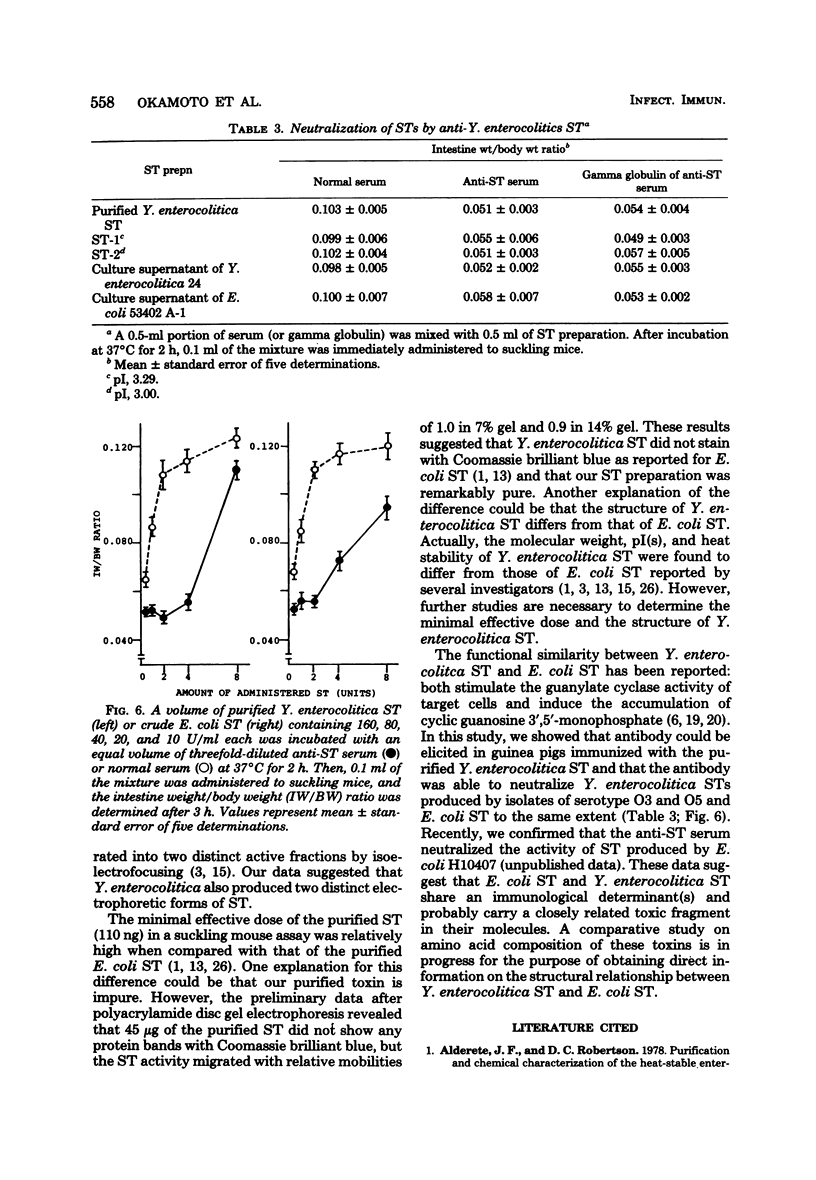
Abstract
By using a suckling mouse assay, heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) was purified from the culture filtrate of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from a diarrheal patient. The purification procedures involve ultrafiltration with an Amicon HIP-10 hollow fiber, ethanol fractionation, protamine sulfate treatment, diethylaminoethyl-Sephacel and hydroxylapatite column chromatographies, and Sephacryl S-200 superfine gel filtration. About 408-fold purification was achieved, with a yield of 12.0%. The minimal effective dose of purified ST was about 110 ng in the suckling mouse assay. The molecular weight of purified ST was 9,000 by Sephadex G-100 superfine gel filtration. The purified ST was stable to heating (100 degrees C for 20 min, 121 degrees C for 20 min) and did not lose its toxicity after treatment with protease, trypsin, lipase, phospholipase C, ribonuclease, deoxyribonuclease, beta-glucosidase, and neuraminidase. The purified ST was separated by isoelectric focusing into two active fractions, with pI's of 3.29 (ST-1) and 3.00 (ST-2), respectively. Antiserum from guinea pigs immunized with the purified ST neutralized the activity of both Y. enterocolitica ST and Escherichia coli ST.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P. Role of exotoxins in bacterial pathogenicity. J Appl Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;44(3):329–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1978.tb00808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Heat-stable enterotoxins from Escherichia coli P16. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1038–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1038-1040.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Moore R. A., Kirschenfeld P. M., Sande M. A. Role of toxigenic and invasive bacteria in acute diarrhea of childhood. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):567–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509182931201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Shimizu M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Isolation of a factor causing morphological changes of chinese hamster ovary cells from the culture filtrate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1028-1033.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Partial purification and properties of Enterobacter cloacae heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1307–1314. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1307-1314.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Purification and properties of Klebsiella pneumoniae heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):373–381. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.373-381.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R., Lariviere S., St-Pierre S. Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: rapid method of purification and some characteristics of the toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):469–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.469-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen G. L., Knoop F. C. Physiochemical properties of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli of human origin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1051–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1051-1053.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Ichikawa H., Kawamoto Y., Miyama A., Yoshii S. Heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from patients. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(5):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira B., Osler A. G., Siraganian R. P., Sandberg A. L. The biologic activities of guinea pig antibodies. I. Separation of gamma1 and gamma2 immunoglobulins and their participation in allergic reactions of the immediate type. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):320–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V. Production of enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):908–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.908-911.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Guandalini S., Laird W. J., Field M. Effects of heat-stable enterotoxin of Yersinia enterocolitica on ion transport and cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate metabolism in rabbit ileum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):875–878. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.875-878.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Still C. S., Miliotis M. D., Koornhof H. J. Mechanism of action of Yersinia enterocolitica enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):680–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.680-684.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Isolation of skin permeability factors from culture filtrates of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):671–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.671-679.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Neutralization of Salmonella toxin-induced elongation of Chinese hamster ovary cells by cholera antitoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):988–992. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.988-992.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Okamoto K., Miwatani T. Toxin from the culture filtrate of Shigella dysenteriae that causes morphological changes in Chinese hamster ovary cells and is distinct from the neurotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):546–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.546-548.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


