Abstract
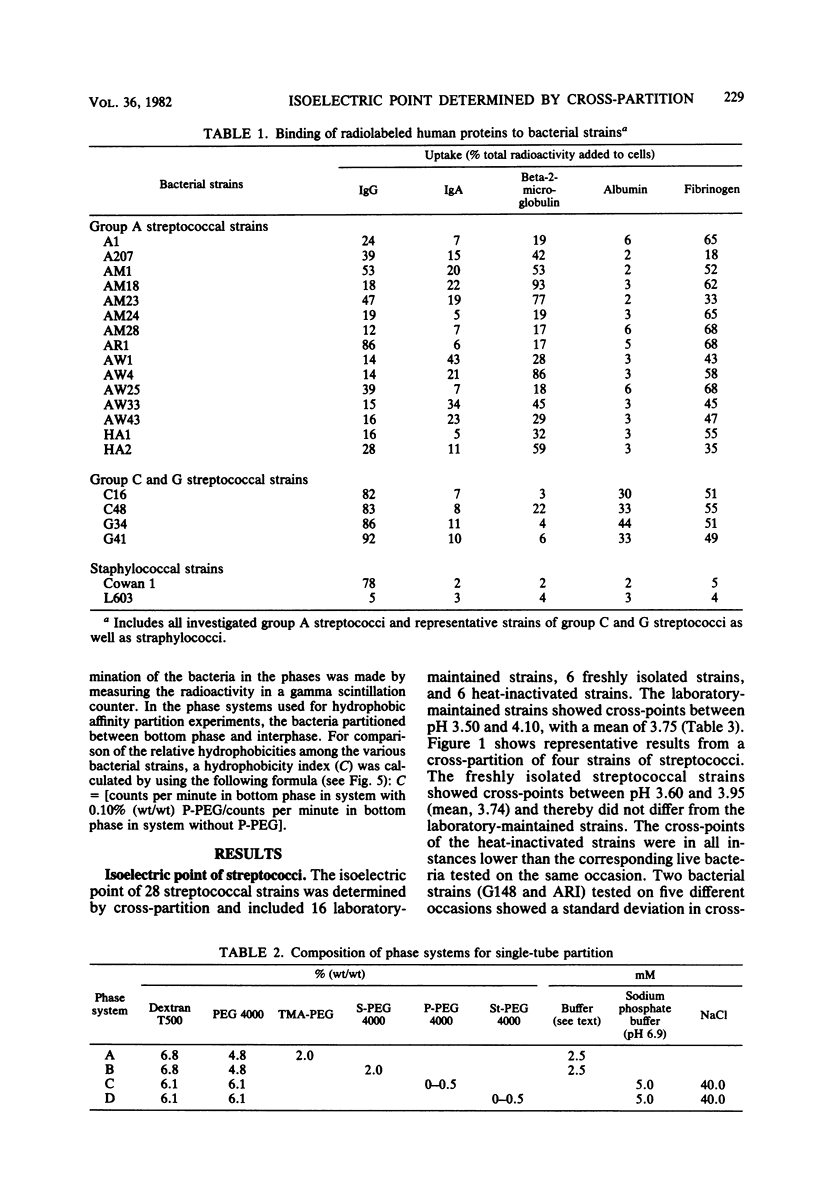
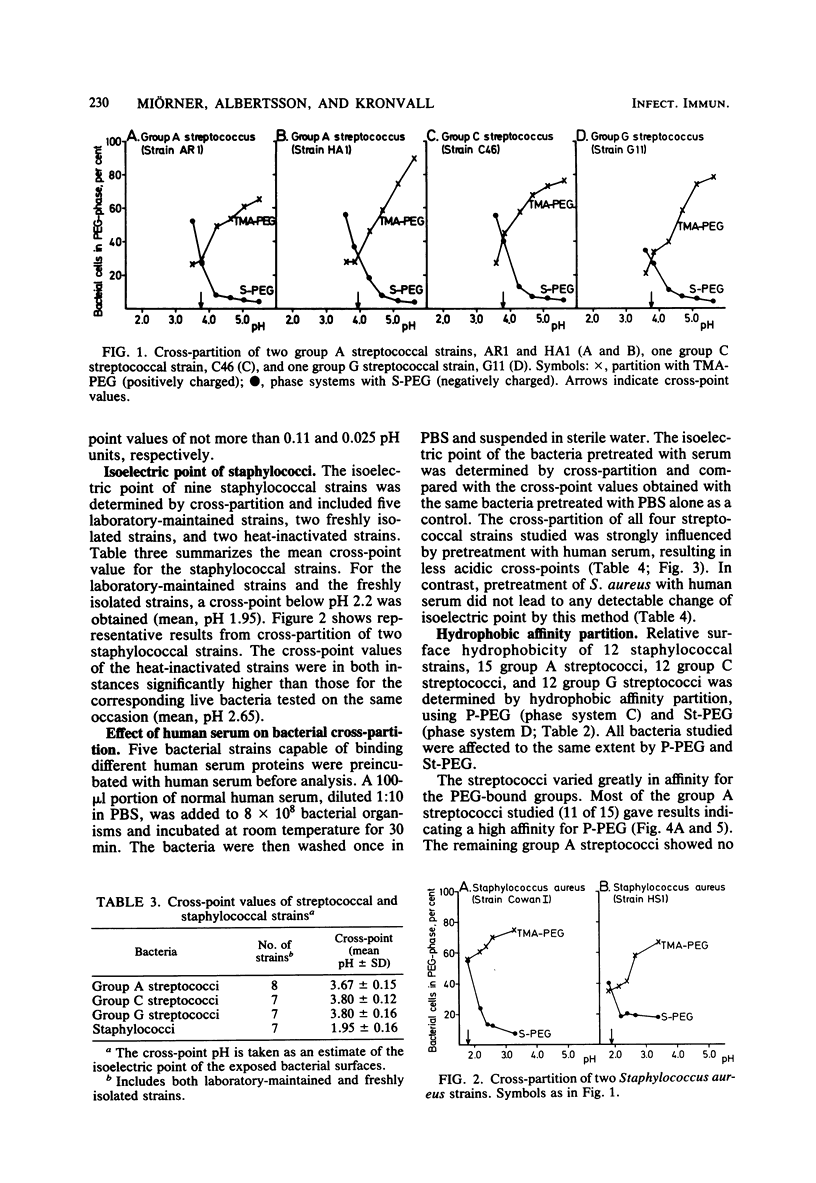
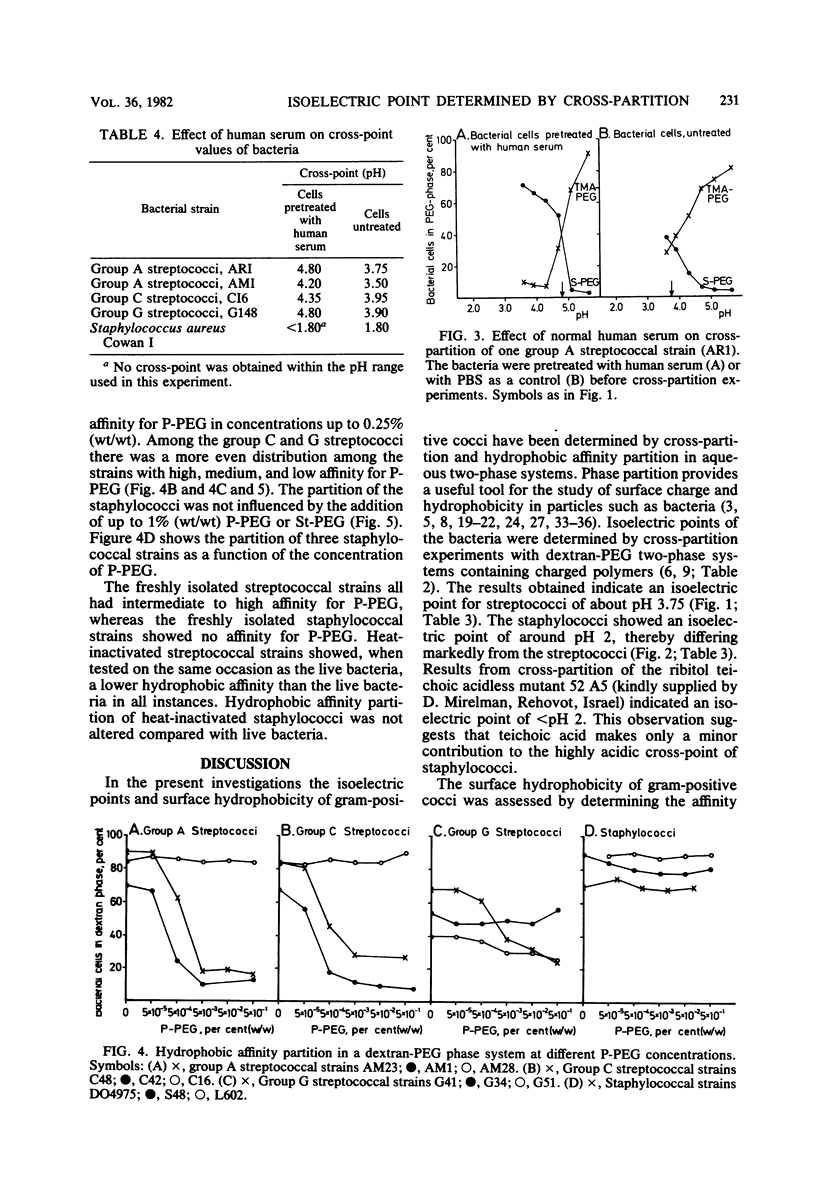
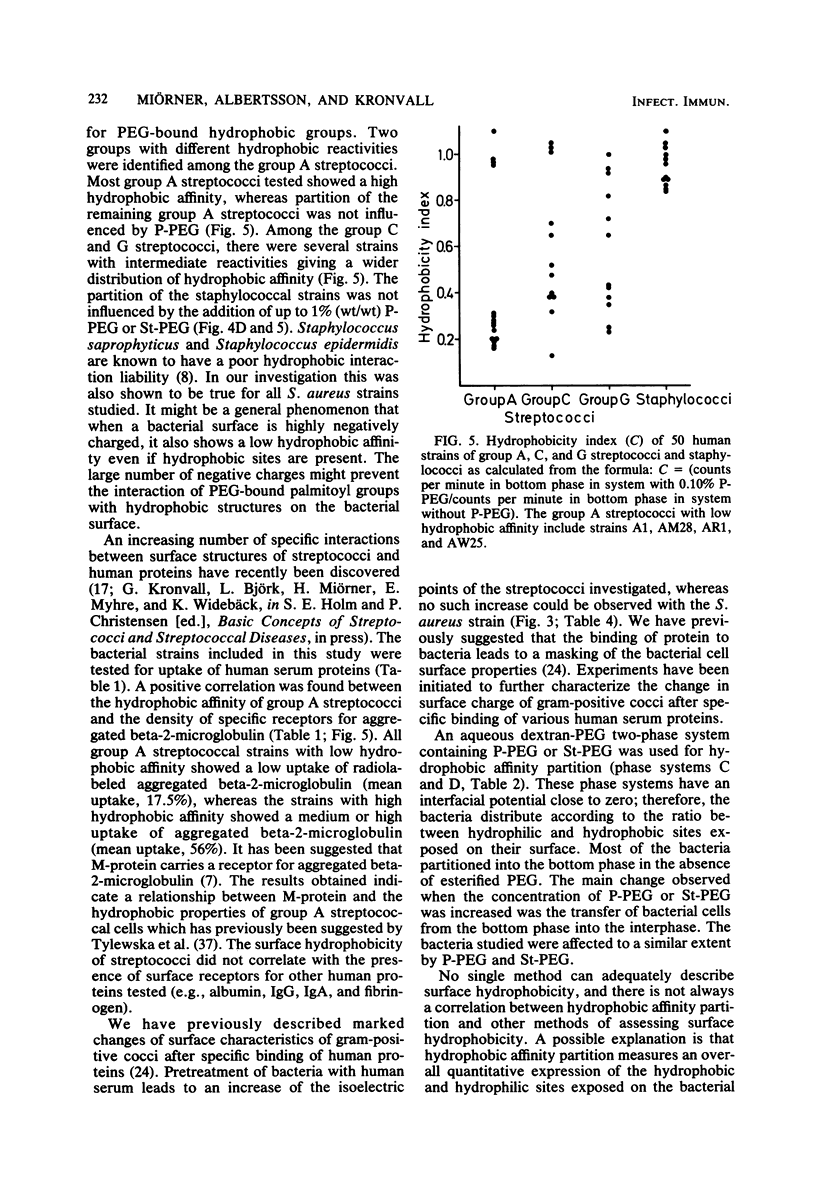
Thirty-nine streptococcal strains belonging to groups A, C, and G and 12 staphylococcal strains were investigated with respect to surface charge and hydrophobicity. Isoelectric points of the bacteria were determined by cross-partition experiments in dextran-polyethylene glycol two-phase systems containing charged polymers. The results obtained indicate that group A, C, and G streptococci have isoelectric points of pH 3.75 +/- 0.15 standard deviation. Staphylococci show an isoelectric point of around pH 2 and thereby differ markedly from the streptococci. Pretreatment of bacteria with human serum resulted in a significant change in the isoelectric points of streptococci. In a second series of experiments, an aqueous dextran-polyethylene glycol two-phase system containing polyethylene glycol palmitate or stearate was used to study the hydrophobic surface properties of the bacterial cells. The partition of the staphylococci was not influenced by the addition of up to 1% (wt/wt) polyethylene glycol palmitate or stearate, whereas the streptococci showed a large variation in affinity for polyethylene glycol-bound hydrophobic groups. The bacterial strains included in the study were also tested for uptake of human serum proteins. A positive correlation was found between the hydrophobic affinity of group A streptococci and the density of receptors for aggregated beta-2-microglobulin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERTSSON P. A., BAIRD G. D. Counter-current distribution of cells. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Nov;28:296–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerlund H. E., Andersson B., Persson A., Albertsson P. A. Isoelectric points of spinach thylakoid membrane surfaces as determined by cross partition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 4;552(2):238–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertsson P. A. Partition of cell particles and macromolecules in polymer two-phase systems. