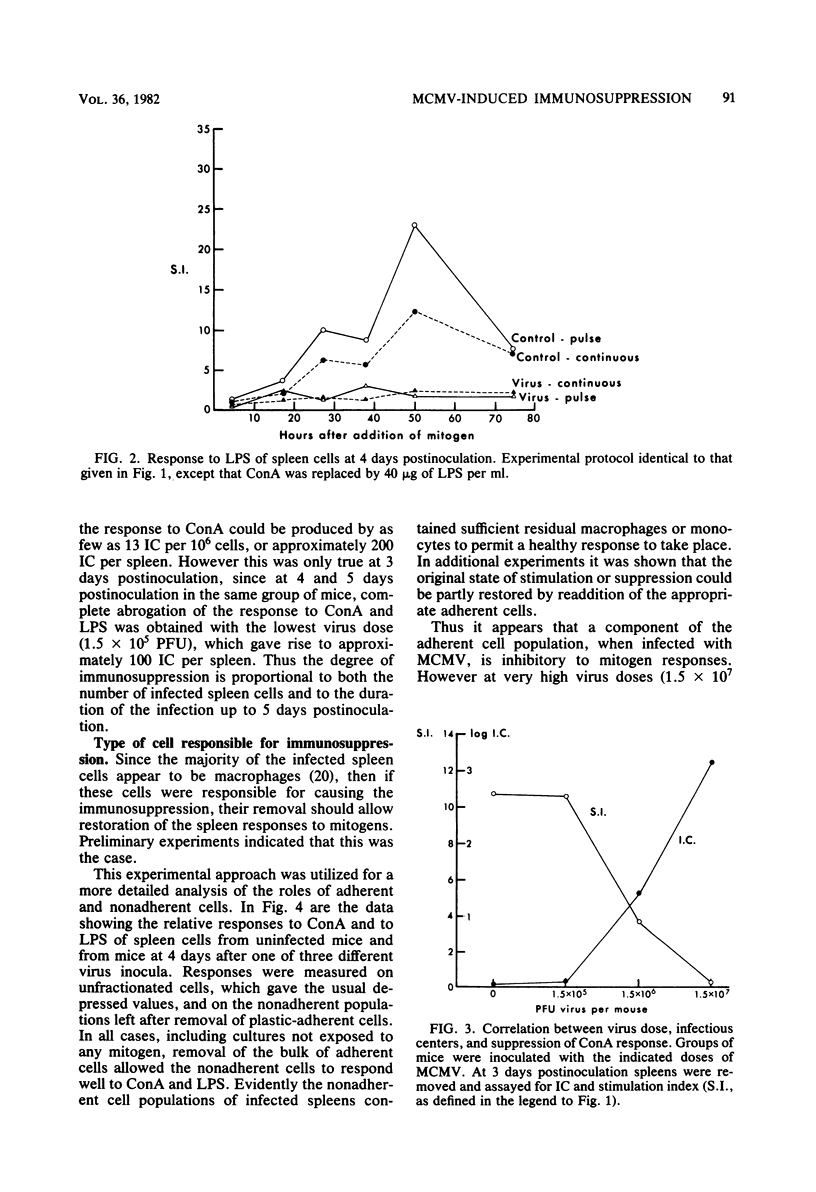
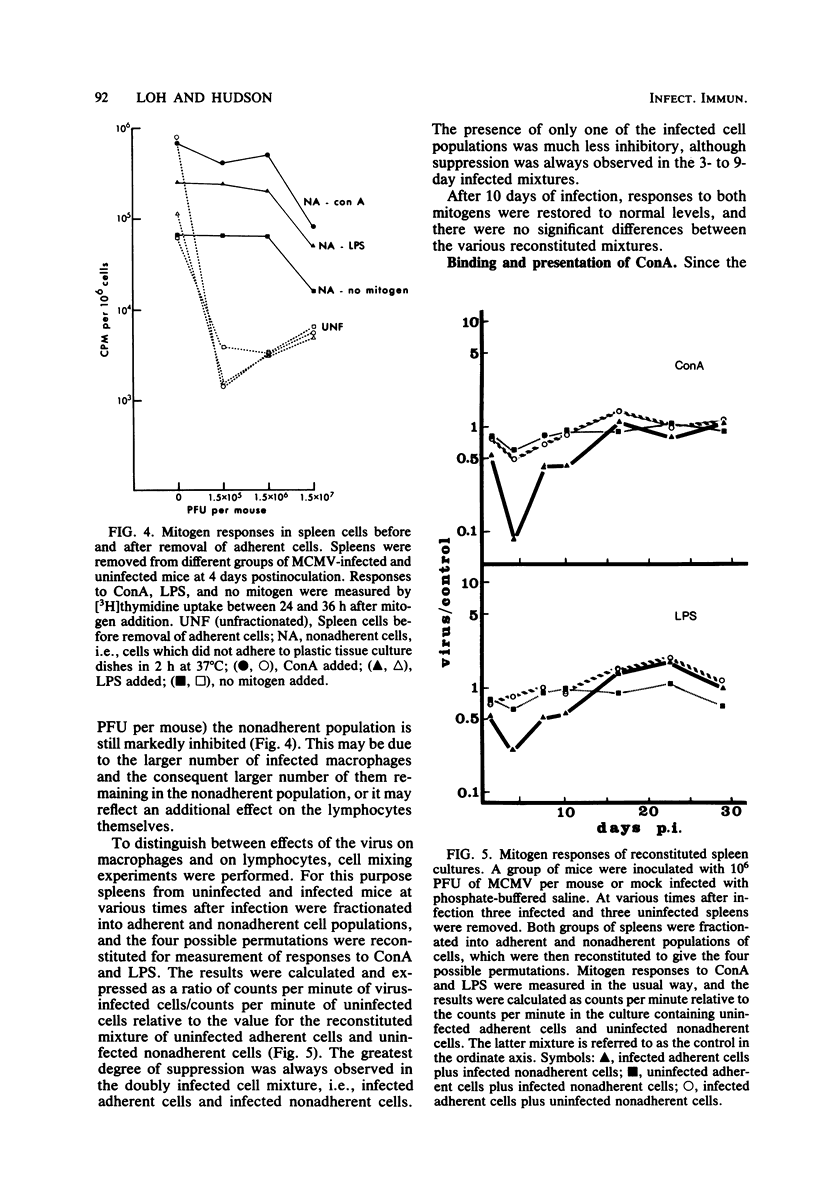
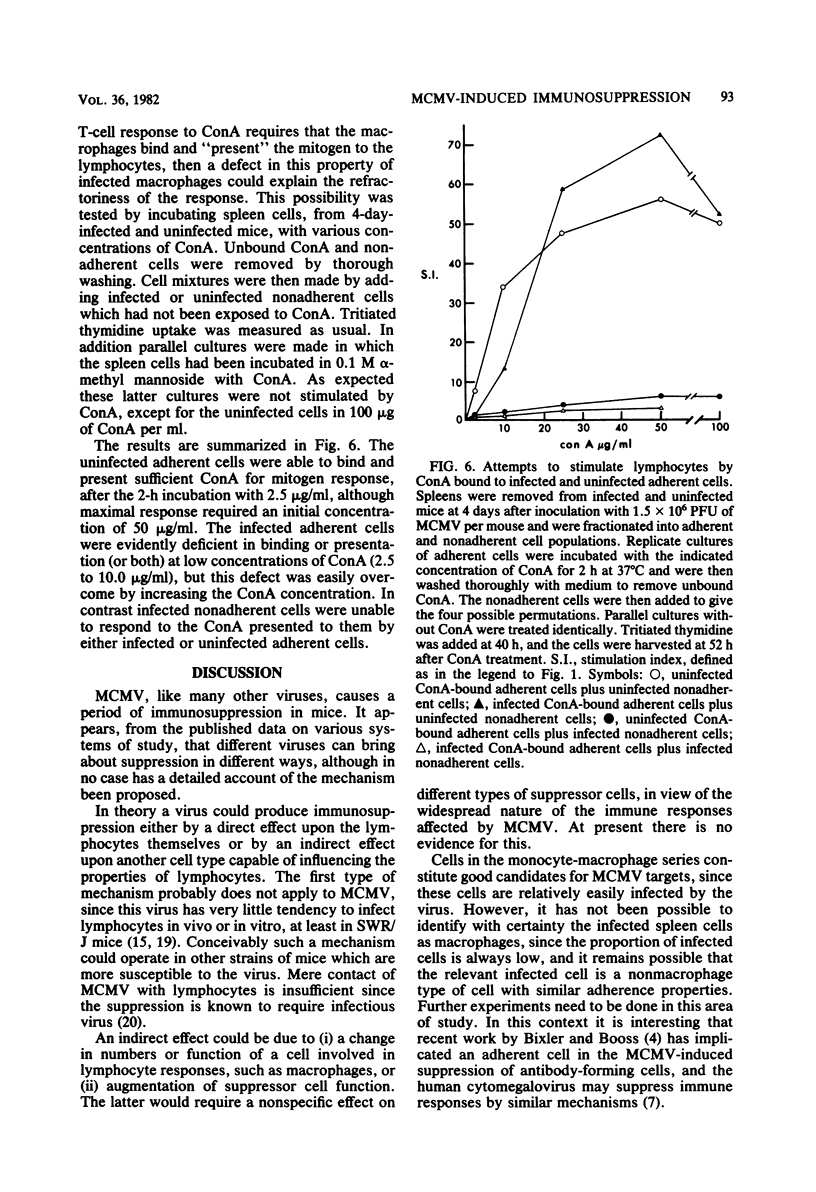
The mechanism of murine cytomegalovirus-induced immunosuppression was investigated by examining the roles played by lymphocytes and adherent cells derived from spleens of infected SWR/J mice. As few as 100 infected cells per spleen were correlated with complete abrogation of mitogen responses at 4 and 5 days after infection. In a series of cell mixing experiments it was shown that the deficiency in infected spleens was due partly to the adherent cells, which apparently secreted an immunosuppressive factor, and partly to the infected lymphocytes, which upon exposure to this factor could no longer respond to concanavalin A presented to them by normal adherent cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. Mechanisms by which activated macrophages inhibit lymphocyte responses. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:3–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araullo-Cruz T. P., Ho M., Armstrong J. A. Protective effect of early serum from mice after cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):840–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.840-842.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixler G. S., Jr, Booss J. Adherent spleen cells from mice acutely infected with cytomegalovirus suppress the primary antibody response in vitro. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1294–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixler G. S., Jr, Booss J. Establishment of immunologic memory concurrent with suppression of the primary immune response during acute cytomegalovirus infection of mice. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):893–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Wheelock E. F. Correlation of survival from murine cytomegalovirus infection with spleen cell responsiveness to Concanavallin A. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jun;149(2):443–445. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Wheelock E. F. Progressive inhibition of T-cell function preceding clinical signs of cytomegalovirus infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):478–481. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney W. P., Hirsch M. S. Mechanisms of immunosuppression in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. II. Virus-monocyte interactions. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi U. C., Shukla M. I., Mathur A. Thymus-dependent lymphocytes of dengue virus-infected mice spleens mediate suppression through prostaglandin. Immunology. 1981 Jan;42(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. R., Overall J. C., Jr Synergistic infection with murine cytomegalovirus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. Role of specific cytotoxic lymphocytes in cellular immunity against murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):767–776. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.767-776.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Mattsson D. M., Seidel M. V., Balfour H. H., Jr Cell-mediated immunity to murine cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):567–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Miller J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. II. Cell-mediated immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):119–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. I. Humoral immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):109–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Loh L., Misra V., Judd B., Suzuki J. Multiple interactions between murine cytomegalovirus and lymphoid cells in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B. The murine cytomegalovirus as a model for the study of viral pathogenesis and persistent infections. Arch Virol. 1979;62(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01314900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel E., Beiss B., Wainberg M. A. Viral abrogation of lymphocyte mitogenesis: induction of a soluble factor inhibitory to cellular proliferation. Immunology. 1980 May;40(1):77–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey D. K., Olsen G. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Alteration of host defense mechanisms by murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):754–760. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.754-760.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey D. K., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Correlation of the suppression of mitogen responsiveness and the mixed lymphocyte reaction with the proliferative response to viral antigen of splenic lymphocytes from cytomegalovirus-infected mice. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):464–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Immunosuppressive effect of murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.54-60.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Interaction of murine cytomegalovirus with separated populations of spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):853–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.853-860.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Murine cytomegalovirus infection in the spleen and its relationship to immunosuppression. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1067-1072.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manischewitz J. E., Quinnan G. V., Jr Antivirus antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity during murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1050–1054. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1050-1054.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Blazkovec A. A., Walker D. L. Immunosuppression during acute murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Manischewitz J. E., Ennis F. A. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to murine cytomegalovirus infection. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):541–543. doi: 10.1038/273541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Mechanisms of viral immunopathology. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1979;23:103–136. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039223-0.50011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Ahmed A., Sell K. W., Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Effect of murine cytomegalovirus on the in vitro responses of T and B cells to mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1459–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L. Mechanisms of immunodepression induced by viruses: possible role of infected macrophages. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):255–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