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:309–341. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertsson P. A., Sasakawa S., Walter H. Cross partition and isoelectric points of proteins. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1329–1330. doi: 10.1038/2281329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Tylewska S. K., Wadström T., Kronvall G. beta 2-Microglobulin is bound to streptococcal M protein. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(4):391–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleen S., Hovelius B., Wieslander A., Mårdh P. A. Surface properties of Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Staphylococcus epidermidis as studied by adherence tests and two-polymer, aqueous phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson I. Determination of the isoelectric point of rat liver mitochondria by cross-partition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90297-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson E., Albertsson P. A., Johansson G. Hydrophobic surface properties of erythrocytes studied by affinity partition in aqueous two-phase systems. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;10(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF01742204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL M. J., JAMES A. M., MAXTED W. R. SOME PHYSICAL INVESTIGATIONS OF THE BEHAVIOUR OF BACTERIAL SURFACES. X. THE OCCURRENCE OF LIPID IN THE STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:414–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90629-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL M. J., JAMES A. M., MAXTED W. R. Some physical investigations of the behaviour of bacterial surfaces. VIII. Studies on the capsular material of Streptococcus pyogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 19;66:264–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Fölling I. Recognition of two distinct groups of human IgM and IgA based on different binding to staphylococci. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):471–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Ishii H., Nakazawa H., Suga T., Orii H. Determination of the cross-points of rat liver peroxisomes, peroxisomal core and the core components by cross-partition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 4;585(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson G. Studies on aqueous dextran-poly (ethylene glycol) two-phase systems containing charged poly (ethylene glycol). I. Partition of albumins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeppeli O., Fiechter A. The mode of interaction between the substrate and cell surface of the hydrocarbon-utilizing yeast Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1976 Jul;18(7):967–974. doi: 10.1002/bit.260180709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Simmons A., Myhre E. B., Jonsson S. Specific absorption of human serum albumin, immunoglobulin A, and immunoglobulin G with selected strains of group A and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longton R. W., Cole J. S., 3rd, Quinn P. F. Isoelectric focusing of bacteria: species location within an isoelectric focusing column by surface charge. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Feb;20(2):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Kihlstrom E., Norqvist A., Davies J., Normark S. Effect of iron on surface charge and hydrophobicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):402–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.402-407.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Kihlström E., Norlander L., Norqvist A., Davies J., Normark S. Effect of colony type and pH on surface charge and hydrophobicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.397-401.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo L., Johansson G. The tendency of smooth and rough Salmonella typhimurium bacteria and lipopolysaccharide to hydrophobic and ionic interaction, as studied in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Jun;85(3):212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Myhre E., Björck L., Kronvall G. Effect of specific binding of human albumin, fibrinogen, and immunoglobulin G on surface characteristics of bacterial strains as revealed by partition experiments in polymer phase systems. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):879–885. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.879-885.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Asai J., Katsumata Y., Kojima K. Role of electric surface charge of cell membrane in phagocytosis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1973 May;23(2):279–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1973.tb00792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perers L., Andåker L., Edebo L., Stendahl O., Tagesson C. Association of some enterobacteria with the intestinal mucosa of mouse in relation to their partition in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):308–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Walter H., Wayne L. G. Altered surface properties of Escherichia coli associated with a specific amino acid change in the S12 ribosomal protein of streptomycin-resistant mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):978–983. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSA U., SCASSELLATI G. A., PENNISI F. LABELLING OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN WITH 131-I BY ELECTROLYTIC IODINATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 8;86:519–526. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Edebo L., Magnusson K. E., Tagesson C., Hjertén S. Surface-charge characteristics of smooth and rough Salmonella typhimurium bacteria determined by aqueous two-phase partitioning and free zones electrophoresis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):334–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Magnusson K. E., Tagesson C., Cunningham R., Edebo L. Characterization of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by counter-current distribution in an aqueous two-polymer phase system. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):573–577. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.573-577.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Normann B., Edebo L. Influence of O and K antigens on the surface properties of Escherichia coli in relation to phagocytosis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Apr;87B(2):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo M. Partition of Salmonella typhimurium in a two-polymer acqueous phase system in relation to liability to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.36-41.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tylewska S. K., Wadström T., Hjerten S. The effect of subinhibitory concentrations of penicillin and rifampicin on bacterial cell surface hydrophobicity and on binding to pharyngeal epithelial cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Mar;6(2):292–294. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter H., Krob E. J., Tung R. Hydrophobic affinity partition in aqueous two-phase systems of erythrocytes from different species. Systems containing polyethylene glycol-palmitate. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 1;102(1):14–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westrin H., Albertsson P. A., Johansson G. Hydrophobic affinity partition of spinach chloroplasts in aqueous two-phase systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 1;436(3):696–706. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


